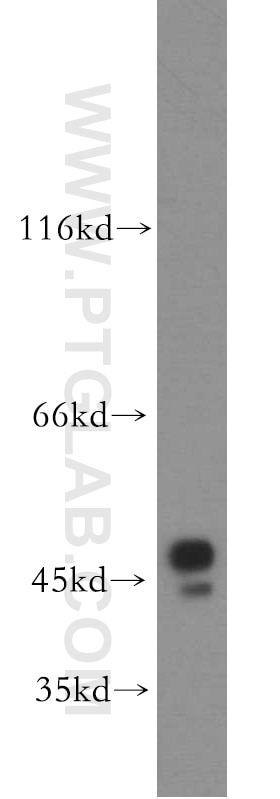
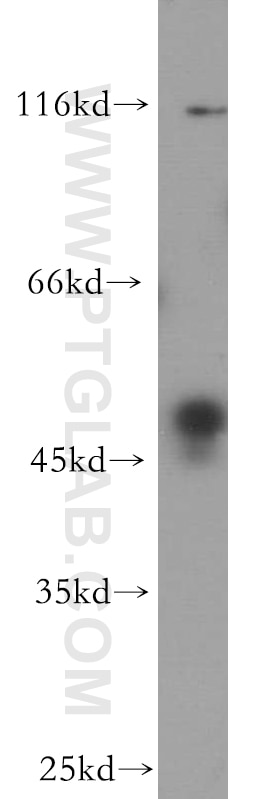
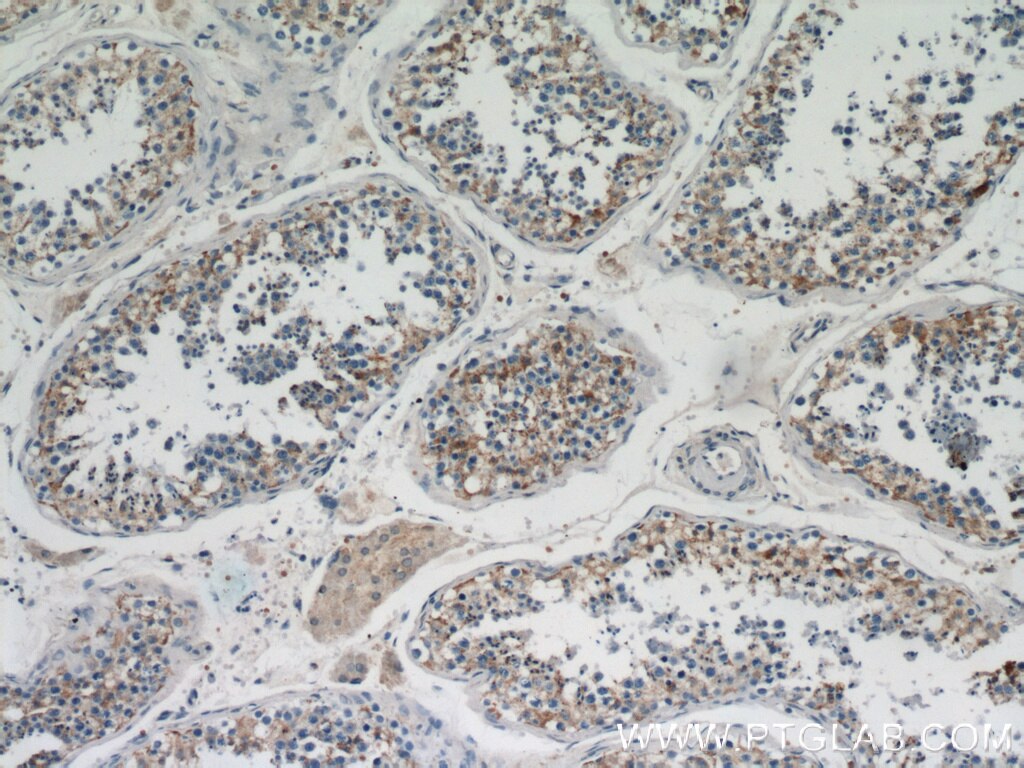
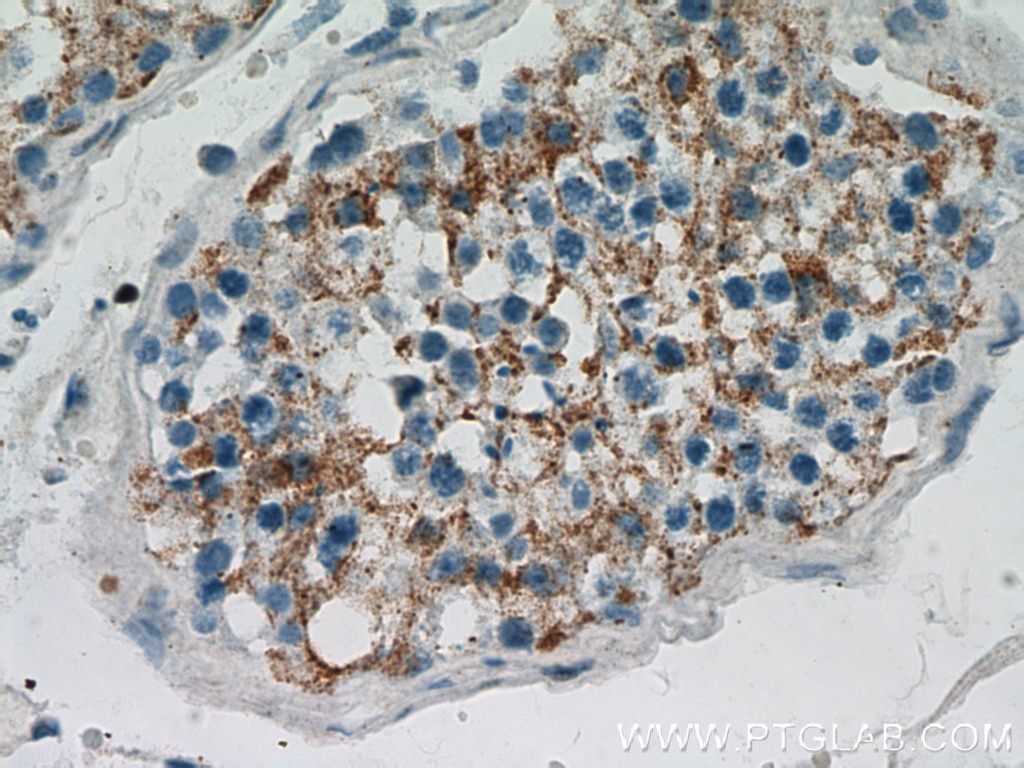
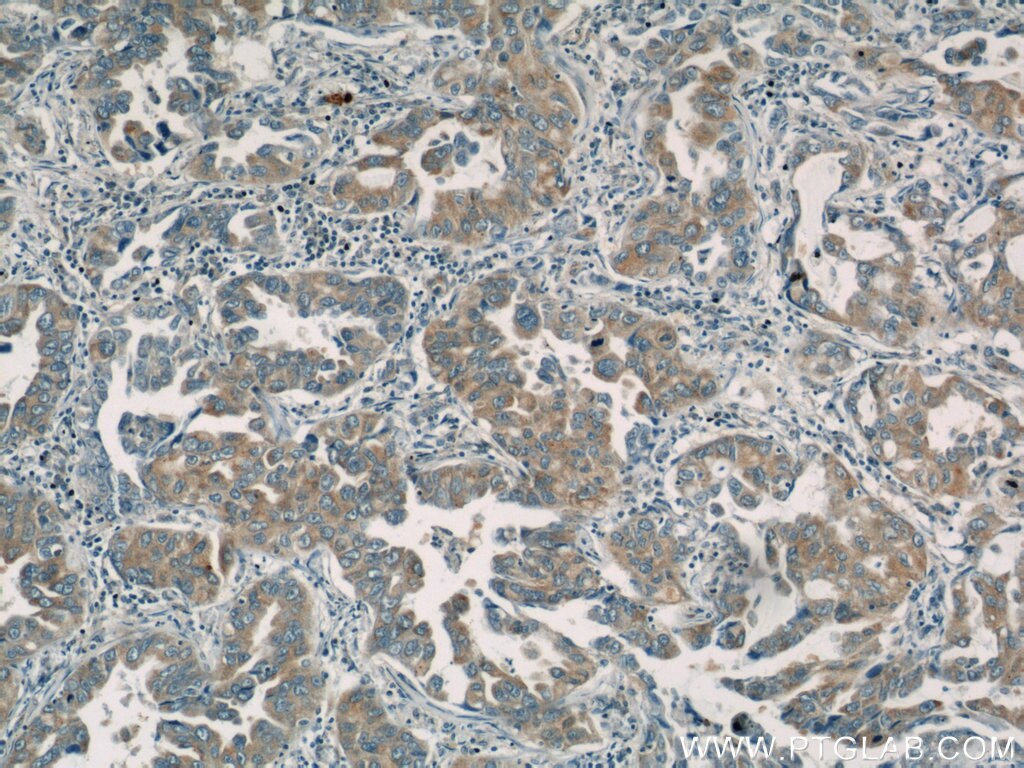
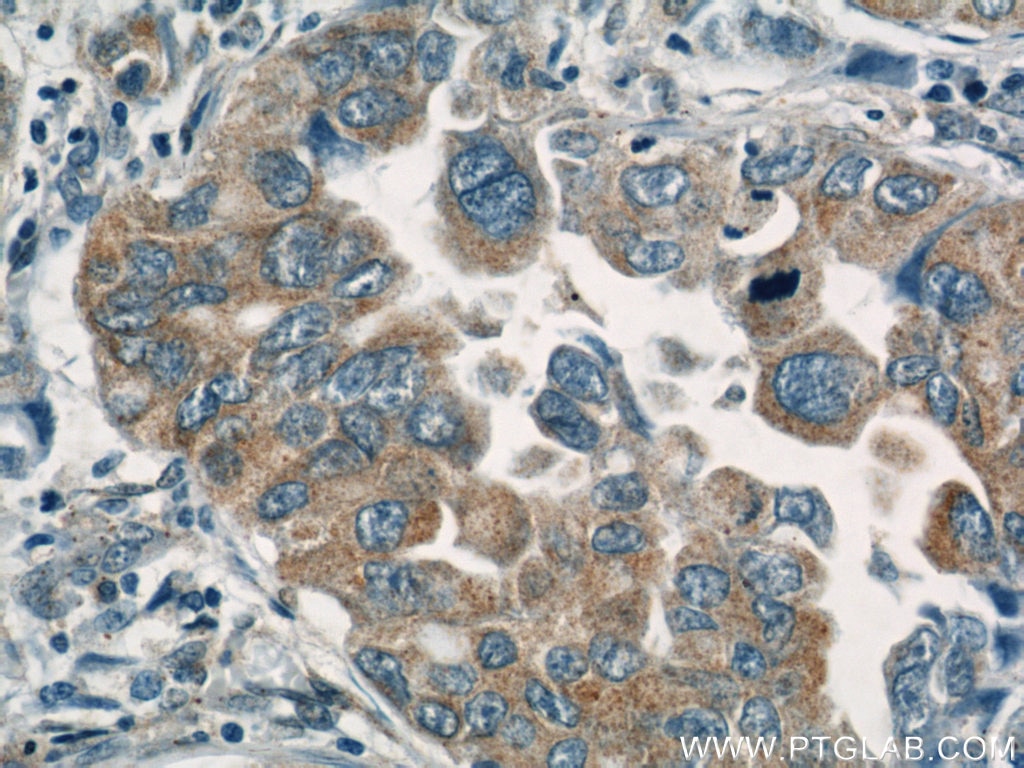
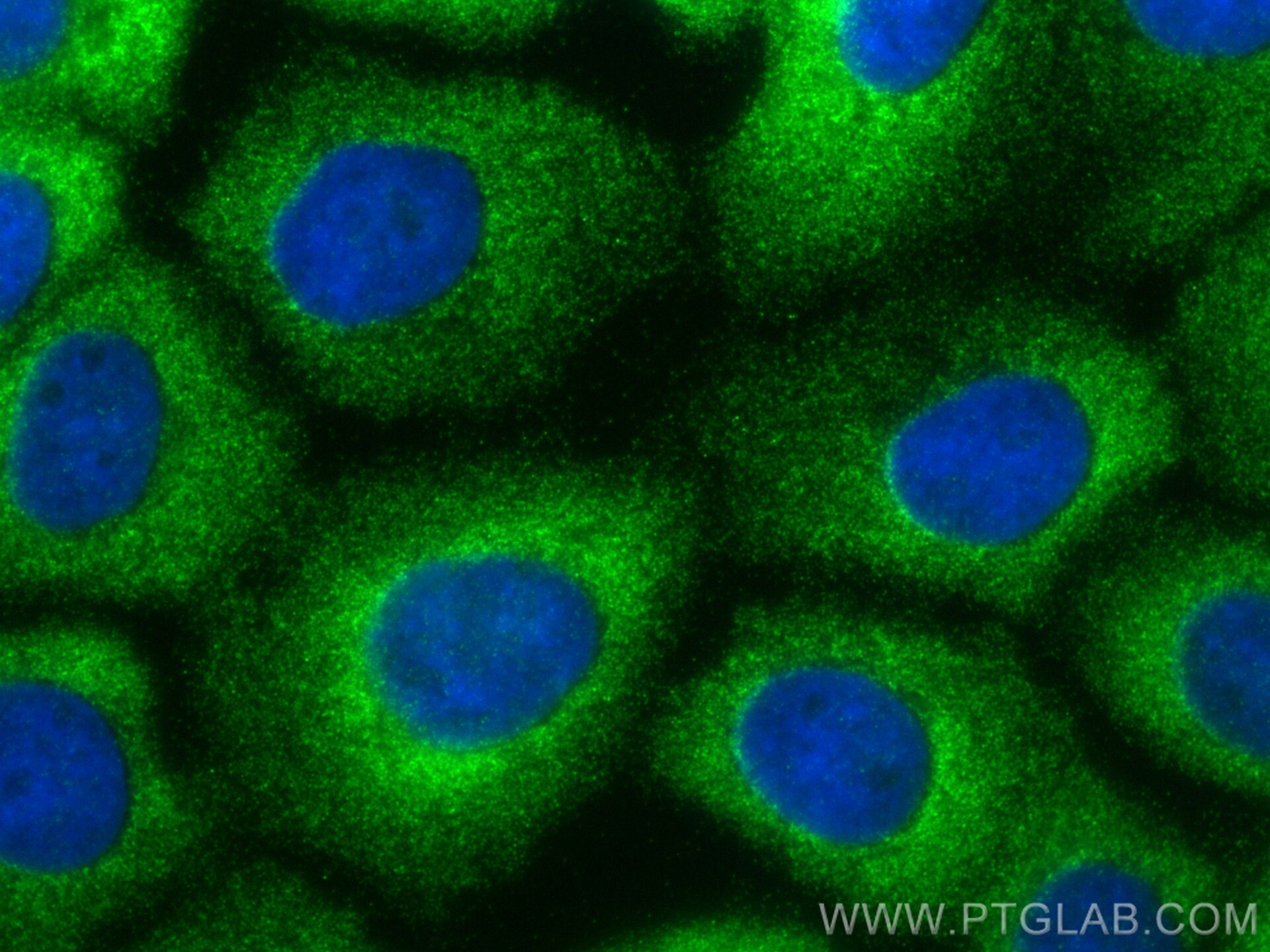
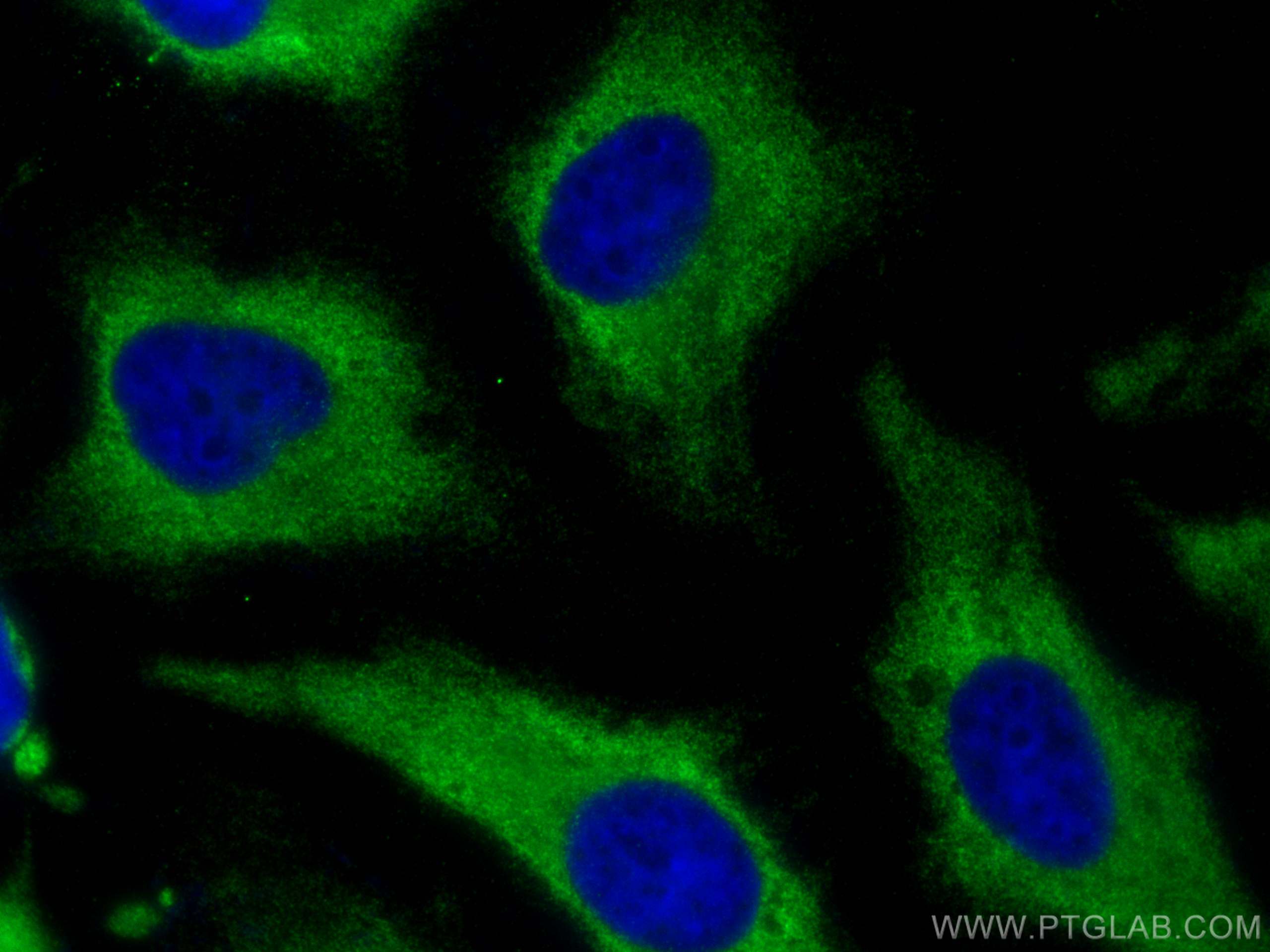
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
19917-1-PBS targets BZW1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | BZW1 fusion protein Ag13830 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | basic