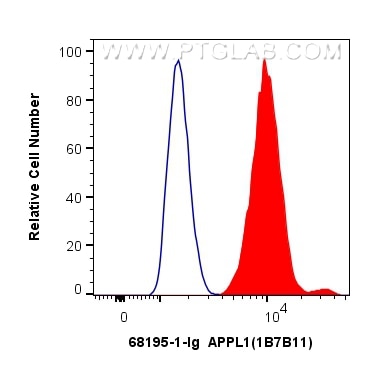
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
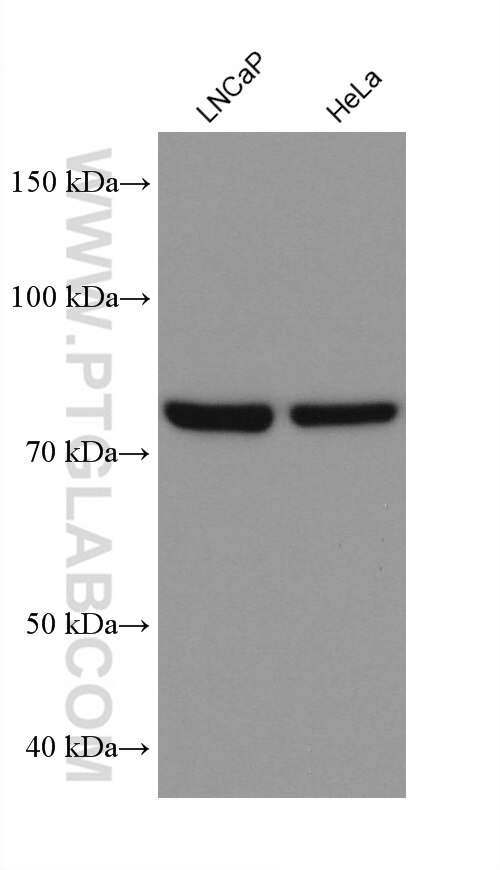
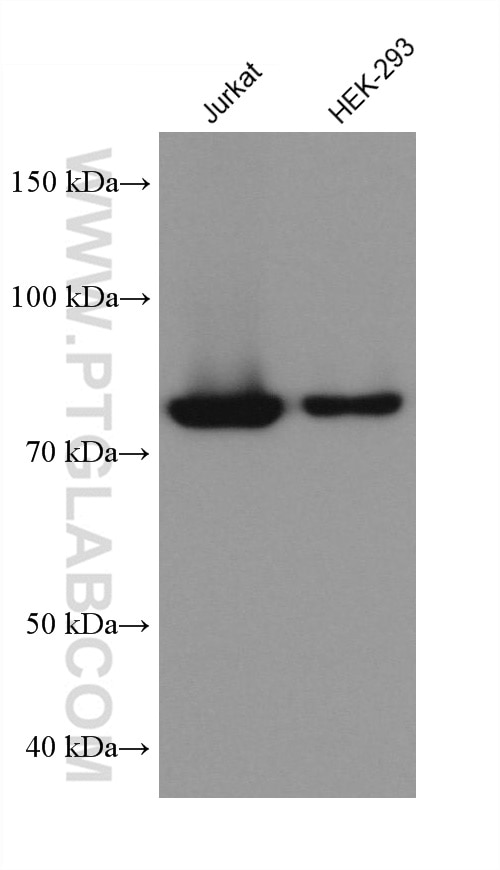
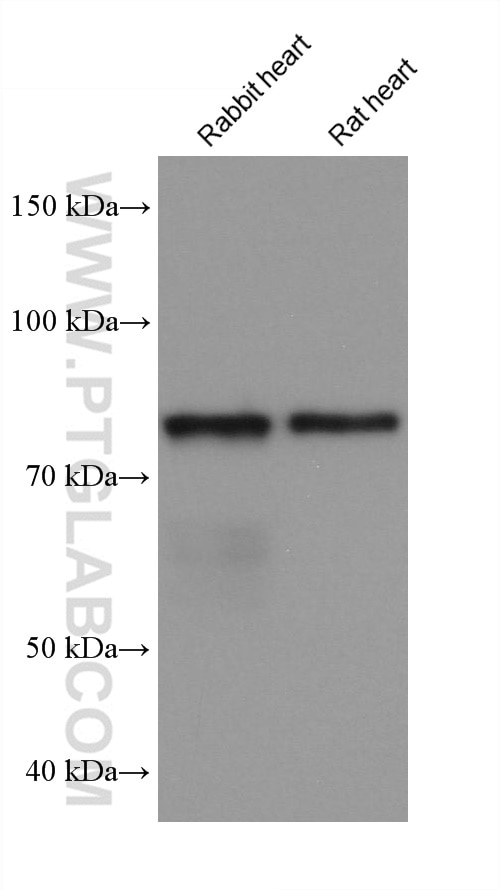
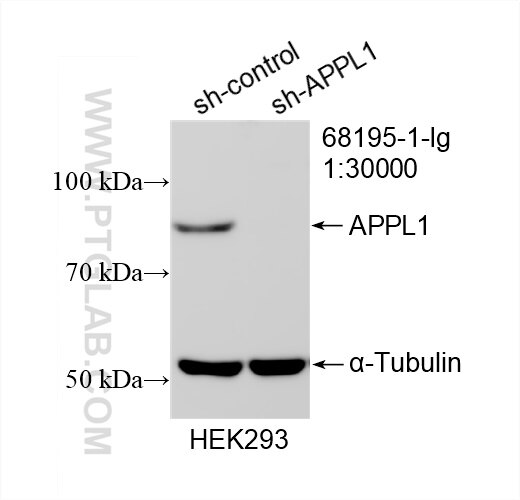
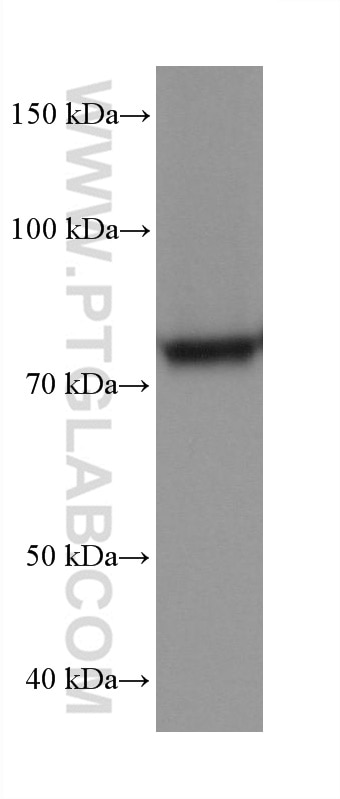
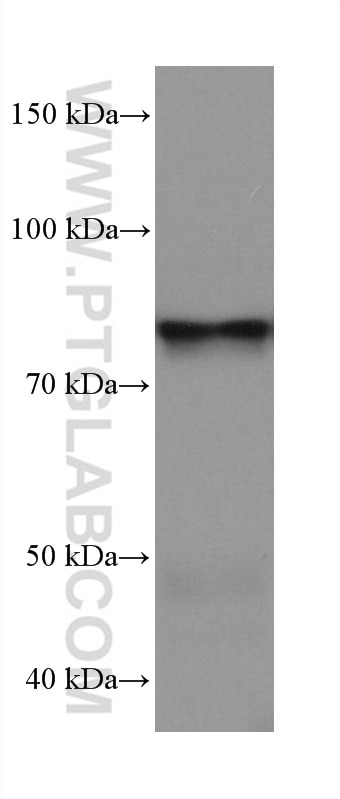
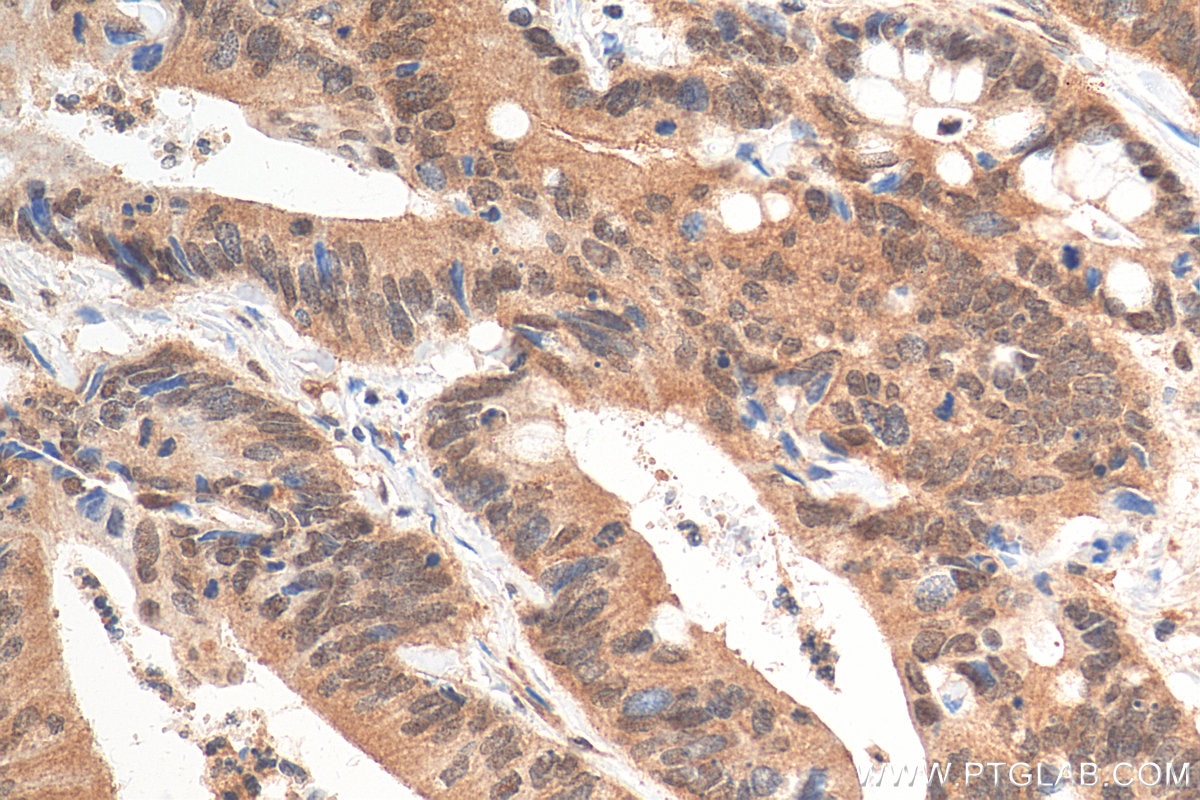
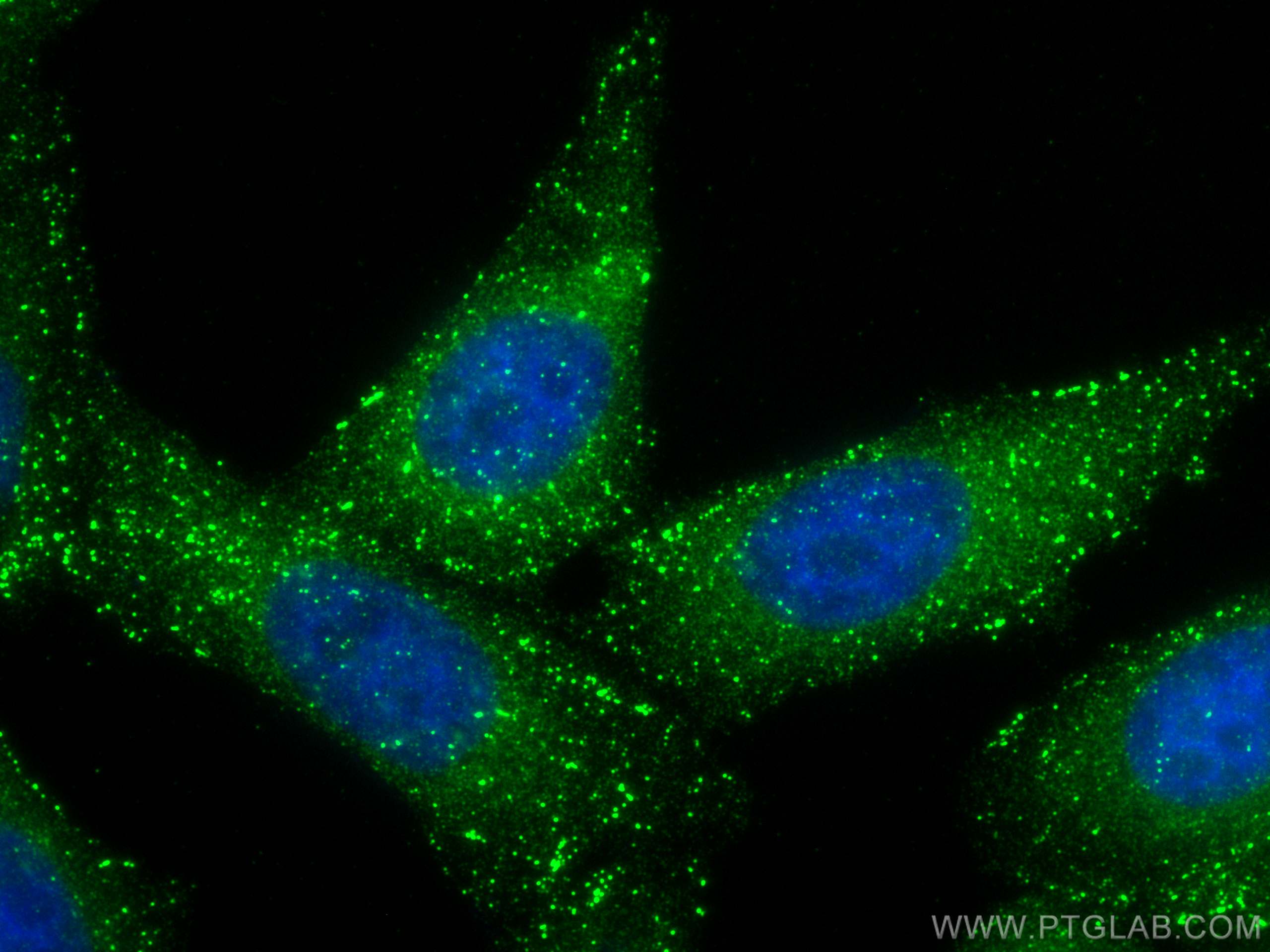
68195-1-PBS targets APPL1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with rabbit, pig, rat, mouse, human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | rabbit, pig, rat, mouse, human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | APPL1 fusion protein Ag3334 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain and leucine zipper containing 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 709 aa, 80 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 80 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC028599 |
| Gene Symbol | APPL1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 26060 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9UKG1 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Adaptor protein, phosphotyrosine interaction, PH domain and leucine zipper containing 1 (APPL1), a binding partner of Akt2 and an important regulator of INS signaling, plays a key role in the regulation of INS secretion [PMID:22615370]. APPL1 interacts with adiponectin receptors and mediates the INS-sensitizing effects of adiponectin in muscle and endothelial cells. It also participates in nuclear signaling and transcriptional regulation, mostly by modulating the activity of various nuclear factors [PMID:22685329]. Apart from its role in endocytosis and endosomal transport, APPL1 was reported to undergo nucleocytoplasmic shuttling and participate in transcriptional regulation, e.g. by interactions with histone deacetylases (HDACs) [PMID:19686092].