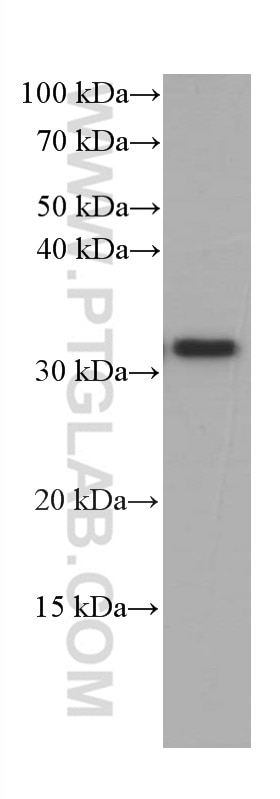
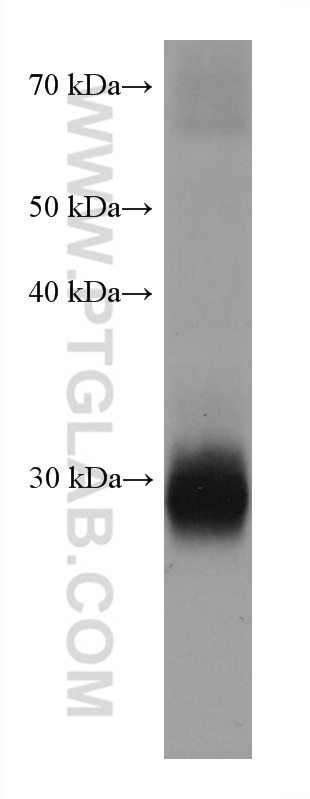
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
66502-1-PBS targets CD40L/CD154 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | CD40L/CD154 fusion protein Ag24941 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | CD40 ligand |
| Calculated molecular weight | 261 aa, 29 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 30 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC071754 |
| Gene Symbol | CD40 Ligand |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 959 |
| RRID | AB_2881866 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P29965 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
The CD40 ligand (CD40L, TRAP, CD154), a member of the TNF superfamily of ligands, is expressed as either a 33-kd transmembrane homologue or 18-kd soluble form (sCD154). CD40L is primarily expressed on activated CD4+ T cells and on a small proportion of CD8+ T cells and platelets. It binds to CD40 on antigen-presenting cells (APC), which leads to many effects depending on the target cell type. Recent studies have suggested that CD40/CD40L interactions regulate oxidative stress and affect various signaling pathways in both the immunological and the cardiovascular systems. The CD40/CD40L system is also involved in tumorigenesis. Its expression is tightly regulated, and abnormal levels of CD40L are associated with the pathogenesis of atheromatous plaque destabilization and thrombotic events. Multiple mutations in CD40LG gene have been identified that are associated with hyper-IgM immunodeficiency syndrome type 1.