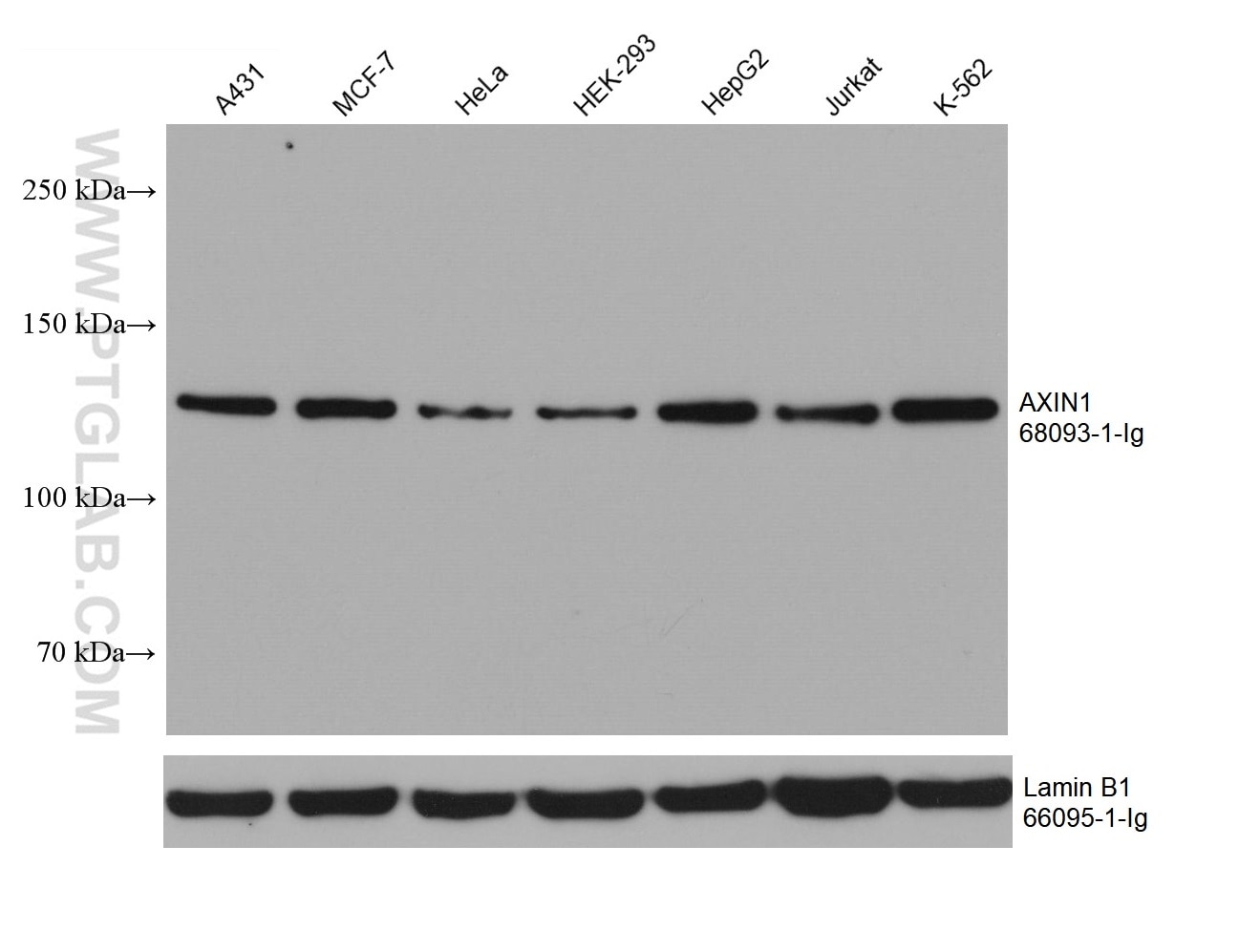
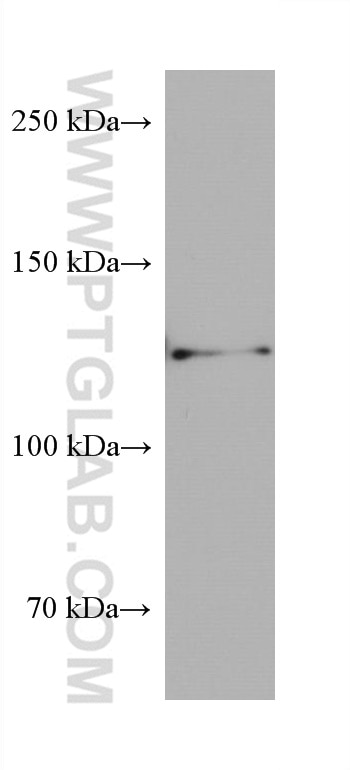
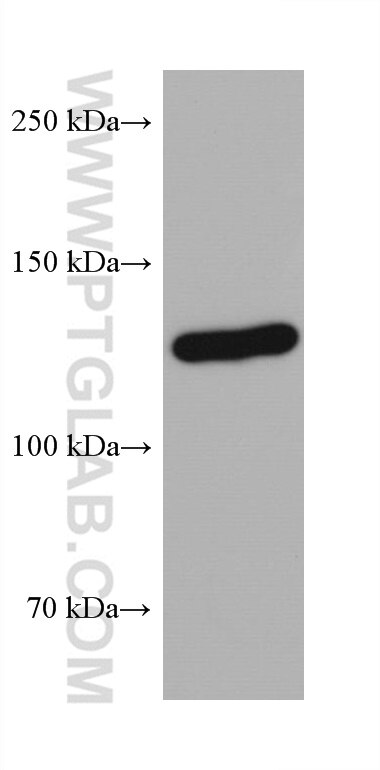
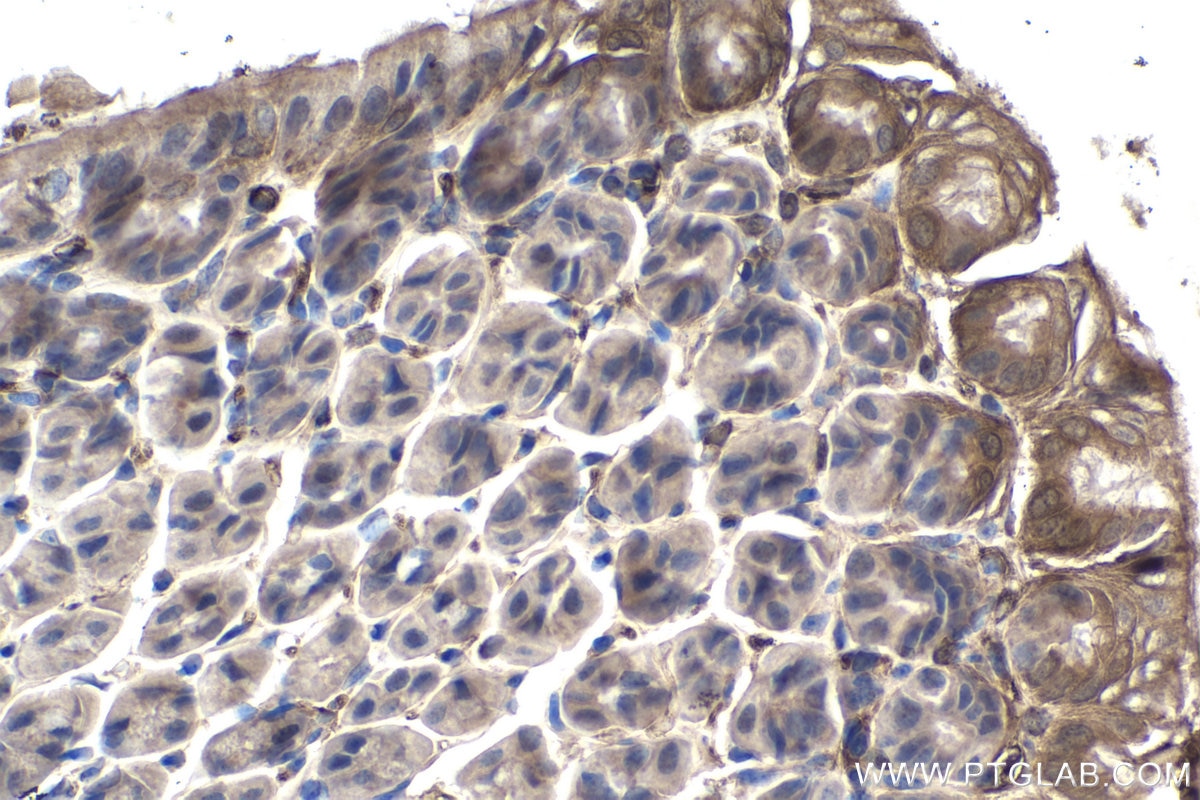
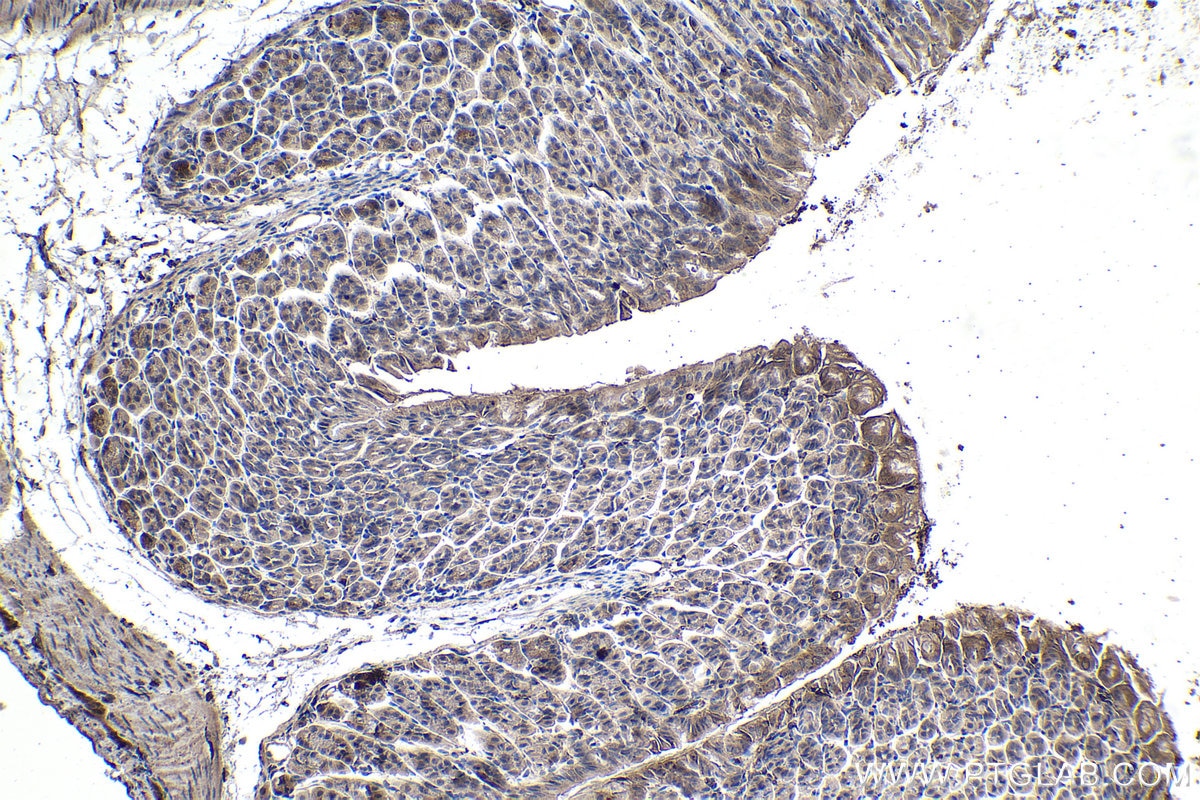
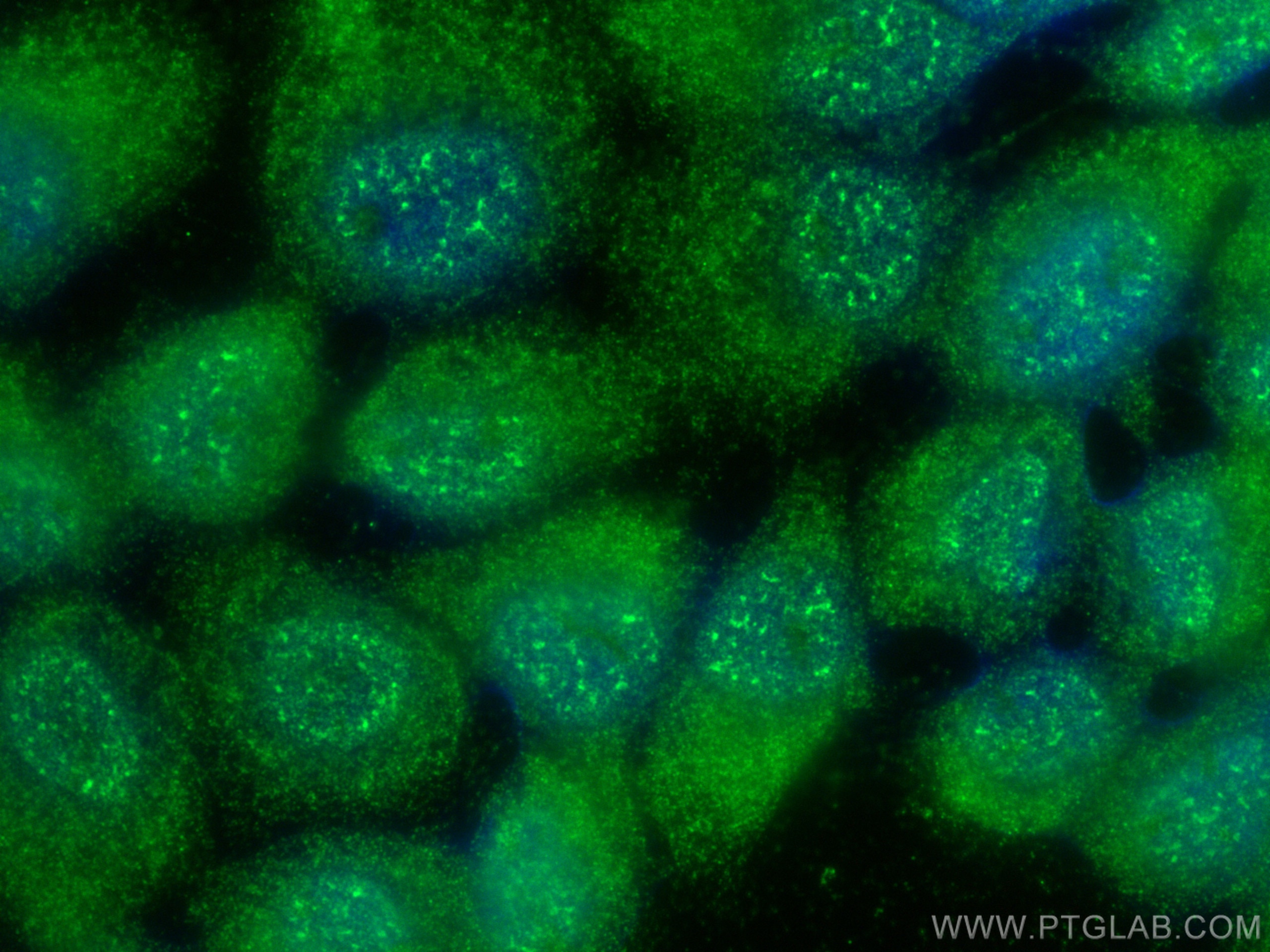
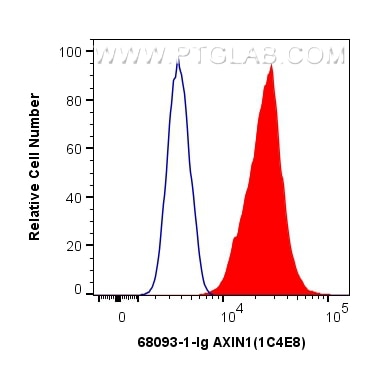
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
68093-1-PBS targets AXIN1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with rat, mouse, human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | rat, mouse, human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | AXIN1 fusion protein Ag10079 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | axin 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 826aa,92 kDa; 862aa,95 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 110-120 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC044648 |
| Gene Symbol | AXIN1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 8312 |
| RRID | AB_2918830 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O15169 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS Only |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Axis inhibition protein1 (AXIN1), also called AXIN, together with AXIN2 are multidomain scaffold proteins that negatively regulate Wnt signaling. AXIN1 is likely to function as a tumor suppressor. Under UV irradiation, AXIN1-HIPK2-TP53 complex forms. The complex also controls cell growth, apoptosis and development. Like AXIN2, AXIN1 undergoes poly(ADP-ribosy)lation by tankyrase TNKS and TNKS2 followed by unbiquitination by RNF146 which leads to its degradation and subsequent activation of Wnt signaling. Its deubiquitination by USP34 is important for nuclear accumulation during Wnt signaling. Recent researches find that CircAXIN1 encodes a novel protein, AXIN1-295aa, which shows at around 40-55 kDa by Western Blot. AXIN1-295aa functions as an oncogenic protein, activating the Wnt signaling pathway to promote GC tumorigenesis and progression, suggesting a potential therapeutic target for GC.