Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
60123-1-PBS targets CXCL16 as part of a matched antibody pair:
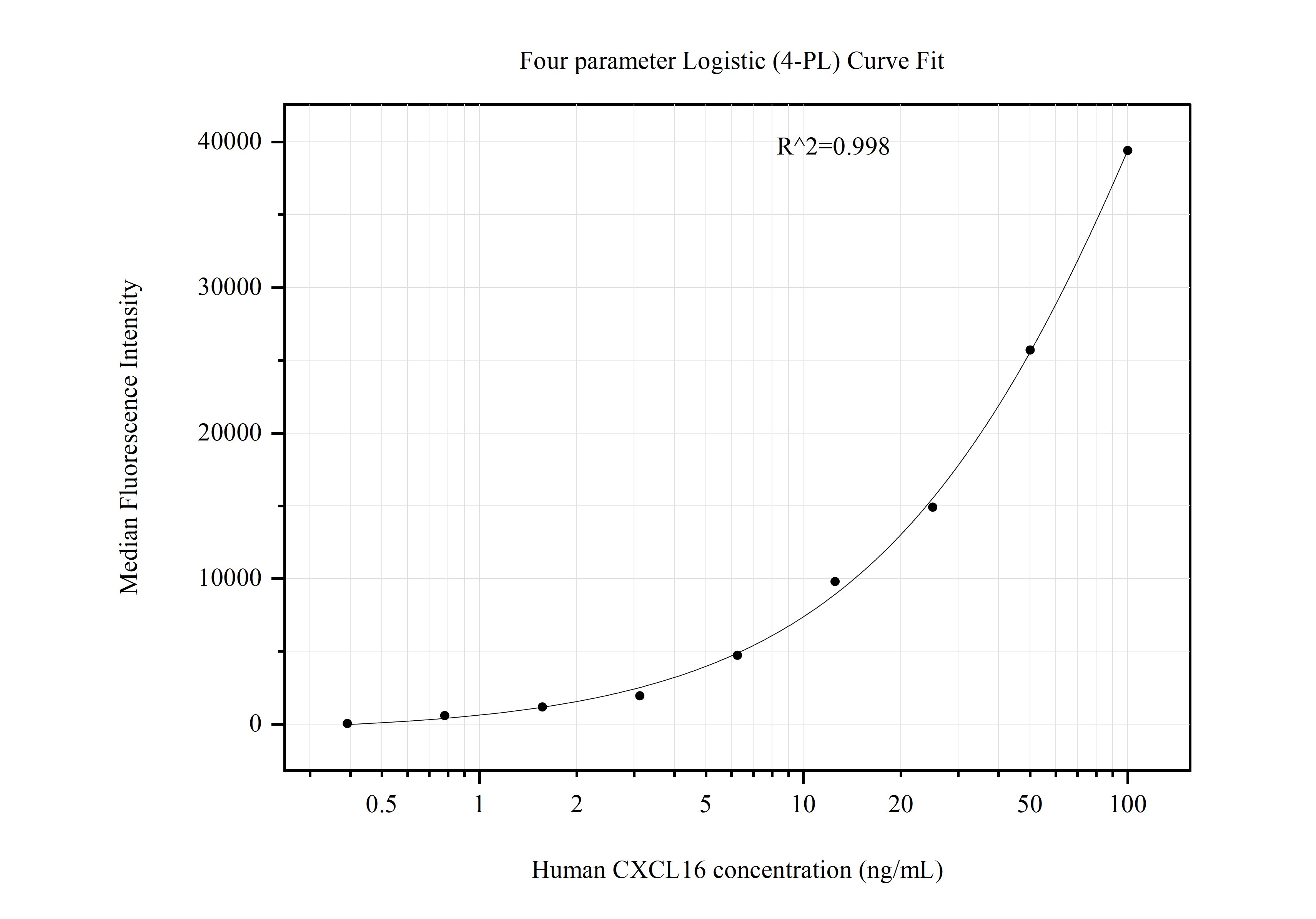
MP51127-1: 60123-2-PBS capture and 60123-1-PBS detection (validated in Cytometric bead array)
Unconjugated mouse monoclonal antibody pair in PBS only (BSA and azide free) storage buffer at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, ready for conjugation.
