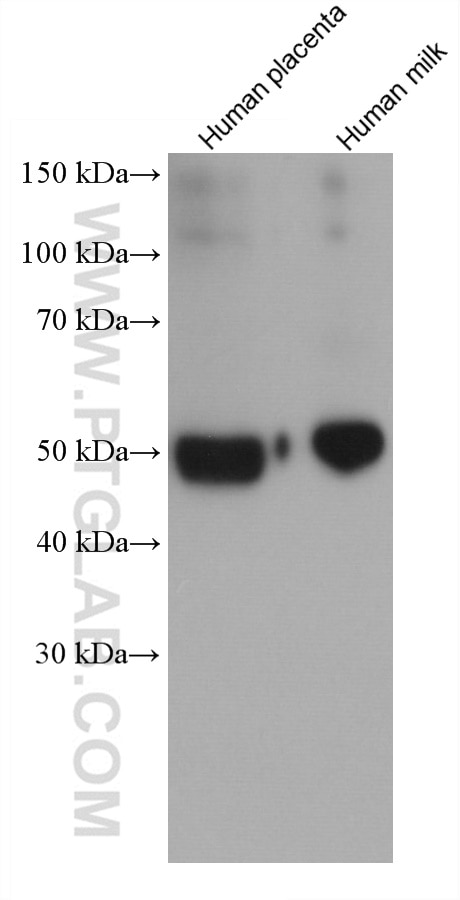
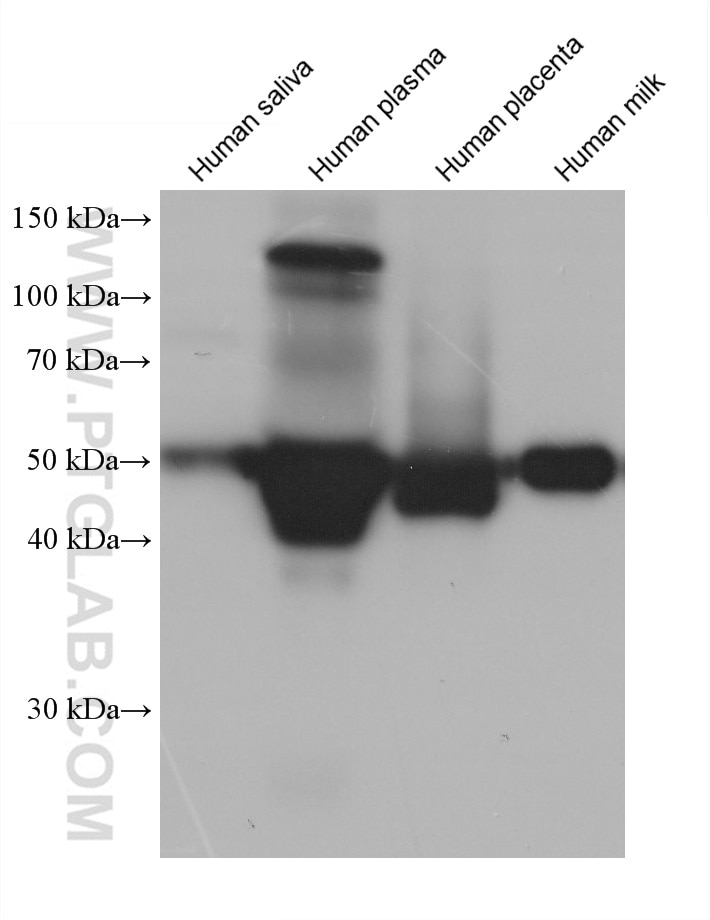
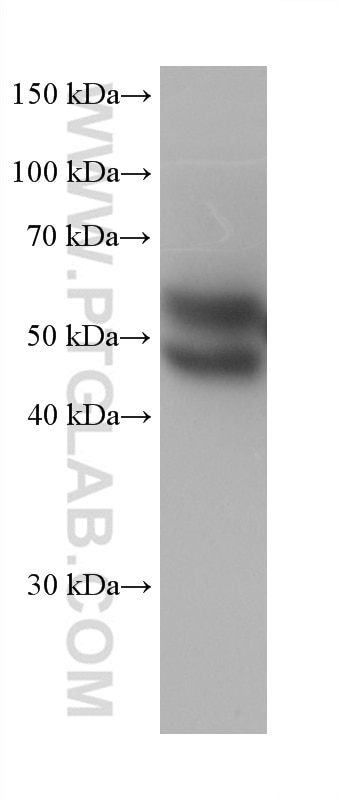
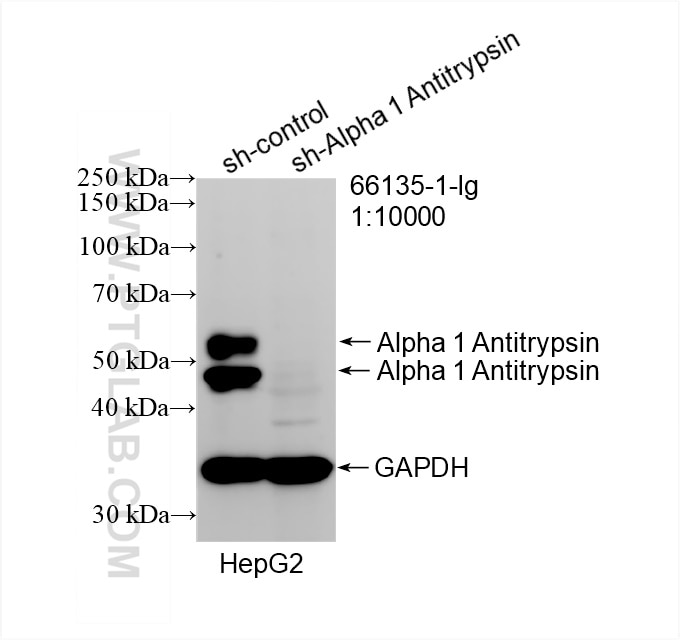
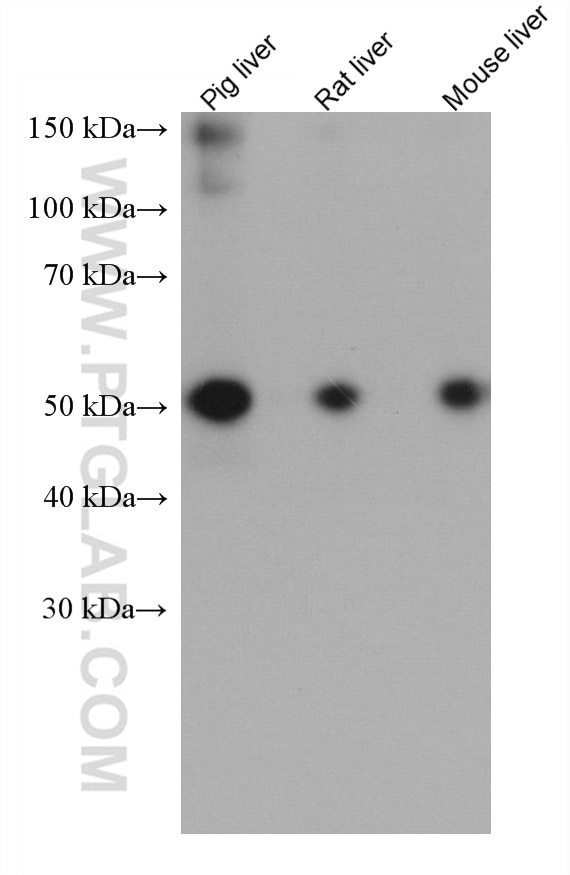
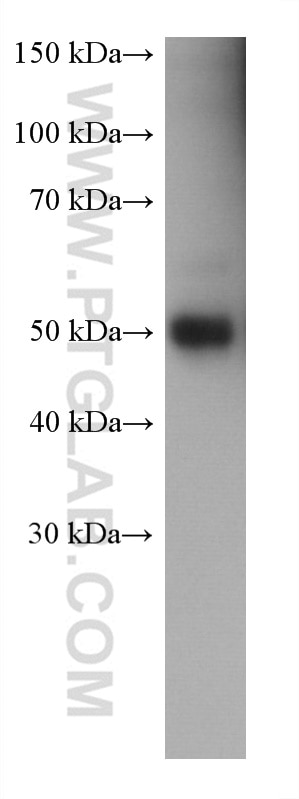
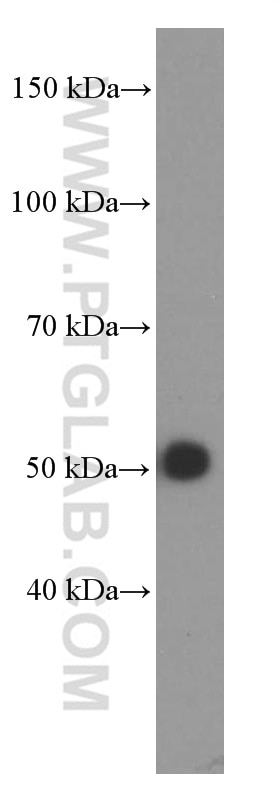
