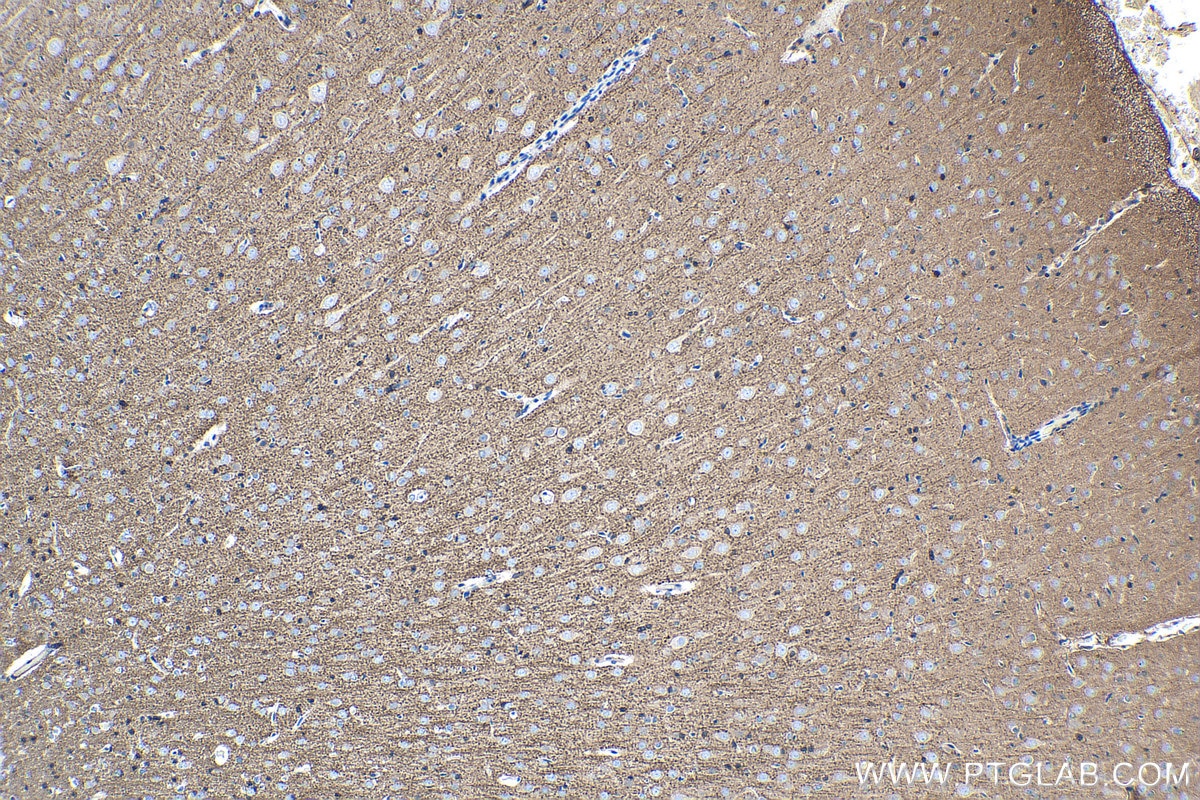
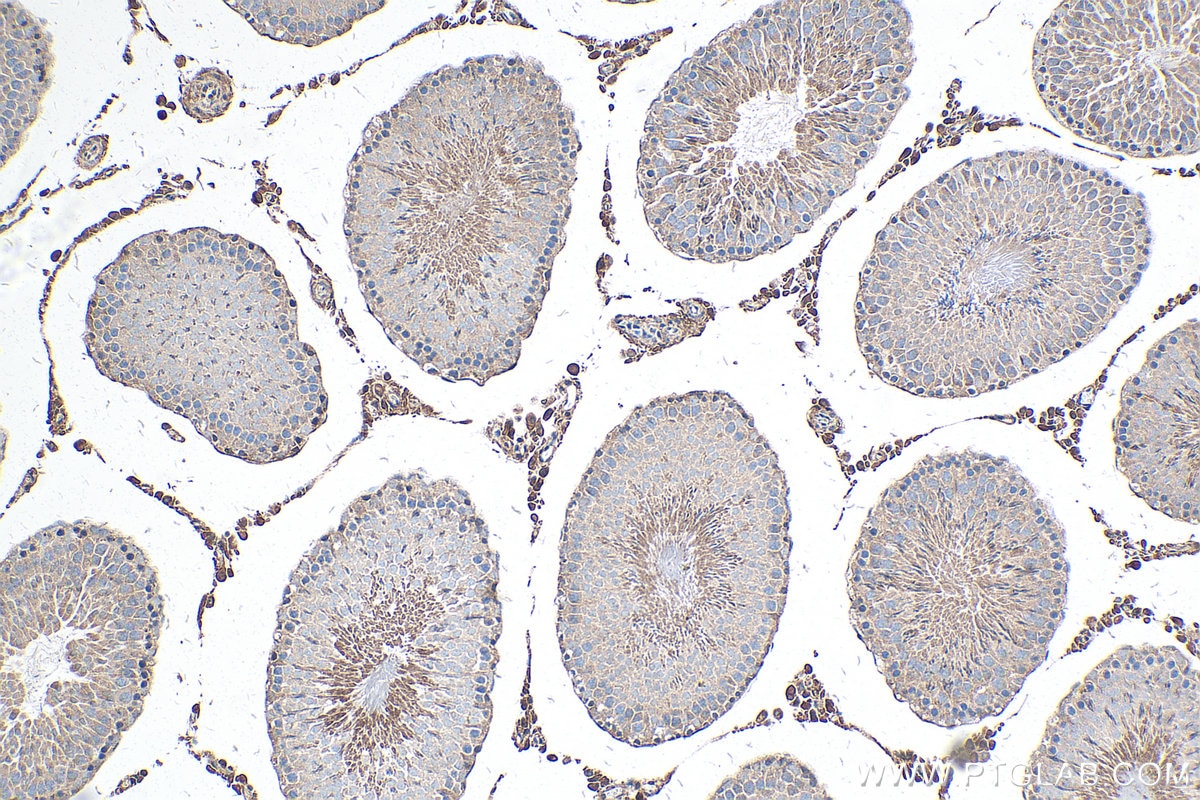
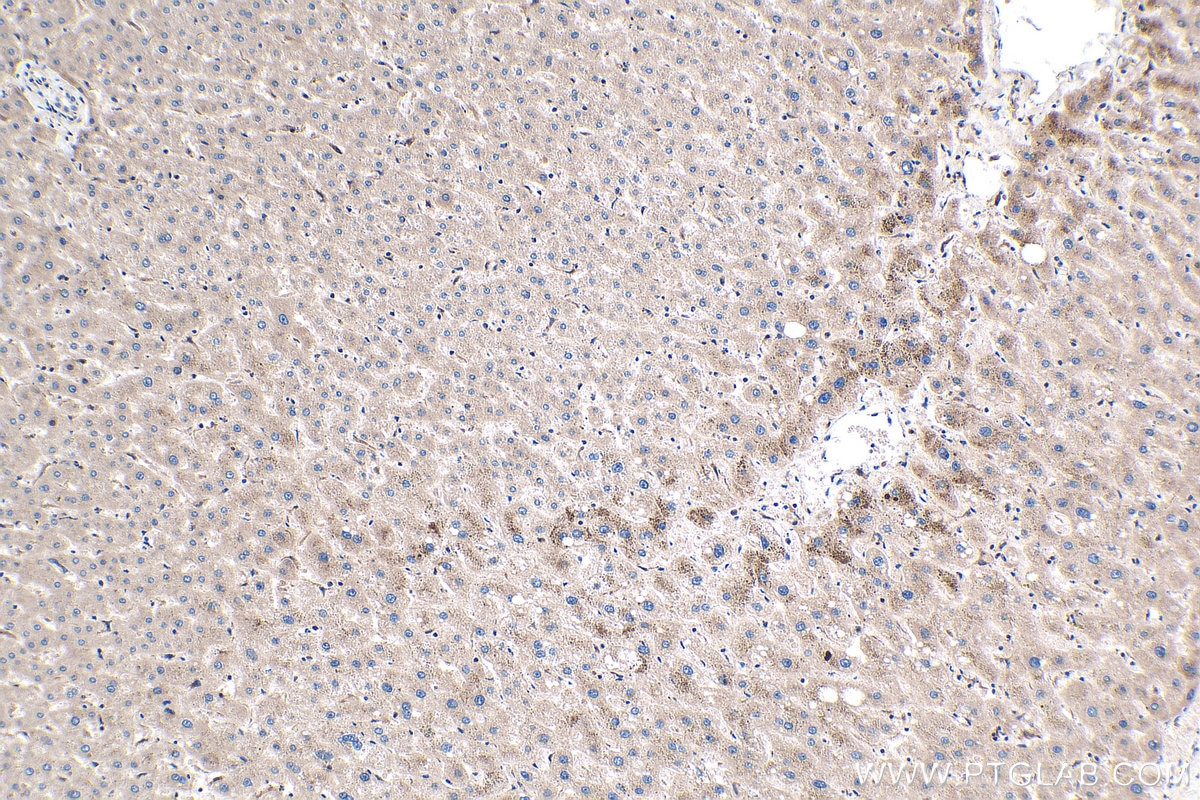
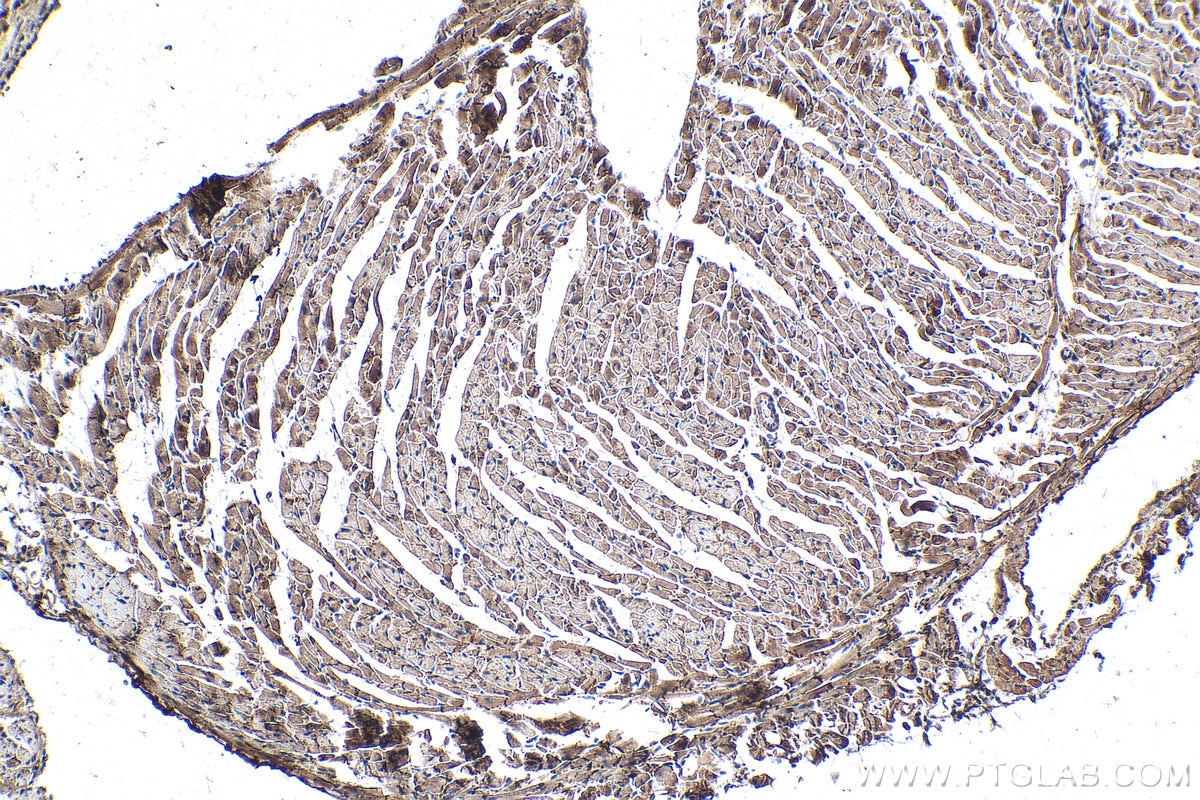
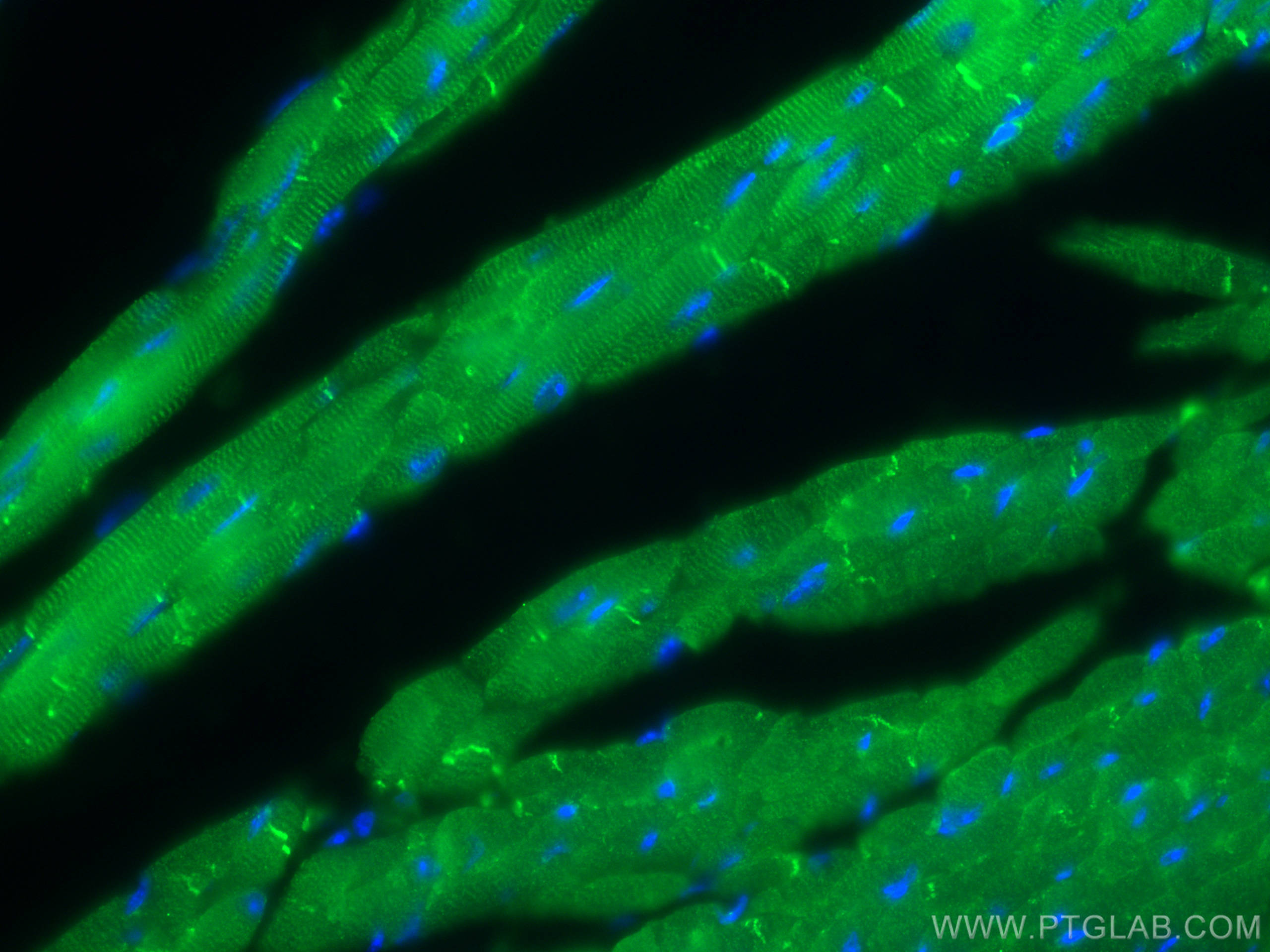
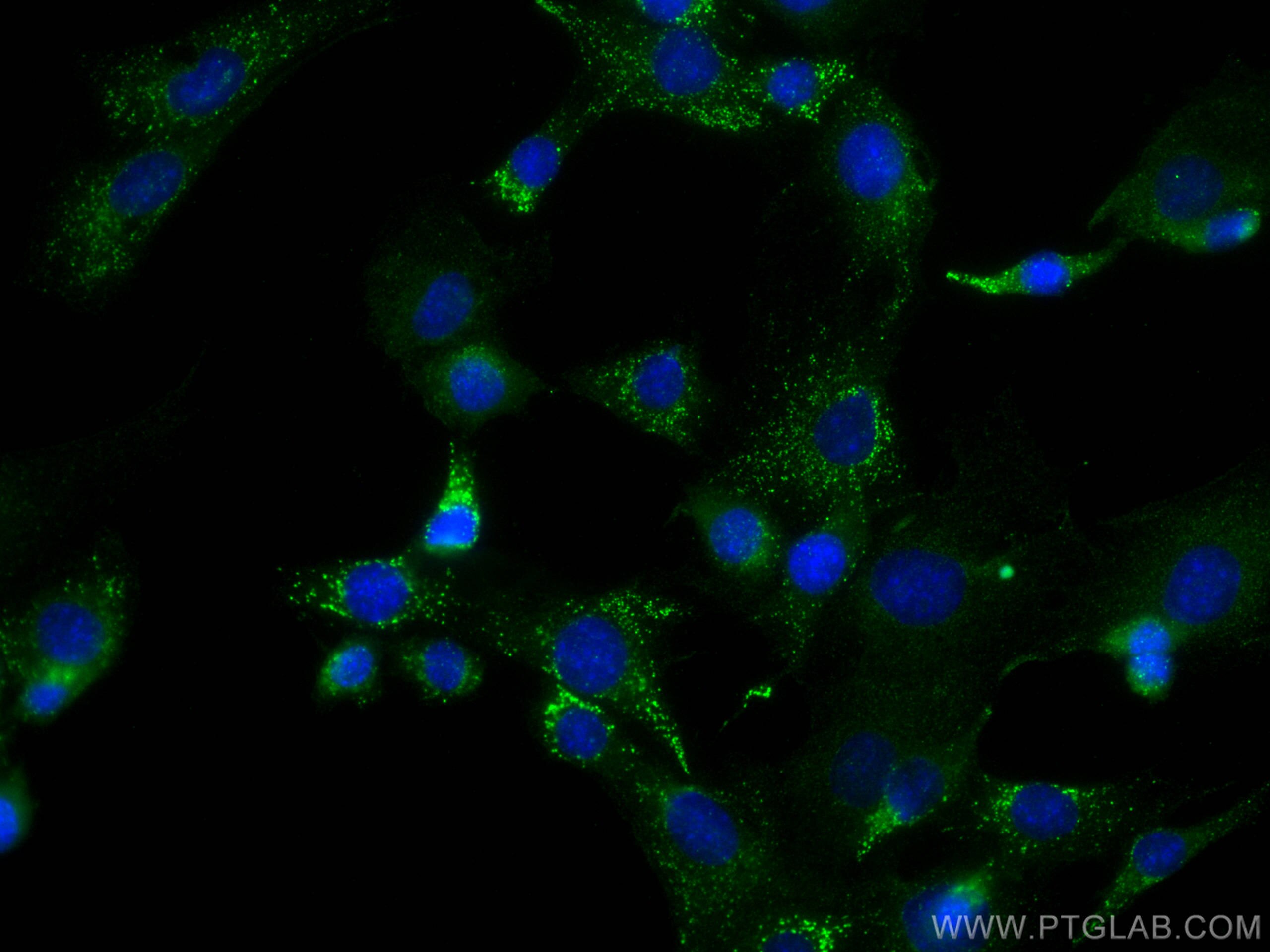
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