This conjugation ready format makes antibodies ideal for use in many applications including: ELISAs, multiplex assays requiring matched pairs, mass cytometry, and multiplex imaging applications.Antibody use should be optimized by the end user for each application and assay.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | CXCL16 fusion protein Ag4883 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 16 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 273 aa, 30 kDa |
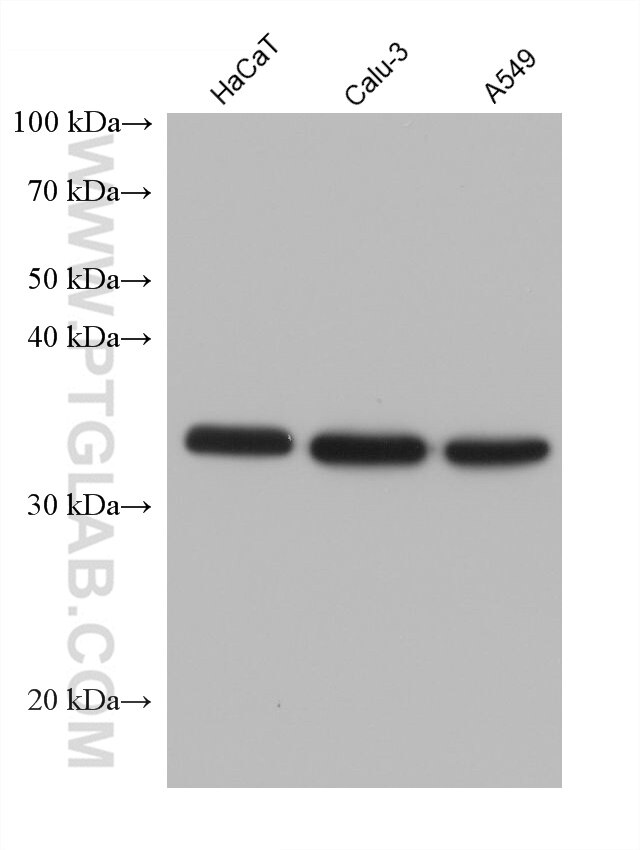
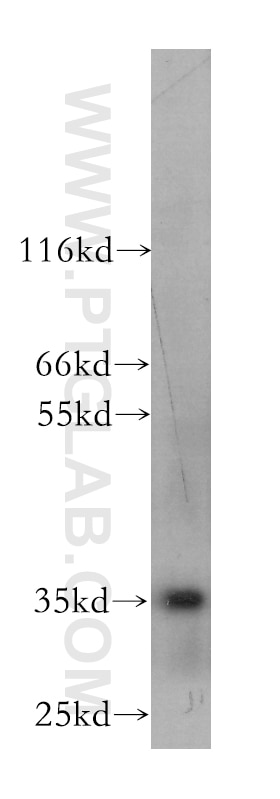
| Observed molecular weight | 35 kDa, 60 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC017588 |
| Gene Symbol | CXCL16 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 58191 |
| RRID | AB_2086188 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9H2A7 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
CXCL16 is a recently discovered cytokine belonging to the CXC chemokine family, which is synthesised in plasmacytoid dendritic cell as a transmembrane molecule. It exists in a transmembrane and soluble form. The transmembrane form of CXCL16 functions as an adhesion molecule for CXCR6-expressing cells, whereas the soluble form of CXCL16 mediates infiltration of circulating cells into sites of injury. CXCL16, has been proposed as an important pathogenic mediator in inflammatory diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, glomerulonephritis, or prostate cancer. CXCL16 has been implicated in some forms of renal disease such as lupus nephritis and antiglomerular basement membrane nephritis. CXCL16 also plays a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of angiotensin II-induced renal injury and fibrosis through regulation of macrophage and T cell infiltration and bone marrow-derived fibroblast accumulation.