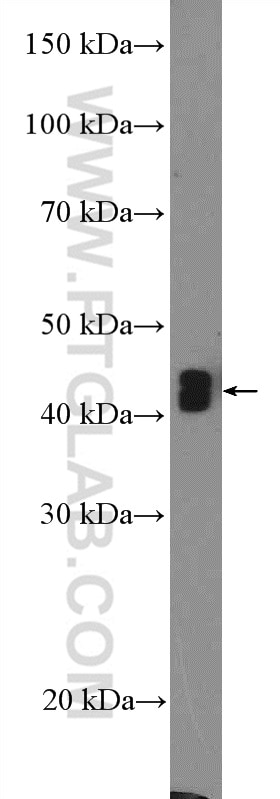
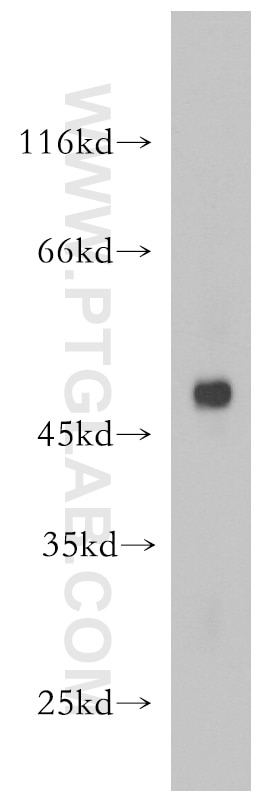
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | MCF-7 cells, Raji cells, mouse spleen tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 14 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
18330-1-AP targets CD24 in WB, IF, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag11679 Product name: Recombinant human CD24 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-80 aa of BC007674 Sequence: MGRAMVARLGLGLLLLALLLPTQIYSSETTTGTSSNSSQSTSNSGLAPNPTNATTKAAGGALQSTASLFVVSLSLLHLYS 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | CD24 molecule |
| Calculated molecular weight | 8 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 30-70 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC007674 |
| Gene Symbol | CD24 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 100133941 |
| RRID | AB_10644293 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P25063 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
CD24 is a cell surface signal transducing molecule, which is also known as a cluster of differentiation 24 or heat stable antigen CD24 (HSA) (PMID: 7959762). It is a sialoglycoprotein that is anchored to the plasma membrane via a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) link. Due to its cell surface localization, it contributes to a wide range of downstream signaling networks and has been shown to play crucial roles during neural development (PMID: 27993646) and the differentiation of various cell types. For example, it promotes antigen-dependent proliferation of B-cells, while preventing their terminal differentiation into antibody-producing cells (PMID: 11313396). CD24 may also play a role in apoptosis regulation, as cross-linking of this protein on the surface of neutrophils induces cell death, which seems to be defective in sepsis (PMID: 24501201). In addition, CD24 has been linked to negative regulation of the immune responses, particularly to danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) (PMID: 24996822).
What is the molecular weight of CD24?
According to NCBI, there are two known isoforms of CD24; the shorter 80 aa (8 kDa) isoform 1, which is considered a canonical sequence that has been experimentally validated, and a longer 120 aa (12,9 kDa) protein (PMIDs: 16344560, 15489334). Isoform 1 is further processed into a mature 32 aa form. Apart from these, 3 potential computationally mapped isoforms have been suggested. The CD24 gene locus is localized on chromosome 6, while other non-transcribed loci have been found on chromosomes 1, 15, 20, and Y (PMID: 7959762).
What is the subcellular localization of CD24?
It is a cell surface protein that can act as an adhesion molecule.
What is the tissue specificity of CD24?
As a rule, CD24 tends to be expressed at higher levels in progenitor cells and metabolically active cells and to a lesser extent in terminally differentiated cells (PMID: 25613900). CD24 is specifically expressed in a number of B-cell lines, granulocytes, and differentiating neuroblasts (PMID: 8753773, 12447971). The expression is lost when primary B-cells are induced to differentiate in antibody-forming cells. CD24 expression has also been linked with various malignancies: epithelial neoplasms (PMID:16164042), erythroleukemia cell and small cell lung carcinoma cell lines. For certain cancers it is considered a prognostic marker, usually associated with poor patient prognosis, e.g., colorectal cancer (PMID: 16166435) and ovarian cancer (PMID: 2368195).
What is the involvement of CD24 in disease?
As mentioned before it is considered a prognostic marker in various malignancies. However, it is also clearly associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). Indeed, a single nucleotide polymorphism V57A has been associated with an over 2-fold increase in the susceptibility to MS and has been generally linked to a quicker progression of the disease in the general population (PMID: 14657362).
What are the main roles of CD24?
Considering its expression patterns, it is clear why CD24 plays the most important roles in immune cells. It can be used as a marker for the differentiation of hematopoietic and neuronal cells, in addition to tissue and tumor stem cells (PMID: 12447971). CD24 has also been found to mediate apoptosis in precursor-B acute lymphoblastic leukemia cell lines in the pro-B and pre-B stages accompanying activation of multiple caspases (PMID: 12496407). It has also been shown to play a role in autoimmune responses, as CD24-deficient mice are resistant to autoimmune encephalomyelitis (PMID: 10791997).
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Commun Necroptosis enhances 'don't eat me' signal and induces macrophage extracellular traps to promote pancreatic cancer liver metastasis | ||
Cancer Lett Cancer stem-like cell characteristics induced by EB virus-encoded LMP1 contribute to radioresistance in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by suppressing the p53-mediated apoptosis pathway. | ||
Cancer Cell Int SOCS6 promotes radiosensitivity and decreases cancer cell stemness in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by regulating c-Kit ubiquitylation. | ||
Biomolecules COL11A1-Driven Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Stemness of Pancreatic Cancer Cells Induce Cell Migration and Invasion by Modulating the AKT/GSK-3β/Snail Pathway. | ||
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) miR-345 inhibits migration and stem-like cell phenotype in gastric cancer via inactivation of Rac1 by targeting EPS8. |