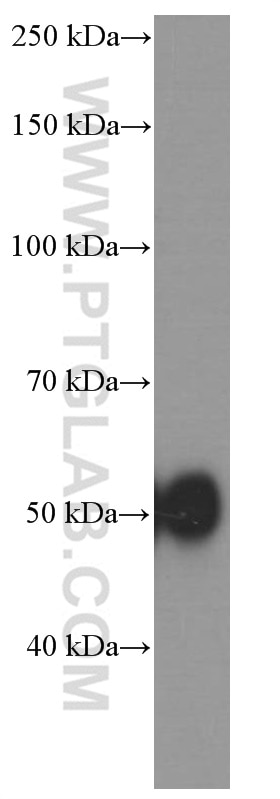
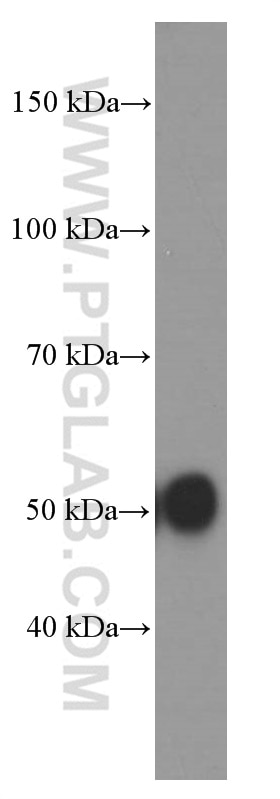
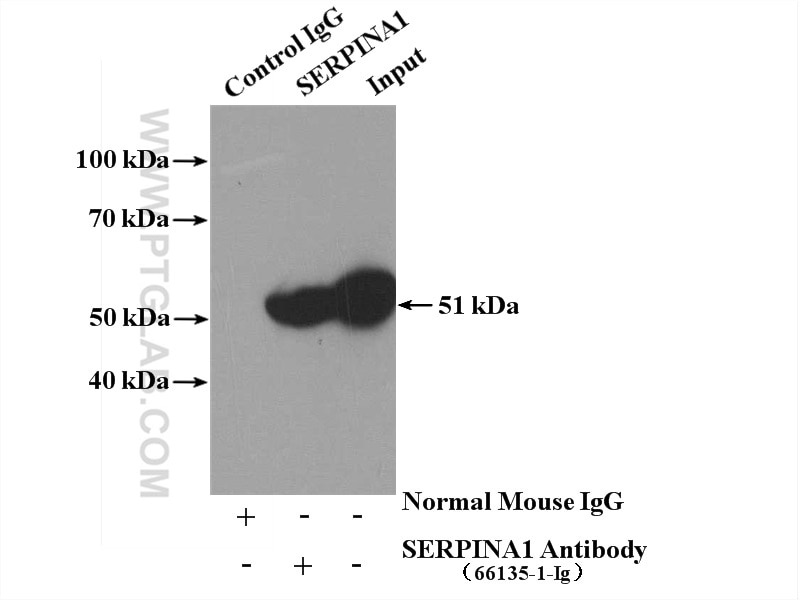
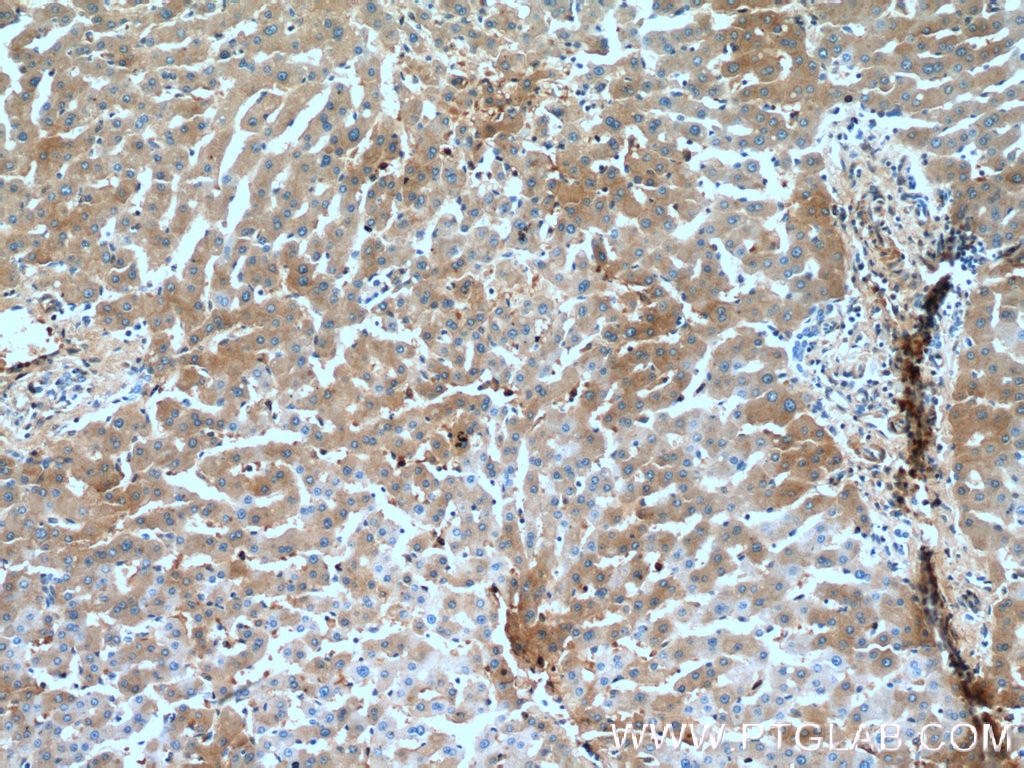
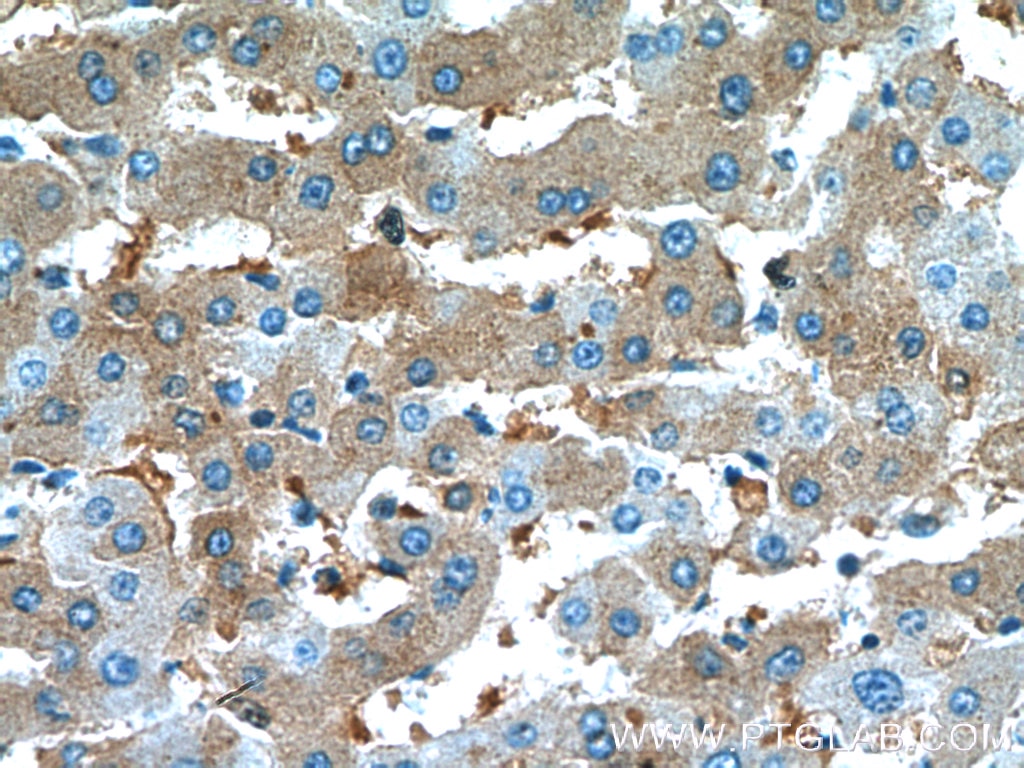
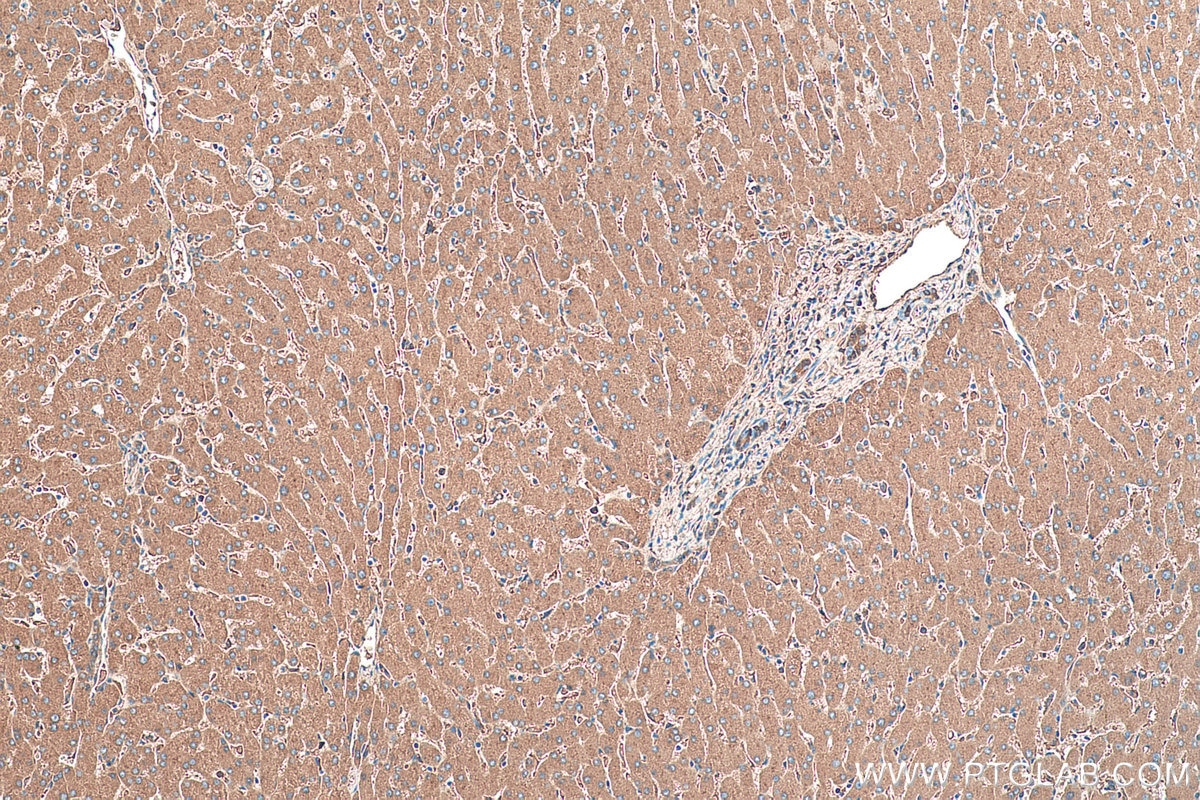
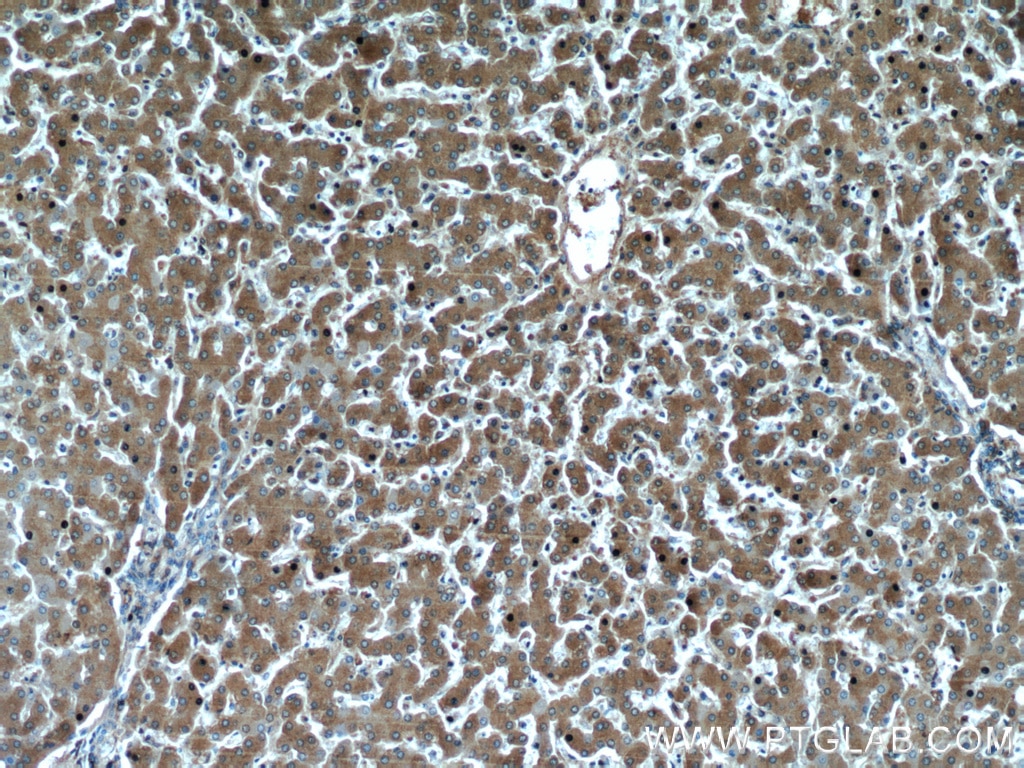
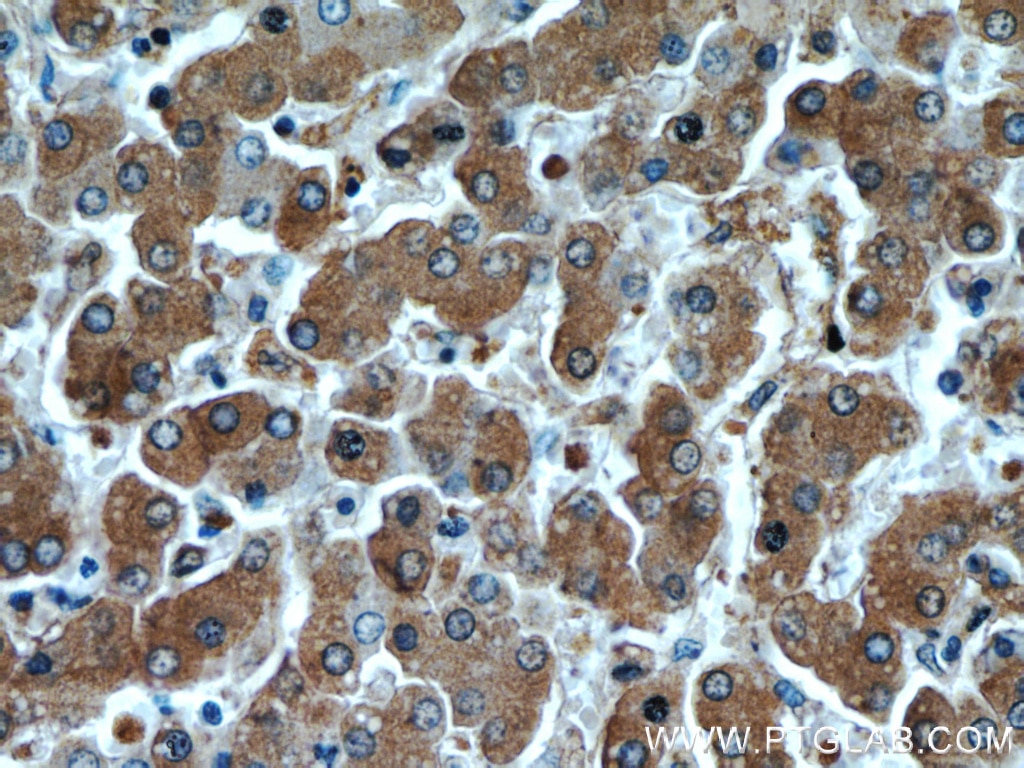