leucine zipper and W2 domains 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 353 aa, 41 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 48 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC001804 |
| Gene Symbol | BZW1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9689 |
| RRID | AB_10693530 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q7L1Q6 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
BZW1, also known as basic leucine zipper and W2 domains 1, is a member of the basic leucine zipper (bZIP) superfamily of transcription factors. It is a 45 kDa protein that contains an N-terminal bZIP domain for protein interactions and a C-terminal nucleotide (ATP or GTP) binding domain. Human BZW1 can activate transcription of the histone H4 gene and serve as a co-regulator with other transcription factors to control the cell cycle. In recent years, BZW1 has been identified as enhancing phosphorylation to promote glycolysis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Moreover, BZW1 has been found to regulate the cell cycle in ovarian cancer, thereby promoting its progression. Additionally, BZW1 plays a crucial role in mucoepidermoid carcinoma of the salivary glands. BZW1 is also involved in the regulation of translation initiation, acting as a translational rheostat and autoregulating its own translation. It has been suggested that BZW1, as well as its paralog BZW2, is an eIF5-mimic protein. BZW1 has been shown to facilitate glycolysis and promote tumor growth in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through potentiating eIF2α phosphorylation, and it may serve as a therapeutic target for patients with pancreatic cancer. In macrophages, activation of BZW1 by CEBPB promotes eIF2α phosphorylation-mediated metabolic reprogramming and endoplasmic reticulum stress. BZW1 has also been found to be associated with the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in lung adenocarcinoma, potentially influencing epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) processes.