Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
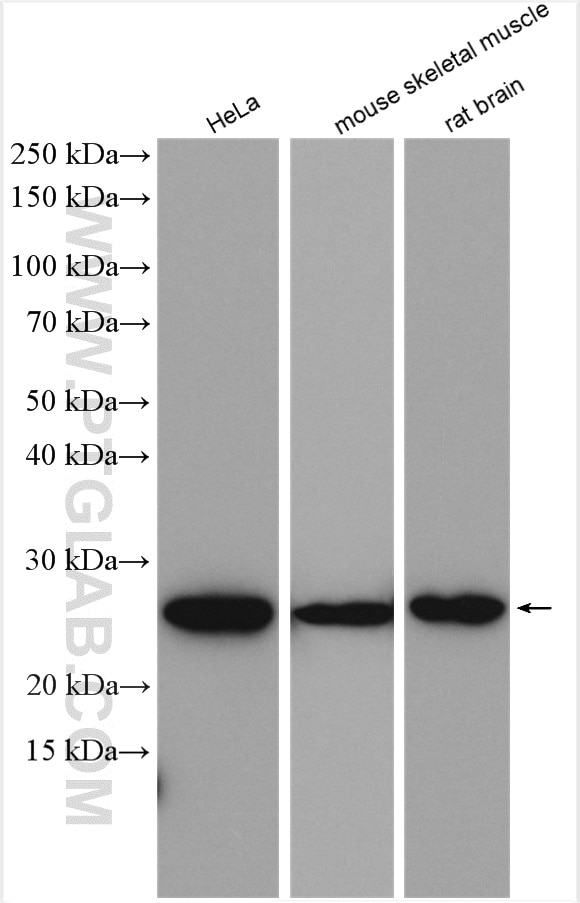
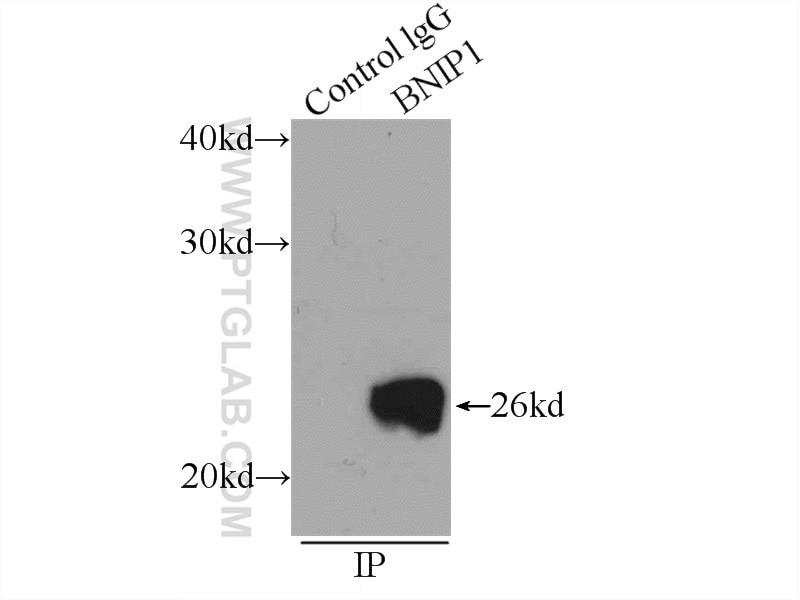
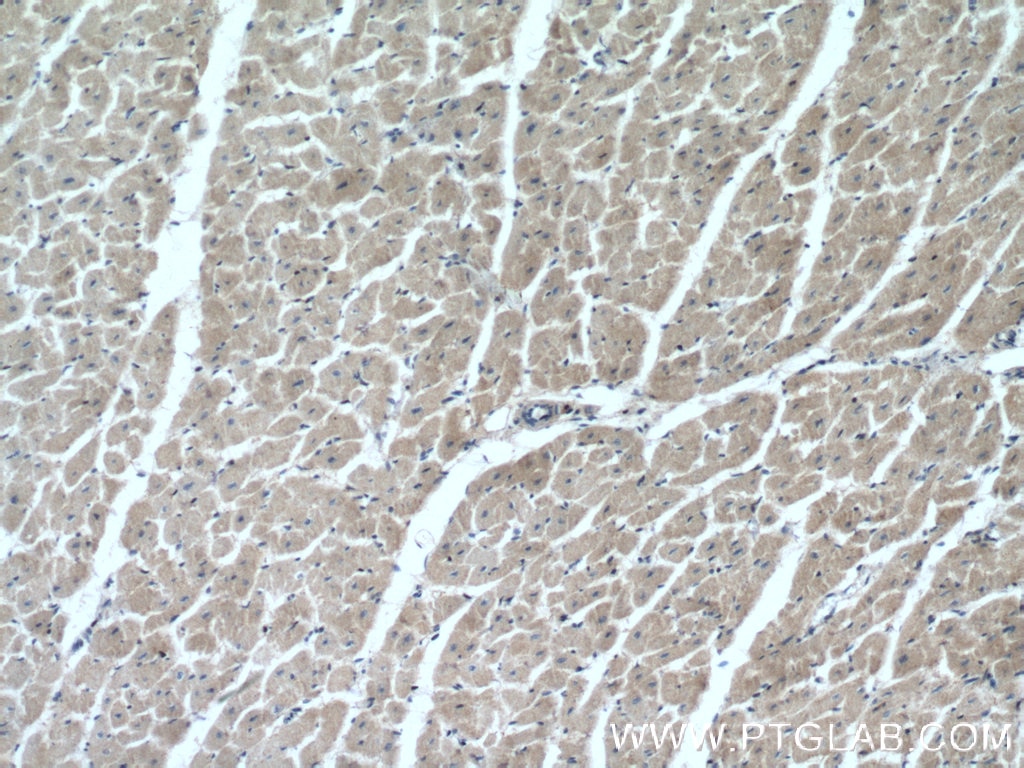
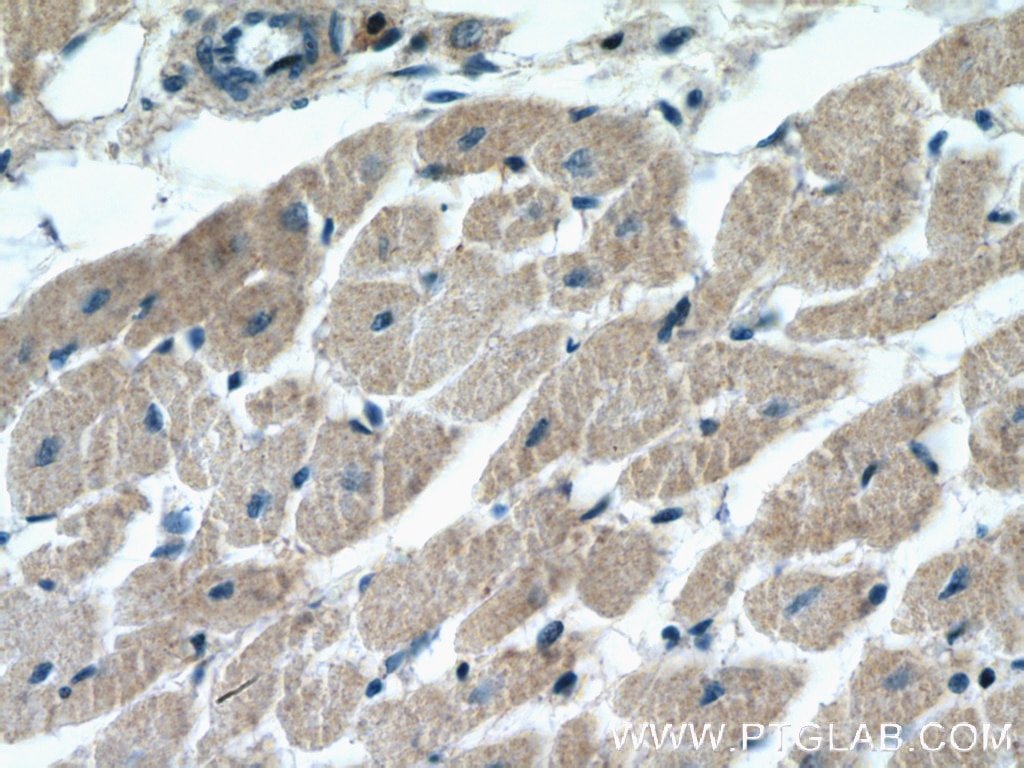
15964-1-PBS targets BNIP1 in WB, IHC, IP, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | BNIP1 fusion protein Ag8737 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19kDa interacting protein 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 228 aa, 26 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 26 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC010959 |
| Gene Symbol | BNIP1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 662 |
| RRID | AB_2066636 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q12981 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
BNIP1 is a member of the BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa-interacting protein (BNIP) family. The encoded protein is predominantly localized to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), is a pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 homology domain 3 (BH3)-only protein. BNIP1, also called SEC20L, is a component of a SNARE complex consisting of STX18, USE1L, BNIP1/SEC20L and SEC22B which is involved in apoptosis and ER membrane fusion. Recent reports showed that expression of BNIP1 induced mitochondrial fragmentation in a BH3 domain-dependent manner via increasing dynamin-related protein 1 (Drp1) expression. RNF185 is a mitochondrial ubiquitin E3 ligase that regulates selective mitochondrial autophagy, BNIP1 colocalizes with RNF185 at mitochondria and is polyubiquitinated by RNF185 through K63-based ubiquitin linkage in vivo and modulatemitochondrial homeostasis through autophagy.