60177-1-PBS targets CKM-Specific in WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Peptide 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | creatine kinase, muscle |
| Calculated molecular weight | 43 kDa |
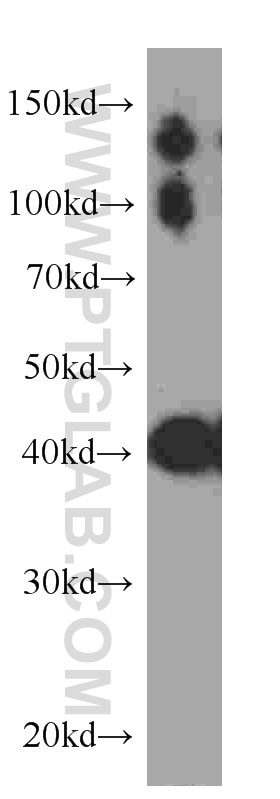
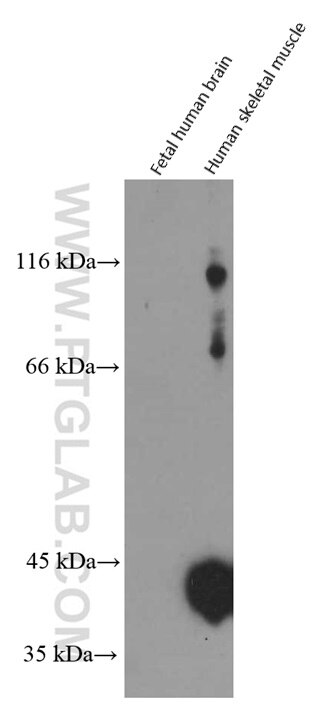
| Observed molecular weight | 43 kDa, 90 kDa, 130 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC007462 |
| Gene Symbol | CKM |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1158 |
| RRID | AB_10897180 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P06732 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
CKM, also named as CKMM and M-CK, is a member of the ATP:guanido phosphotransferase protein family. It is a cytoplasmic enzyme involved in energy homeostasis and is an important serum marker for myocardial infarction. CKM reversibly catalyzes the transfer of phosphate between ATP and various phosphogens such as creatine phosphate. It acts as a homodimer in striated muscle as well as in other tissues, and as a heterodimer with a similar brain isozyme in heart. CK isoenzymes play a central role in energy transduction in tissues with large, fluctuating energy demands, such as skeletal muscle, heart, brain and spermatozoa. CK MB consists of a dimer of nonidentical chains. With MM being the major form in skeletal muscle and myocardium, MB existing in myocardium. CKM has a calculated molecular mass of 43 kDa, and the 90-kDa and 130-kDa bands could be due to acovalent cross-linking of two and three CKm subunits, respectively (PMID: 20195383).