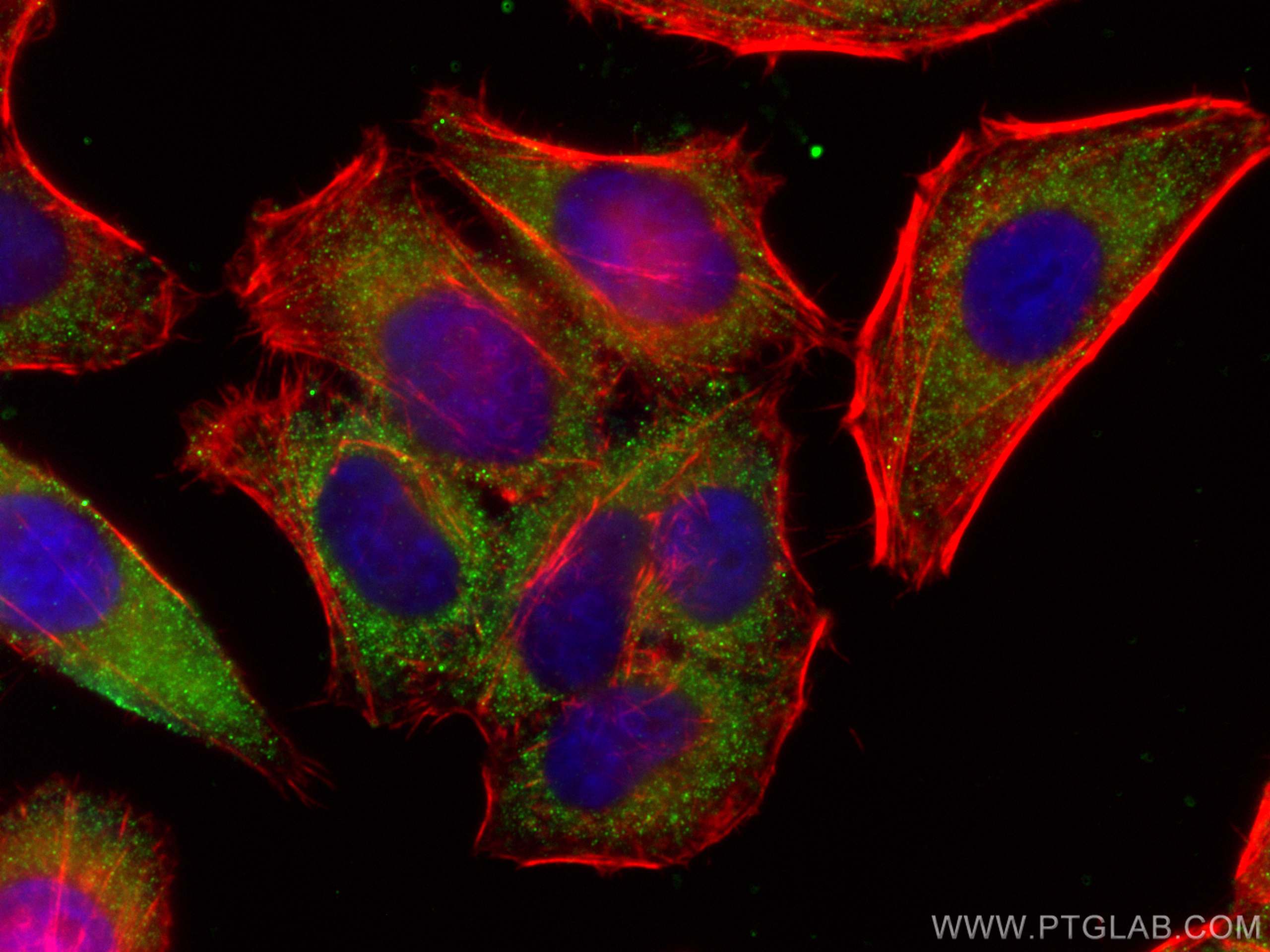
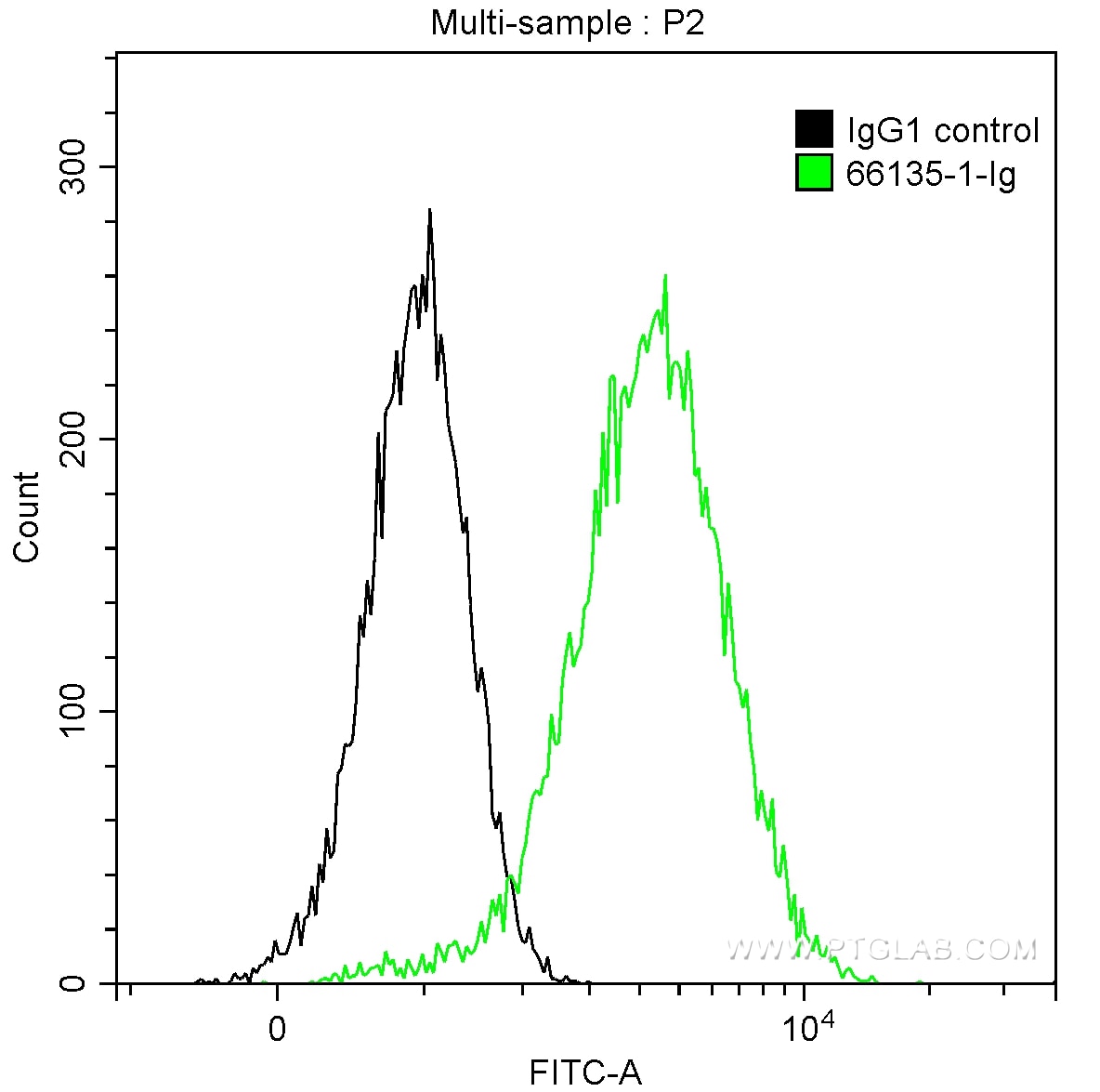
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
66135-1-PBS targets Alpha-1-Antitrypsin in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, pig samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, pig |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Alpha-1-Antitrypsin fusion protein Ag9516 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | serpin peptidase inhibitor, clade A (alpha-1 antiproteinase, antitrypsin), member 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 418 aa, 47 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 51 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC015642 |
| Gene Symbol | Alpha 1-Antitrypsin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5265 |
| RRID | AB_2881534 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P01009 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
SERPINA1 is the gene for a protein called alpha-1-antitrypsin (AAT), which is a serine protease inhibitor whose targets include elastase, plasmin, thrombin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, and plasminogen activator. AAT is a glycoprotein synthesized primarily by hepatocytes, with smaller amountssynthesized by intestinal epithelial cells, neutrophils, pulmonary alveolar cells and macrophages. AAT is the most abundant, endogenous serine protease inhibitor in blood circulation and it has been implicated in regulating vital fluid phase biological events such as blood coagulation, fibrinolysis, complement activation, apoptosis, reproduction, tumor progression and inflammatory response. The primary function of AAT is thought to be the inactivation of neutrophil elastase and other endogenous serine proteases. Defects in SERPINA1 can cause emphysema or liver disease.