Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
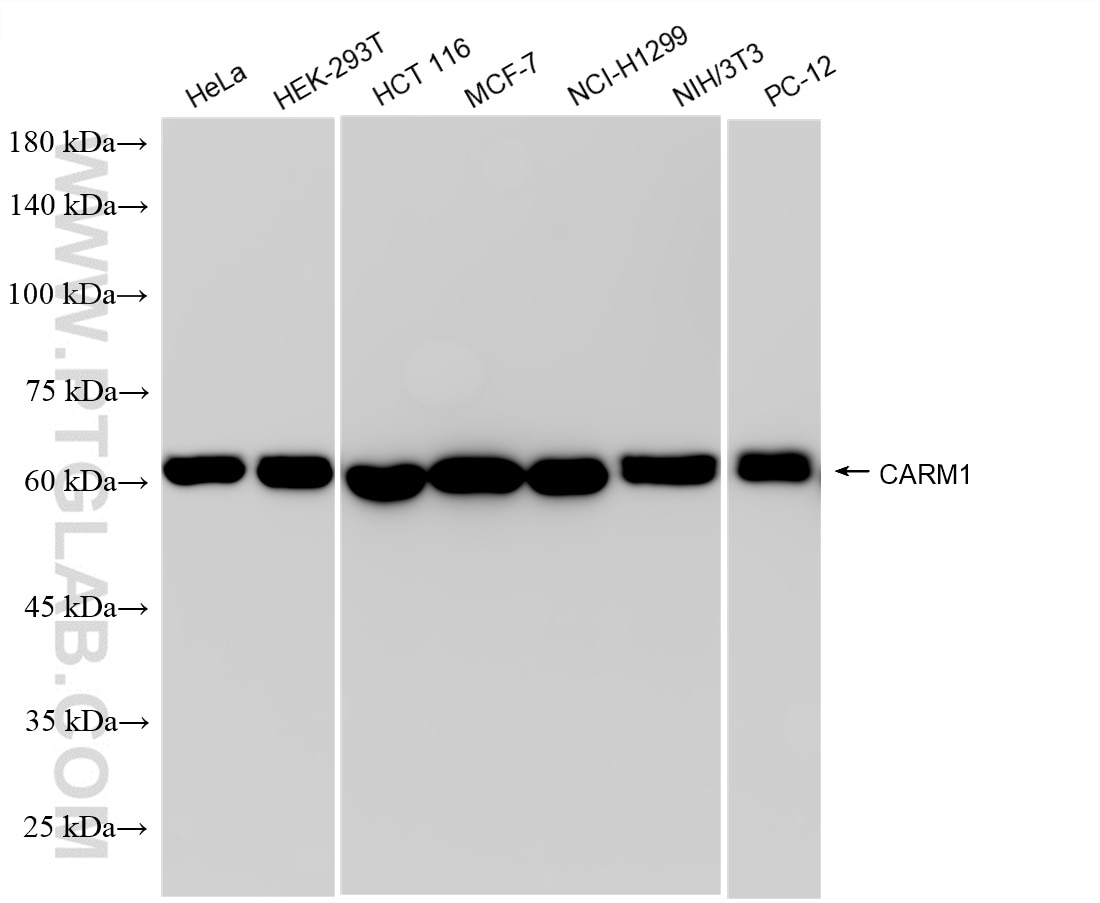
85146-3-PBS targets CARM1 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Peptide 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | coactivator-associated arginine methyltransferase 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 66 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 63-65 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_199141 |
| Gene Symbol | CARM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10498 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q86X55 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
CARM1, also named as PRMT4, belongs to the protein arginine N-methyltransferase family. It is a dual functional coregulator that facilitates transcription initiation by methylation of Arg17 and Arg26 of histone H3 and also dictates the subsequent coactivator complex disassembly by methylation of the steroid receptor coactivator family coactivators and p300/cAMP-response element-binding protein. CARM1 functions as a coactivator for many nuclear receptors, such as oestrogen receptor, androgen receptor, thyroid receptor and farnesoid X-receptor. It also coactivates other transcription factors such as myocyte enhancer factor 2C (MEF2C), β-catenin, p53, nuclear factor (NF)-kB and the cAMP-responsive element-binding factor. The enzymatic activity and coactivator function of CARM1 has been found to be inactivated through phosphorylation at a conserved serine residue at mitosis stage. This antibody was generated against a synthetic peptide corresponding to a fragment of human CARM1. It is expected to specifically recognize the CRAM1. In certain type of cells, like Hela, double bands can be detected with this antibody. This may due to the additional PTM sites in cells themselves.