Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
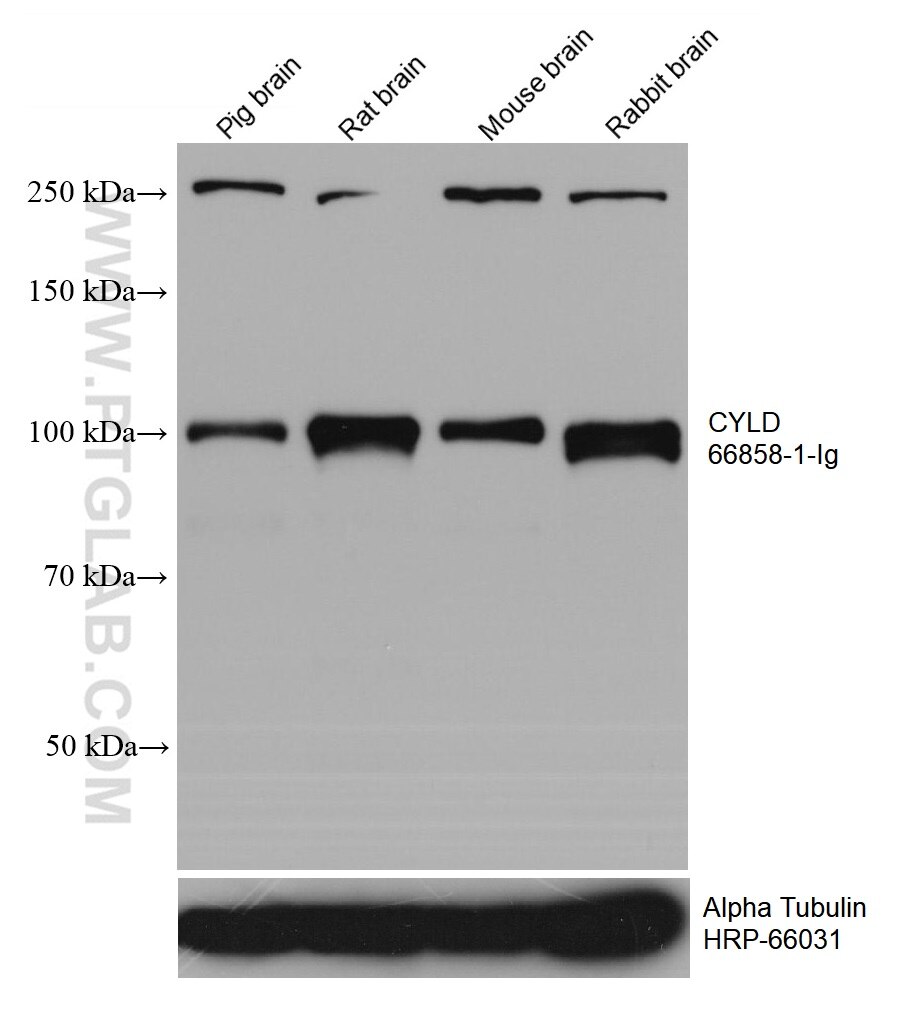
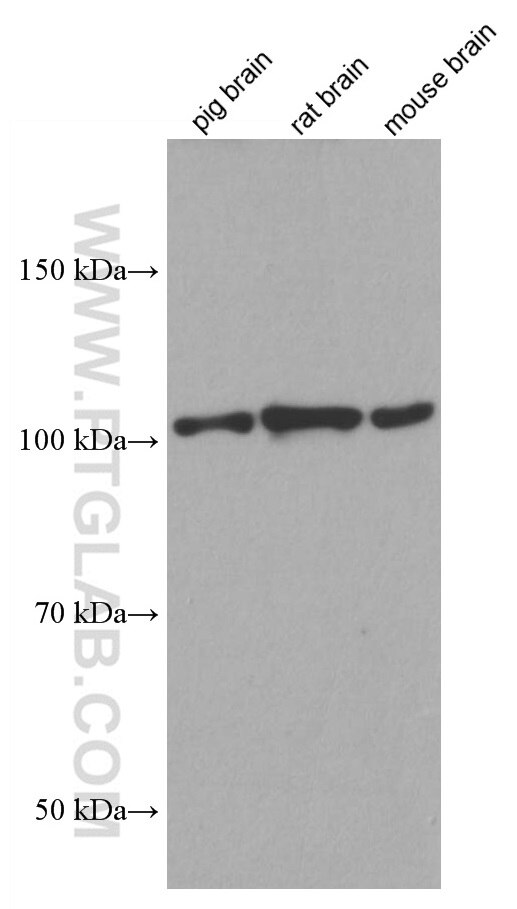
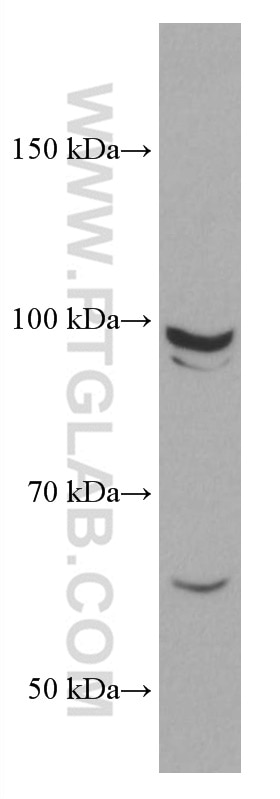
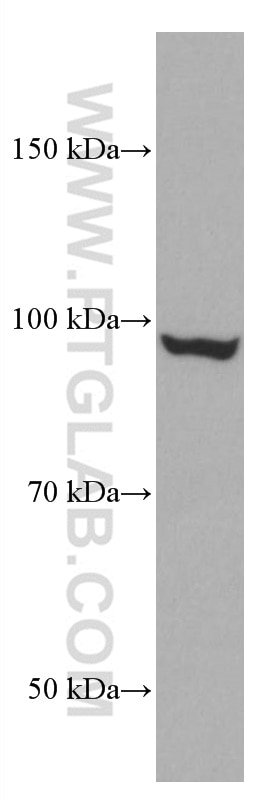
66858-1-PBS targets CYLD in WB, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human, mouse, rat, pig, rabbit samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human, mouse, rat, pig, rabbit |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | CYLD fusion protein Ag28333 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | cylindromatosis (turban tumor syndrome) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 107 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 110 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC012342 |
| Gene Symbol | CYLD |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1540 |
| RRID | AB_2882197 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9NQC7 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
CYLD, also named as CYLD1, belongs to the peptidase C67 family. It is the protease that specifically cleaves 'Lys-63'-linked polyubiquitin chains. CYLD has endodeubiquitinase activity and plays an important role in the regulation of pathways leading to NF-kappa-B activation. CYLD contributes to the regulation of cell survival, proliferation and differentiation via its effects on NF-kappa-B activation. It is a negative regulator of Wnt signaling. CYLD inhibits HDAC6 and thereby promotes acetylation of alpha-tubulin and stabilization of microtubules. CYLD plays a role in the regulation of microtubule dynamics, and thereby contributes to the regulation of cell proliferation, cell polarization, cell migration, and angiogenesis. It is required for normal cell cycle progress and normal cytokinesis. CYLD inhibits nuclear translocation of NF-kappa-B and plays a role in the regulation of inflammation and the innate immune response, via its effects on NF-kappa-B activation. It is dispensable for the maturation of intrathymic natural killer cells, but required for the continued survival of immature natural killer cells. CYLD negatively regulates TNFRSF11A signaling and osteoclastogenesis.