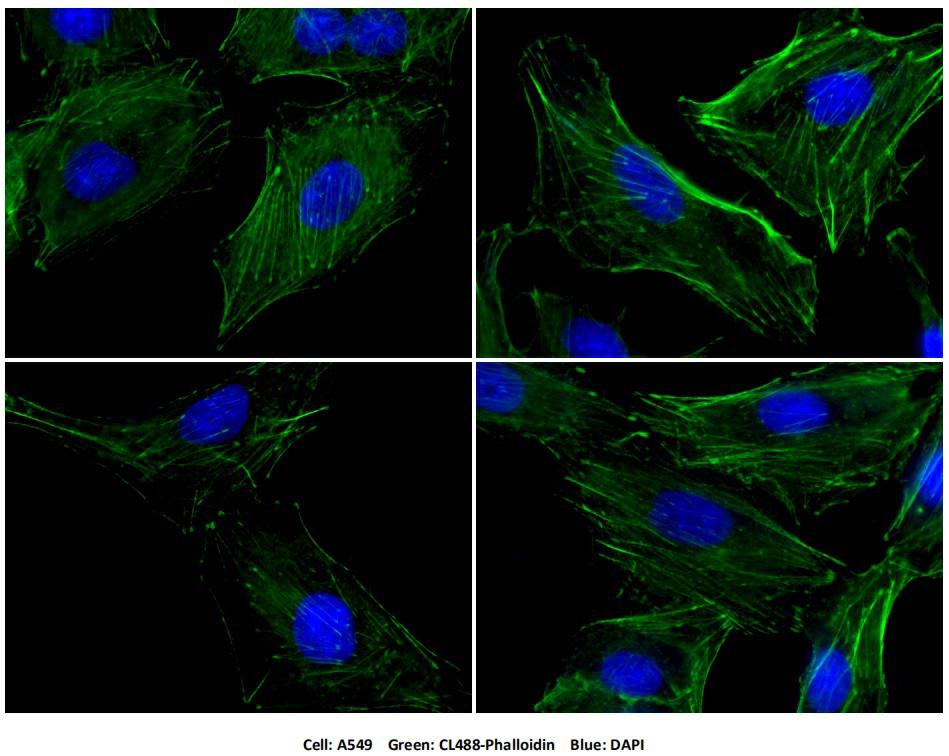
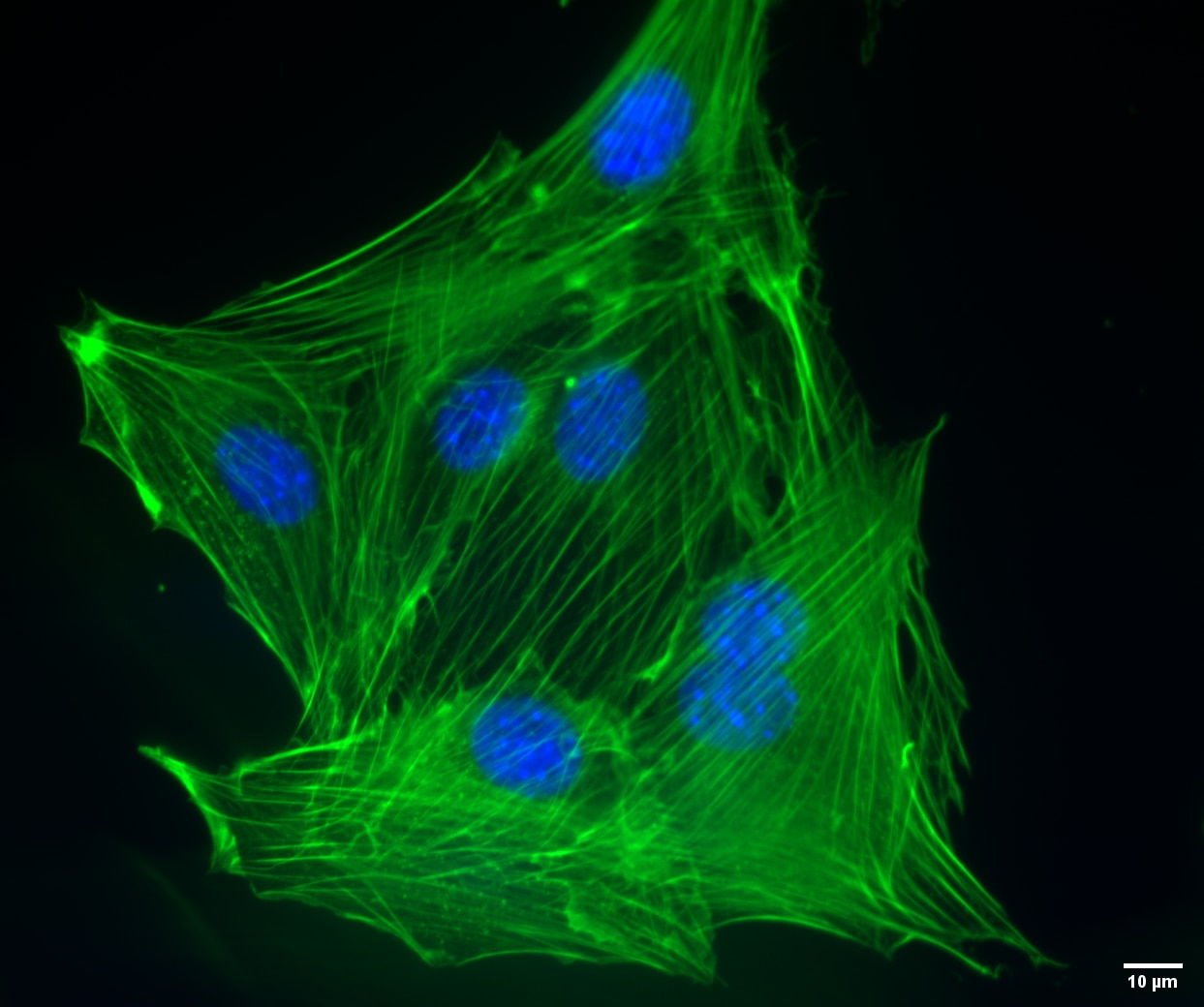
Product Information
Phalloidin is a toxin isolated from mushrooms that binds F-Actin in the cytoskeleton. This product is conjugated to our fluorescent CoraLite(R) dye to stain F-actin for labeling, identifying and quantifying actin filaments in immunostaining studies. Compared to many fluorescent dyes, CoraLite(R) dyes have advantages in brightness, light stability and water solubility. Excitation/Emission maxima wavelengths are 490 nm/515 nm.
Conjugated
CoraLite® Plus 488-Phalloidin (green)
Ex/Em: 490/515 nm
Storage
Store at -20°C. Avoid exposure to light. Stable for 2 years after shipment.
Protocol
Stock preparation: Prepare a 200T/mL stock solution by dissolving lyophilized phalloidin (300T) in 1.5 mL sterile water and protect solution from light.
Cautions
This product is formulated as a freeze-dried powder. Please centrifuge it immediately before use and dissolve it in a suitable solvent before use. Phalloidin is highly toxic, please take protective measures while handling.
Stock preparation
Prepare a 200T/mL stock solution by dissolving lyophilized phalloidin (300T) in 1.5 mL sterile water and protect solution from light.
Cited in Article as
pf00001, CoraLite® Plus 488-Phalloidin (green), Proteintech, IL, USA
Publications
| Application | Title |
|---|---|
Research (Wash D C) Youthful Brain-Derived Extracellular Vesicle-Loaded GelMA Hydrogel Promotes Scarless Wound Healing in Aged Skin by Modulating Senescence and Mitochondrial Function | |
Acta Biomater Porous composite hydrogels with improved MSC survival for robust epithelial sealing around implants and M2 macrophage polarization | |
J Nanobiotechnology Exosome-transmitted circCABIN1 promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma via sustaining ErbB downstream signaling | |
Cancer Lett CD63+ cancer-associated fibroblasts confer CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance to breast cancer cells by exosomal miR-20 | |
Bioact Mater A novel mechanism of inhibiting in-stent restenosis with arsenic trioxide drug-eluting stent: Enhancing contractile phenotype of vascular smooth muscle cells via YAP pathway. | |
Mater Today Bio Stiffness and surface topology of silicone implants competitively mediate inflammatory responses of macrophages and foreign body response |