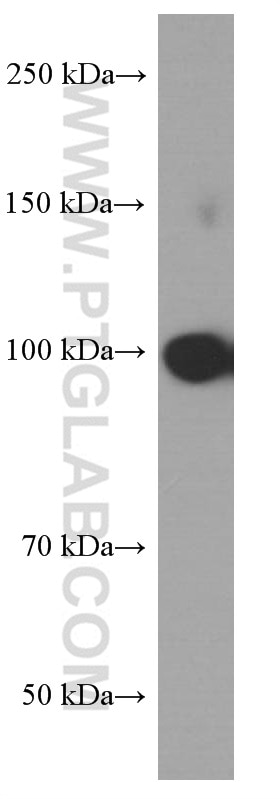
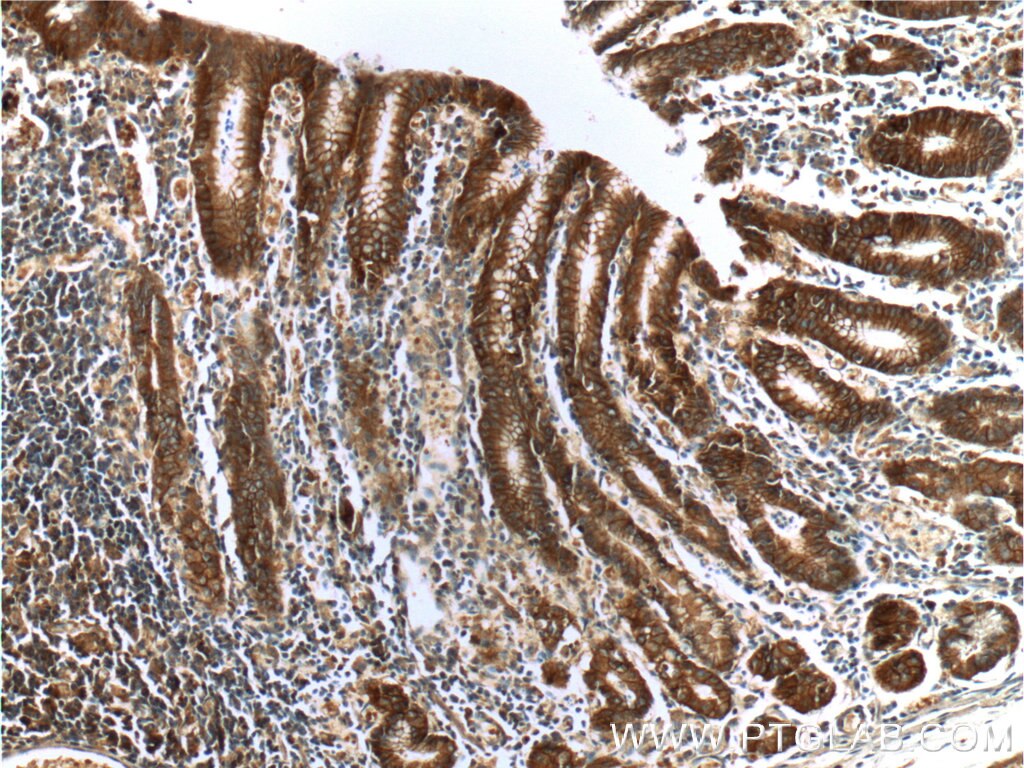
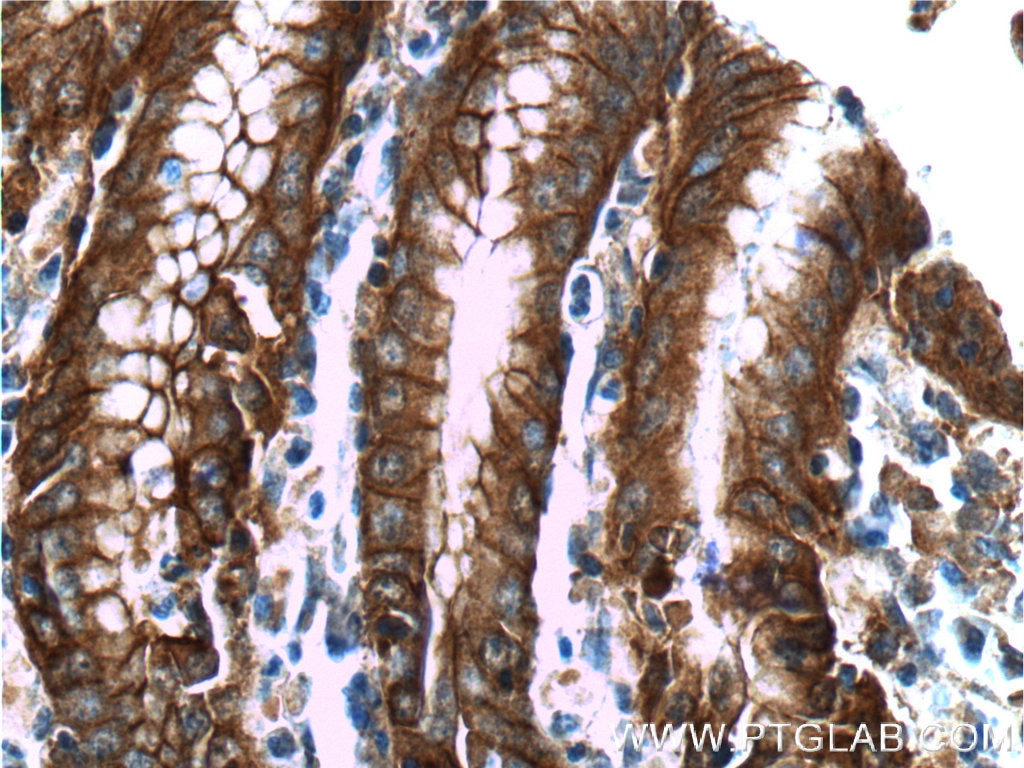
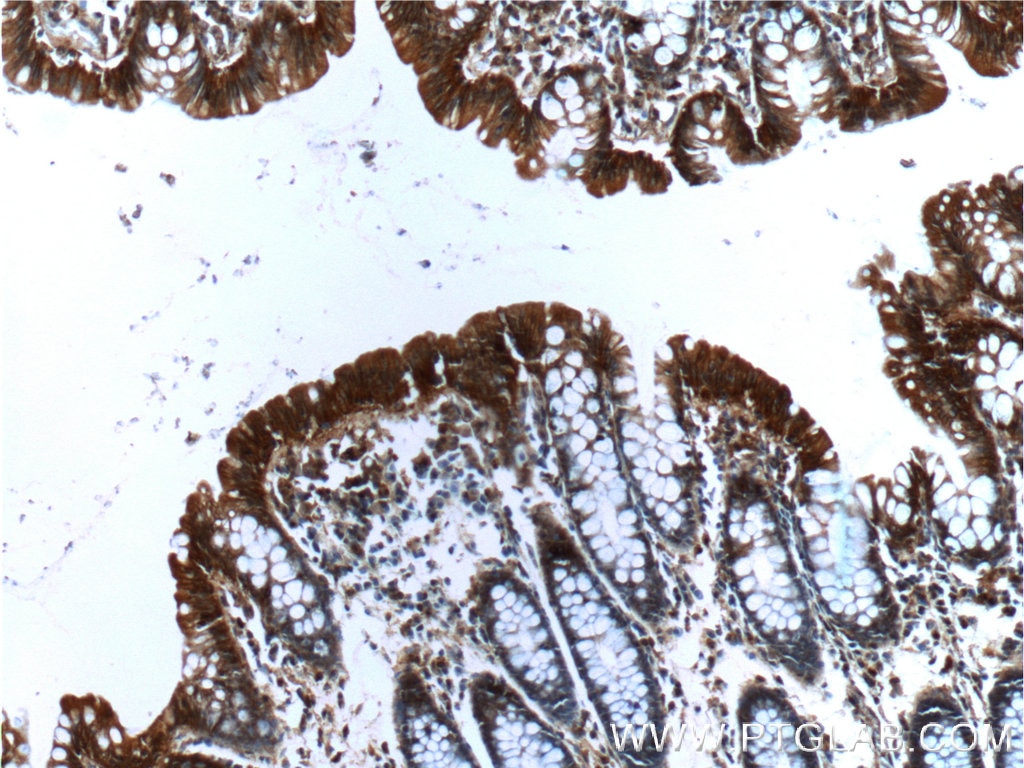
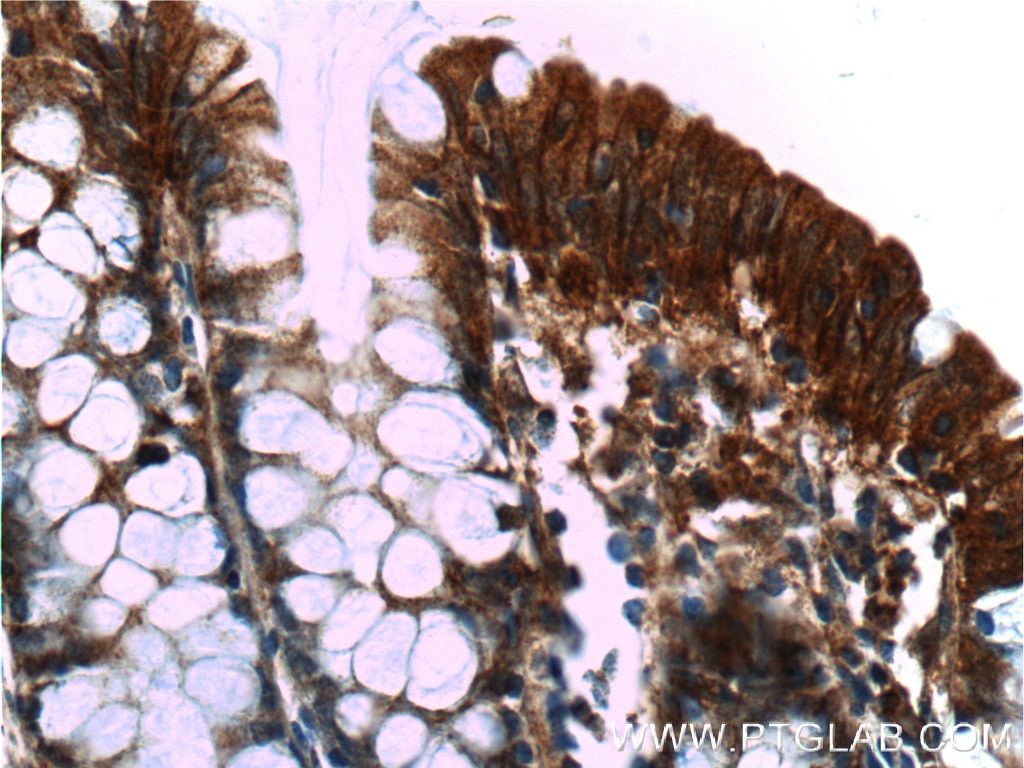
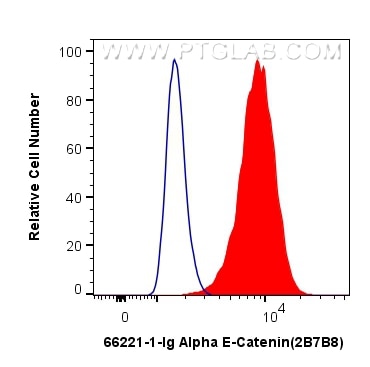
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
66221-1-PBS targets Alpha E-Catenin in WB, IHC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Alpha E-Catenin fusion protein Ag23603 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | catenin (cadherin-associated protein), alpha 1, 102kDa |
| Calculated molecular weight | 906 aa, 100 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 95-100 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC031262 |
| Gene Symbol | Alpha E-Catenin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1495 |
| RRID | AB_2881612 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P35221 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Alpha catenin is an essential component of adherens junctions that connects E-cadherin-β-catenin complexes with the actin cytoskeleton. It also recruits a range of other important proteins to developing intercellular junctions. Three alpha catenins exist in human: alpha-E-catenin, alpha-N-catenin, and alpha-T-catenin, which share substantial amino-acid sequence similarity but have distinct tissue distribution. alpha-E-catenin is ubiquitously expressed, alpha-N-catenin is restricted to neuronal tissue, and alpha-T-catenin is primarily expressed in heart tissue. Reduced levels of alpha-E-catenin protein seem to be characteristic of many different human cancers, including malignant tumours of the breast, colon, stomach, oesophagus, bladder and liver. In addition, the loss of alpha-E-catenin often correlates with the degree of tumour differentiation and metastasis.