Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
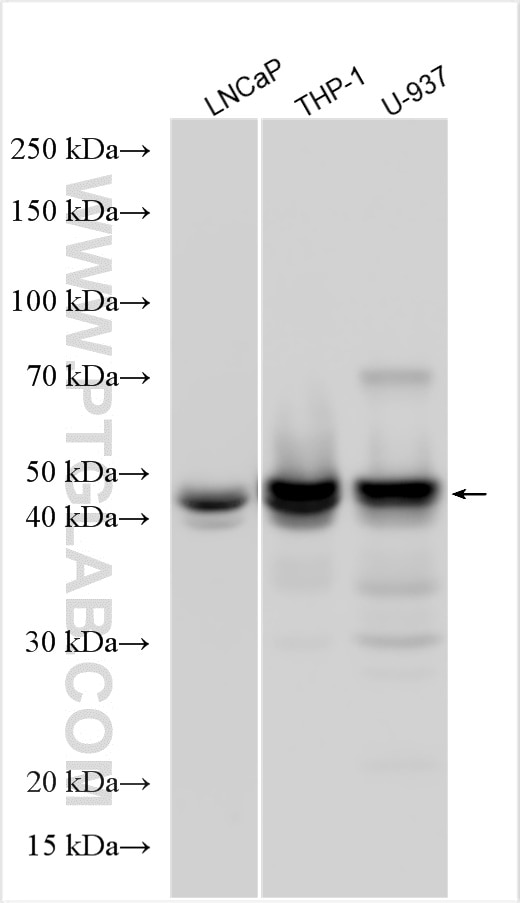
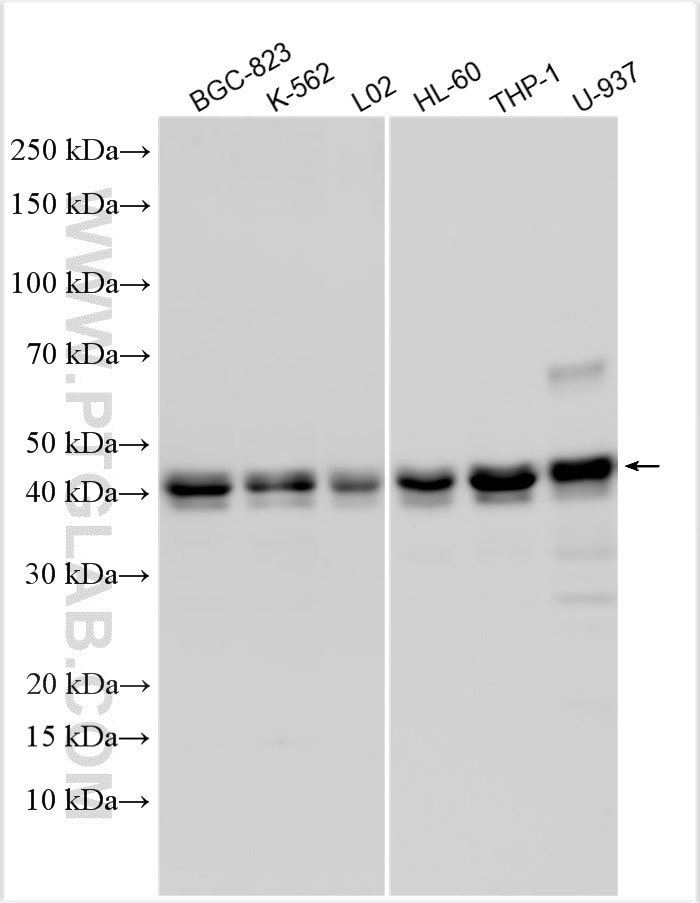
| Positive WB detected in | BGC-823 cells, LNCaP cells, THP-1 cells, U-937 cells, K-562 cells, L02 cells, HL-60 cells |
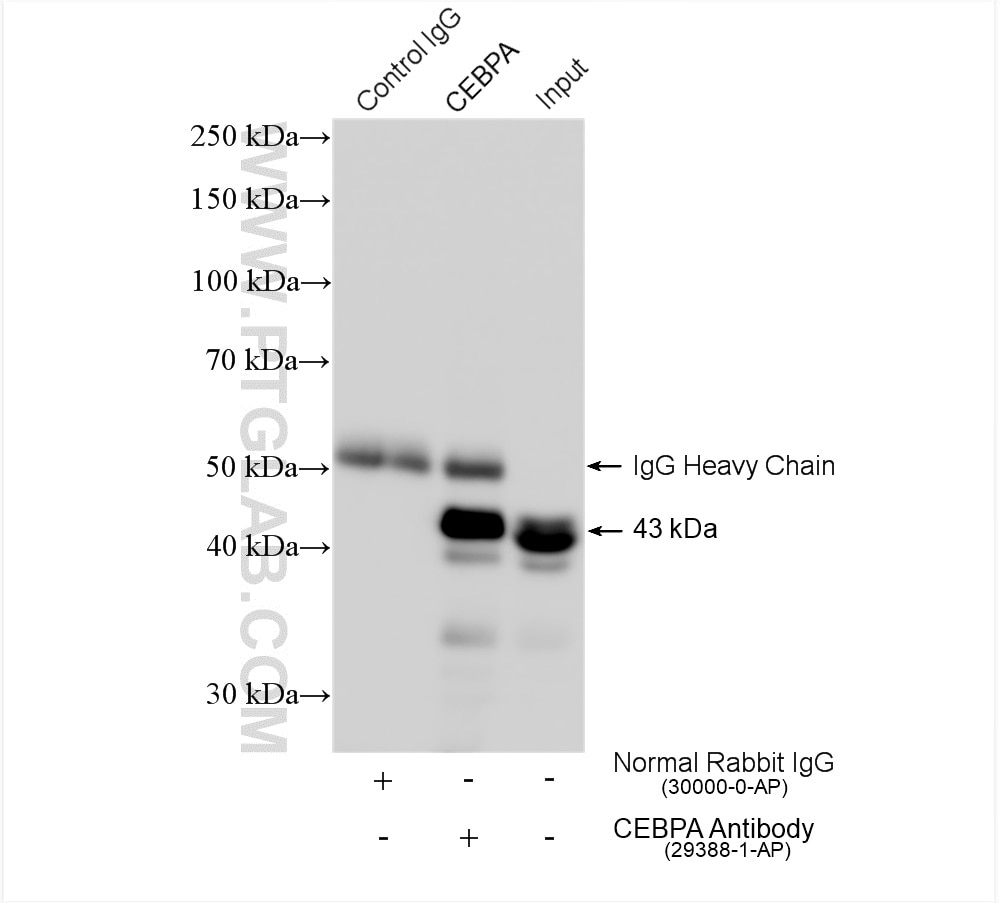
| Positive IP detected in | THP-1 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:1000-1:6000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 1 publications below |
| WB | See 11 publications below |
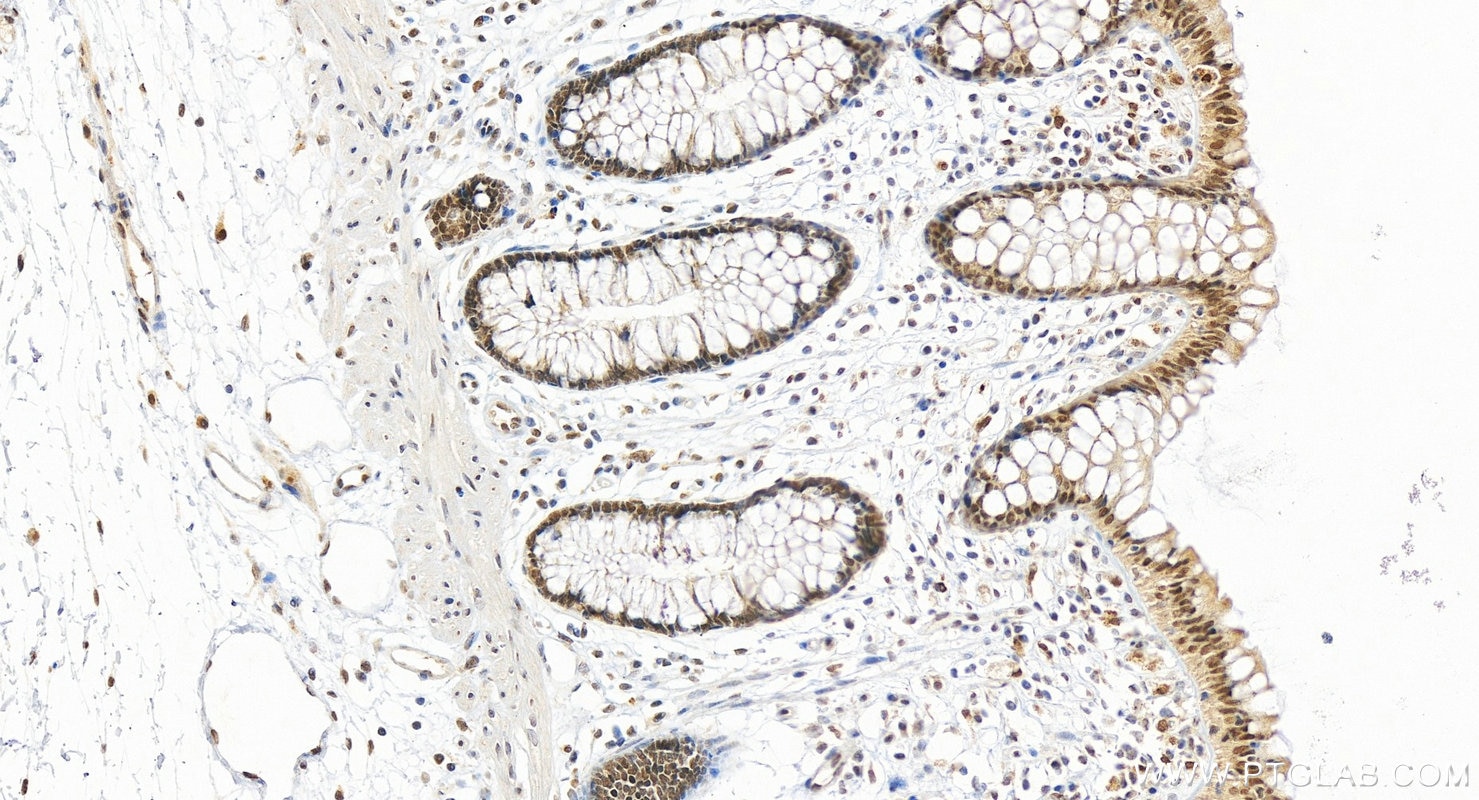
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
29388-1-AP targets CEBP Alpha/CEBPA in WB, IHC, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | CEBP Alpha/CEBPA fusion protein Ag29947 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), alpha |
| Calculated molecular weight | 38 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 40-45 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_004364 |
| Gene Symbol | CEBPA |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1050 |
| RRID | AB_3086127 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P49715 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
CEBPA and its isoforms play important roles in lineage determination and gene activation in a variety of cell types by activating transcription from lineage-specific promoters. CEBPA is a DNA-binding protein that recognizes two different motifs: the CCAAT homology common to many promoters and the enhanced core homology common to many enhancers. In hematopoiesis, C/EBPa is a key factor in driving the development of myeloid cells interacting with a variety of factors, including c-Myc, PU.1, and microRNAs. It can also form heterodimers with the related proteins CEBP-beta and CEBP-gamma. The encoded protein has been shown to bind to the promoter and modulate the expression of the gene encoding leptin which plays an important role in body weight homeostasis. CEBPA can interact with CDK2 and CDK4, thereby inhibiting these kinases and causing growth arrest in cultured cells. Several pathways have been implicated as the means by which CEBPA mediates cell cycle arrest and proliferation, including p21, cyclin-dependent kinases and the E2F complex via c-Myc. The calcualted molecular weight of CEBPA is 38 kDa, but modified CEBPA is about 42 kDa (PMID: 19623175).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for CEBP Alpha/CEBPA antibody 29388-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for CEBP Alpha/CEBPA antibody 29388-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Front Pharmacol Bushen Huoxue formula attenuates lipid accumulation evoking excessive autophagy in premature ovarian insufficiency rats and palmitic acid-challenged KGN cells by modulating lipid metabolism | ||
J Virol Dengue virus NS1 leads to downregulation of HNF4 alpha in liver cells resulting in a decrease in coagulation factors I, V, X, and XIII, contributing to coagulopathy | ||
Pharmaceuticals (Basel) Potential Anti-Obesity Effect of Hazel Leaf Extract in Mice and Network Pharmacology of Selected Polyphenols | ||
Sci Rep A comprehensive analysis of CEBPA on prognosis and function in uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma | ||
Genes Dis MAFB-mediated CEBPA regulated human urothelium growth through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway | ||
Mol Med Ginsenoside Rb1 affects mitochondrial Ca2+ transport and inhibits fat deposition and fibrosis by regulating the wnt signaling pathway to treat rotator cuff tears via docking with SFRP1 |