Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
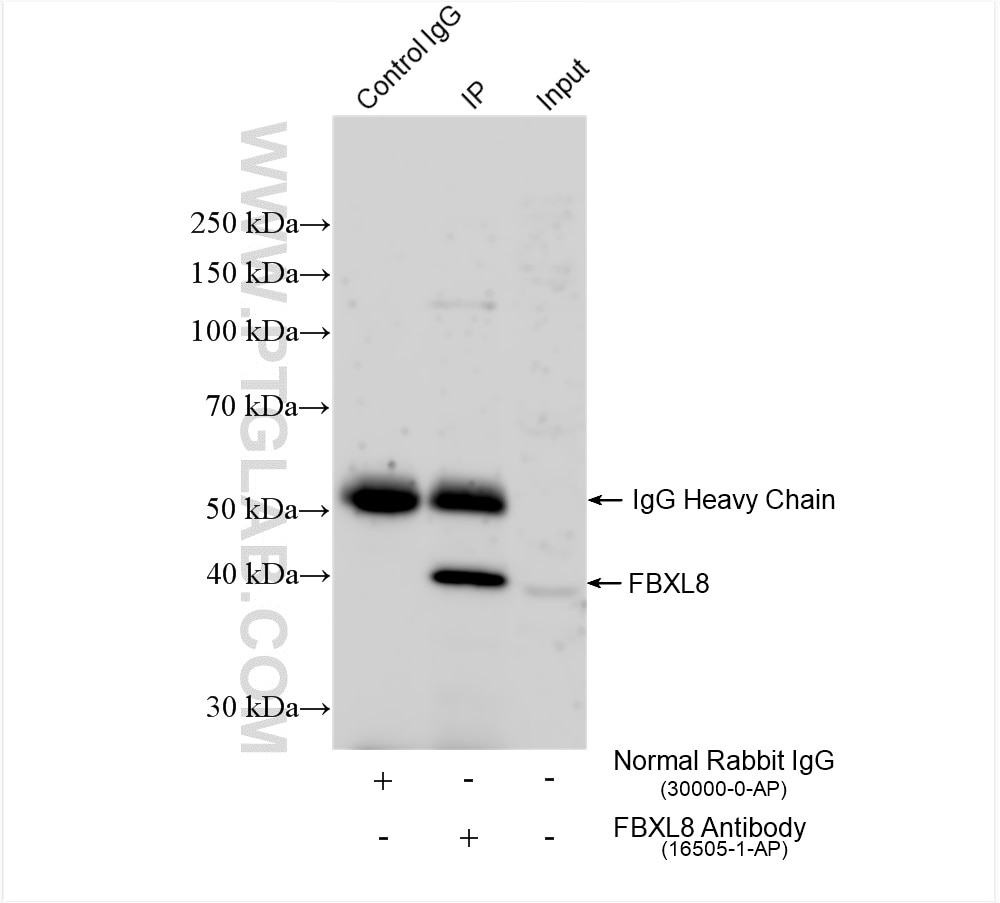
| Positive IP detected in | HCT 116 cells |
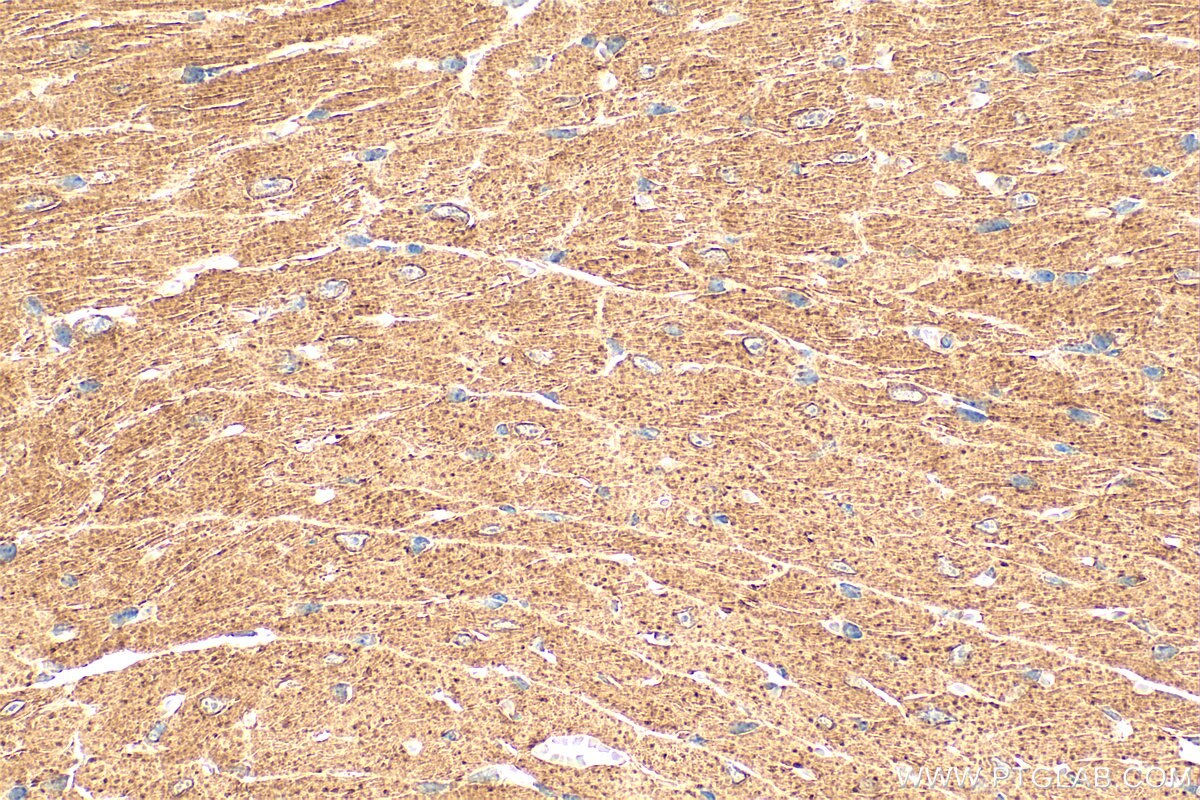
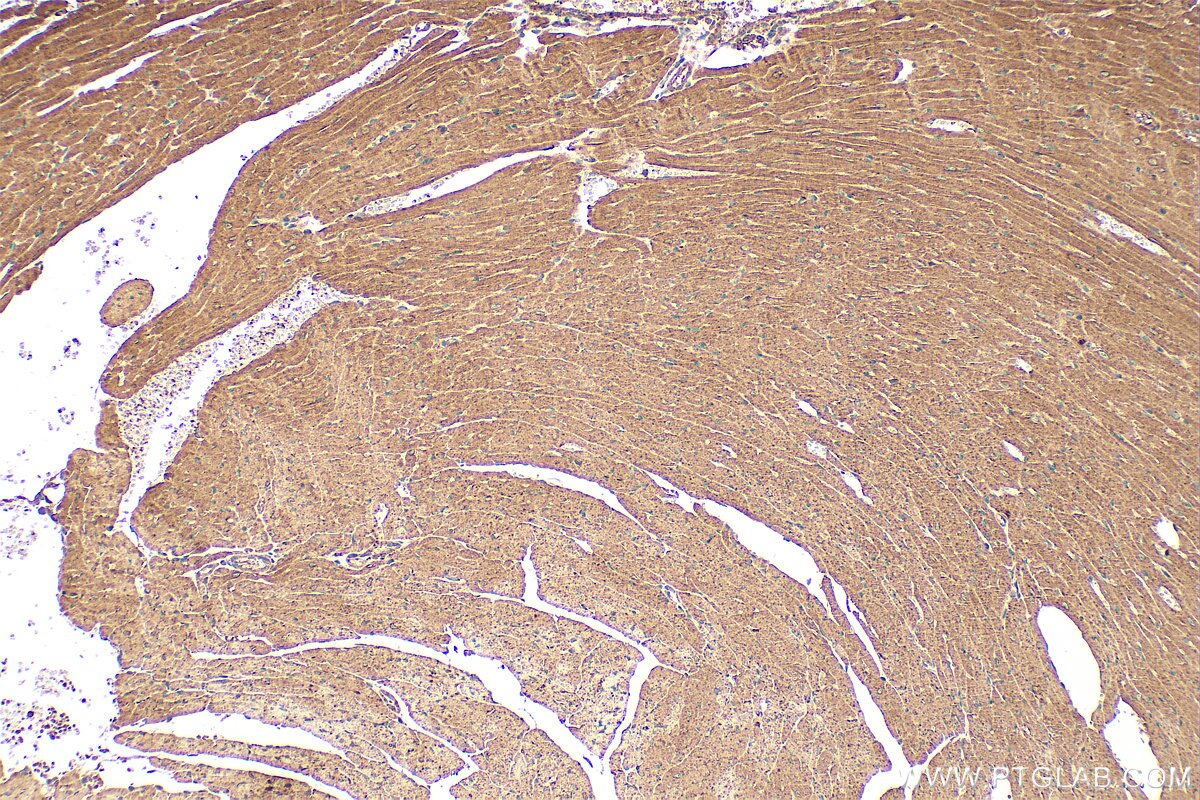
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse heart tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
16505-1-AP targets FBXL8 in IHC, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag9685 Product name: Recombinant human FBXL8 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-374 aa of BC014414 Sequence: MAEPGEGLPEEVLALIFRHLSLRDRAAAARVCRAWAAAATCSAVWHDTKISCECELEGMLPPYLSACLDHIHNLRLEFEPSRKPSRRAAIELLMVLAGRAPGLRGLRLECRGEKPLFDAGRDVLEAVHAVCGAASQLRHLDLRRLSFTLDDALVLQAARSCPELHSLFLDNSTLVGSVGPGSVLELLEACPRLRALGLHLASLSHAILEALAAPDRAPFALLALRCACPEDARASPLPNEAWVALRRRHPGLAVELELEPALPAESVTRVLQPAVPVAALRLNLSGDTVGPVRFAAHHYAATLCALEVRAAASAELNAALEELAARCAALREVHCFCVVSHSVLDAFRAHCPRLRTYTLKLTREPHPWRPTLVA 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 8 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 374 aa, 41 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 41 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC014414 |
| Gene Symbol | FBXL8 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 55336 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q96CD0 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
FBXL8 is a conserved F-box protein that belongs to the ubiquitin ligase complex. It plays a significant role in various cellular processes, including tumorigenesis and metastasis. In colorectal cancer, FBXL8 promotes liver metastasis and stem-cell-like features by mediating ubiquitination and degradation of TP53. Additionally, FBXL8 has been shown to inhibit lymphoma growth and hematopoietic malignancies by targeting specific substrates for degradation. In the context of cardiac fibrosis, FBXL8 inhibits post-myocardial infarction cardiac fibrosis by regulating the ubiquitination of key proteins (PMID: 36855778, PMID: 33122824, PMID: 38615011).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IHC protocol for FBXL8 antibody 16505-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for FBXL8 antibody 16505-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |