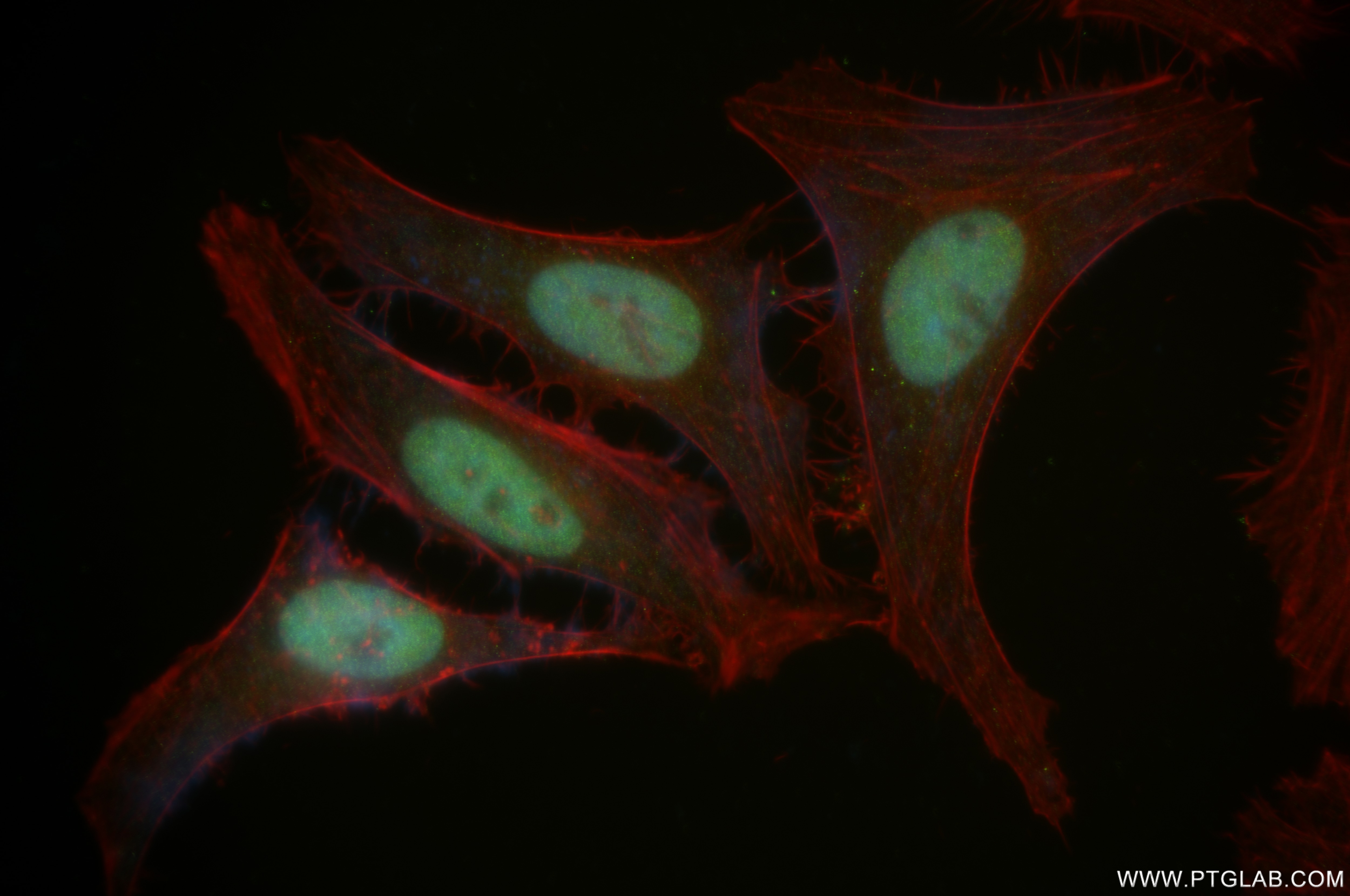
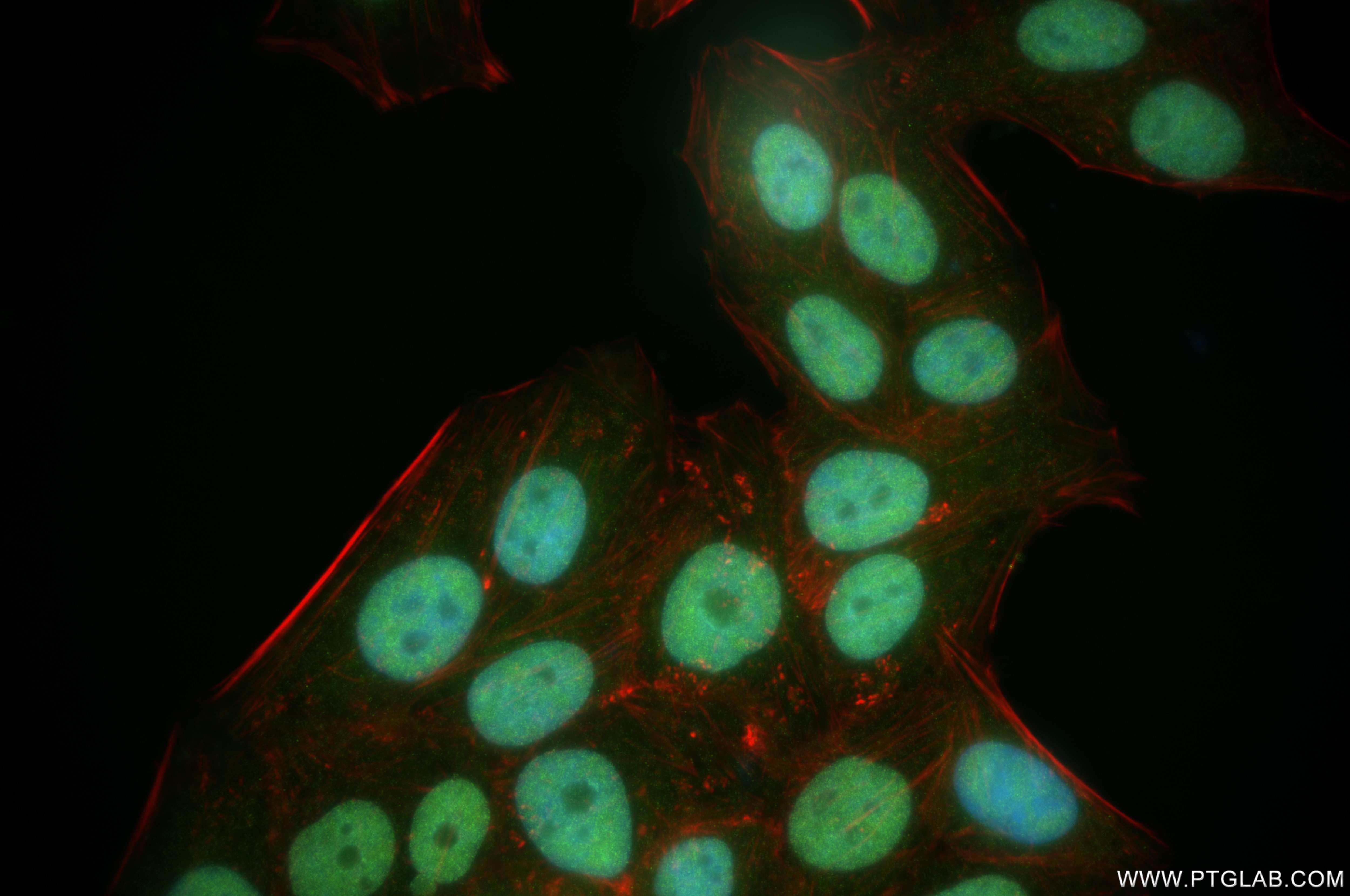
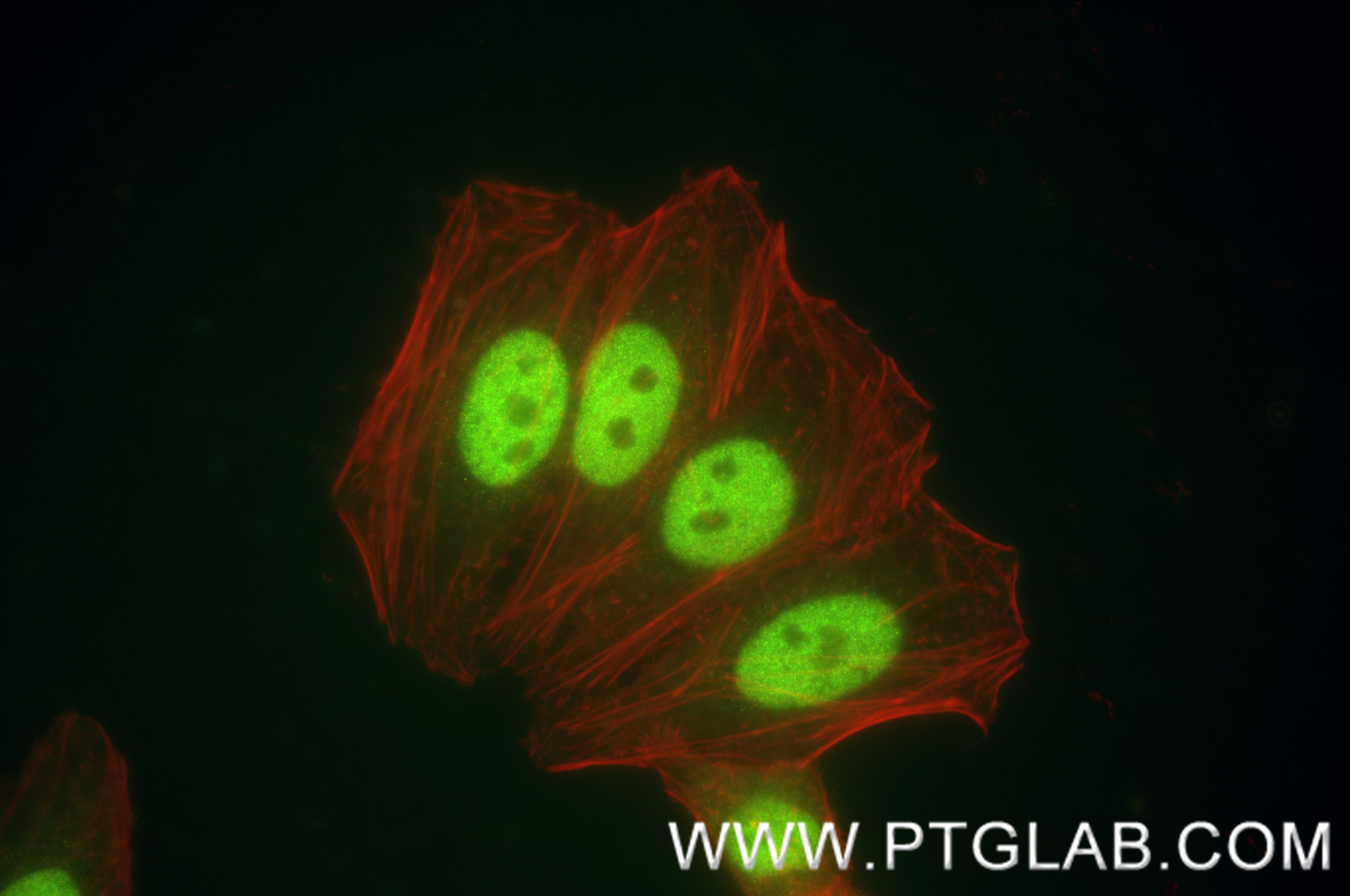
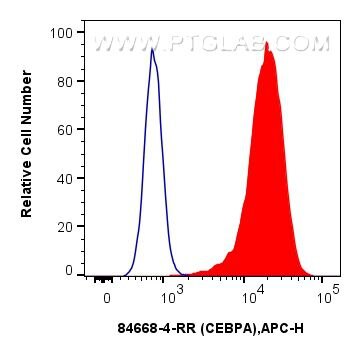
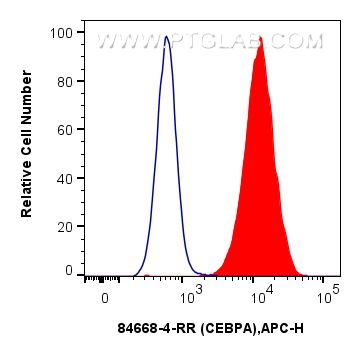
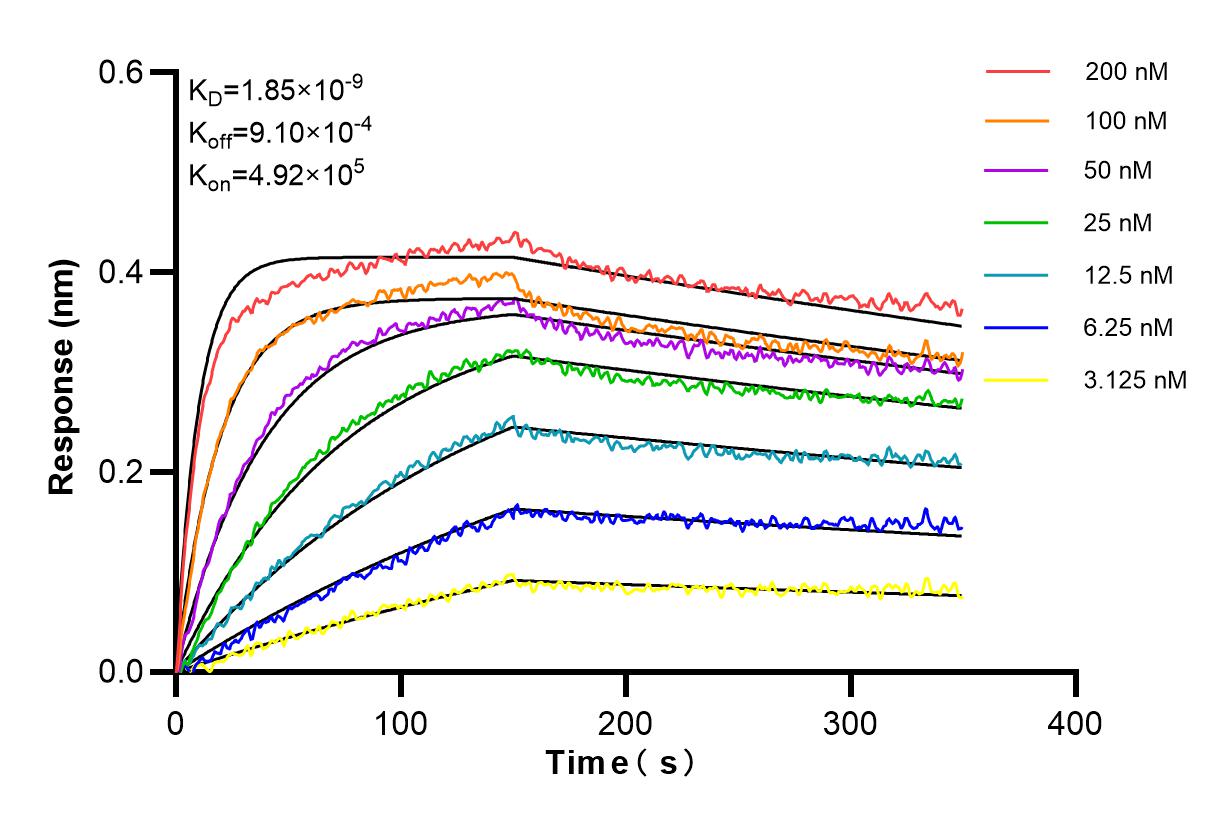
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
84668-4-PBS targets CEBP Alpha/CEBPA in IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | CEBP Alpha/CEBPA fusion protein Ag29947 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), alpha |
| Calculated molecular weight | 38 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 40-45 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_004364 |
| Gene Symbol | CEBPA |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1050 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | P49715 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
CEBPA and its isoforms play important roles in lineage determination and gene activation in a variety of cell types by activating transcription from lineage-specific promoters. CEBPA is a DNA-binding protein that recognizes two different motifs: the CCAAT homology common to many promoters and the enhanced core homology common to many enhancers. In hematopoiesis, C/EBPa is a key factor in driving the development of myeloid cells interacting with a variety of factors, including c-Myc, PU.1, and microRNAs. It can also form heterodimers with the related proteins CEBP-beta and CEBP-gamma. The encoded protein has been shown to bind to the promoter and modulate the expression of the gene encoding leptin which plays an important role in body weight homeostasis. CEBPA can interact with CDK2 and CDK4, thereby inhibiting these kinases and causing growth arrest in cultured cells. Several pathways have been implicated as the means by which CEBPA mediates cell cycle arrest and proliferation, including p21, cyclin-dependent kinases and the E2F complex via c-Myc.