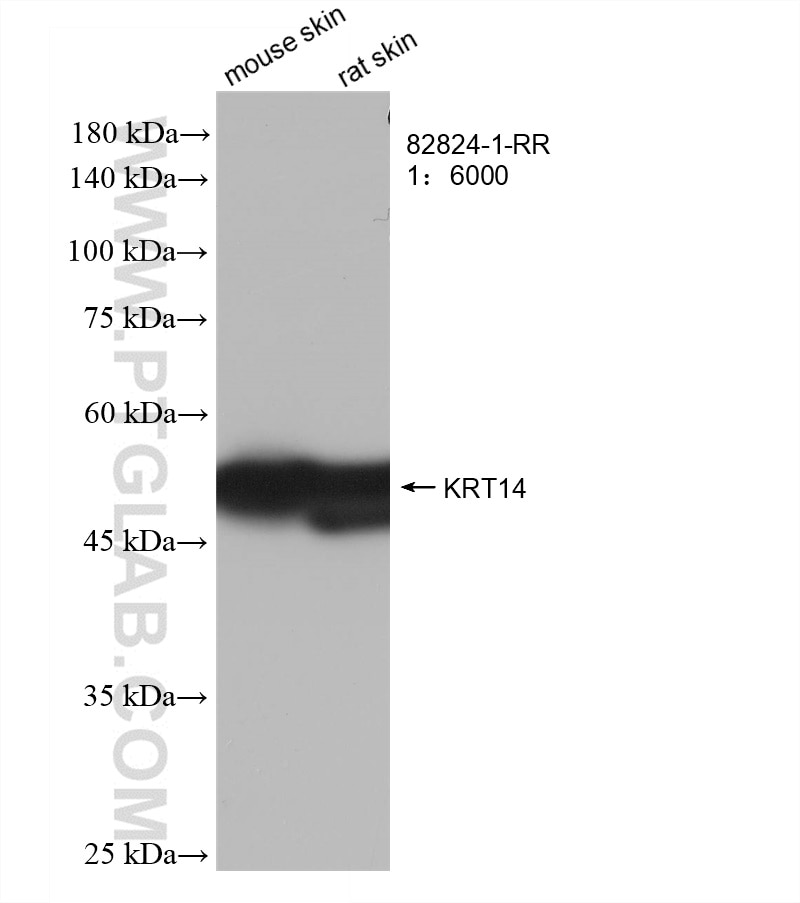
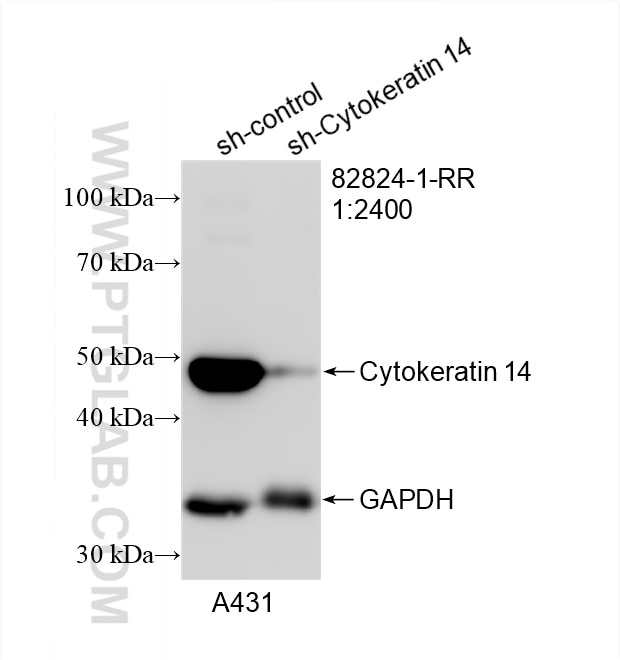
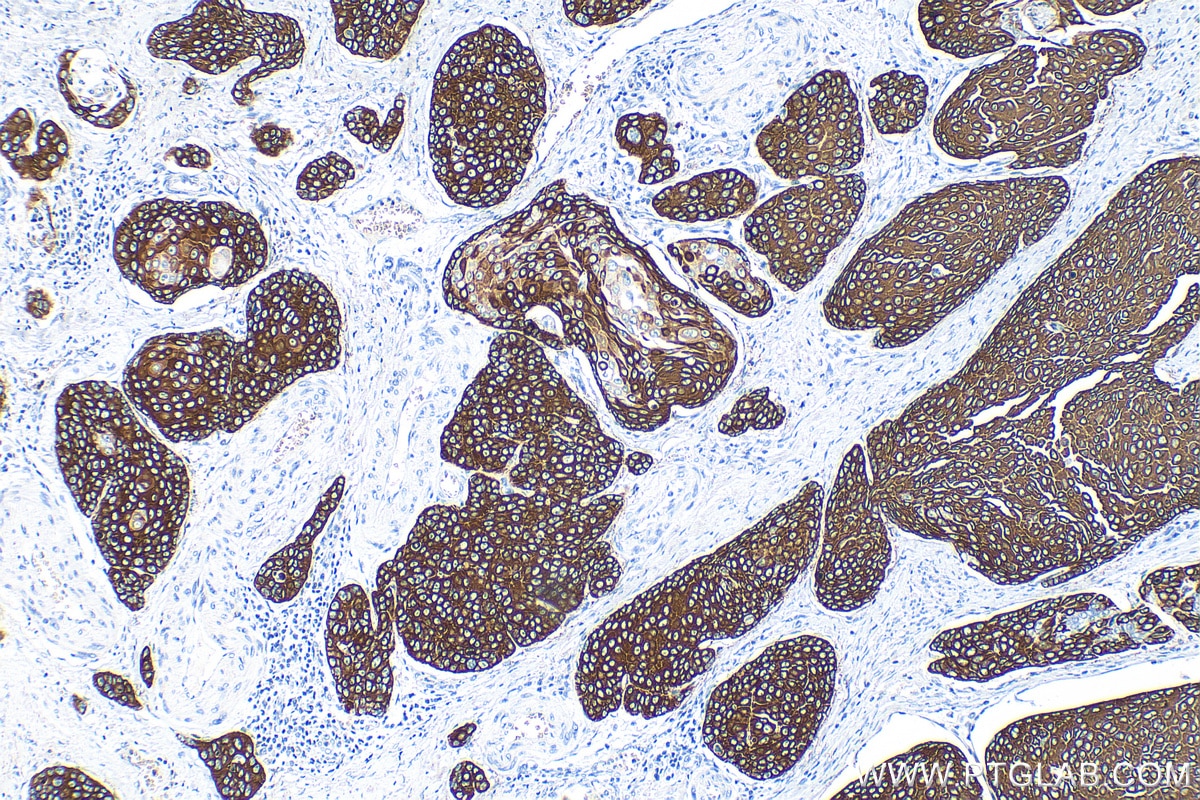
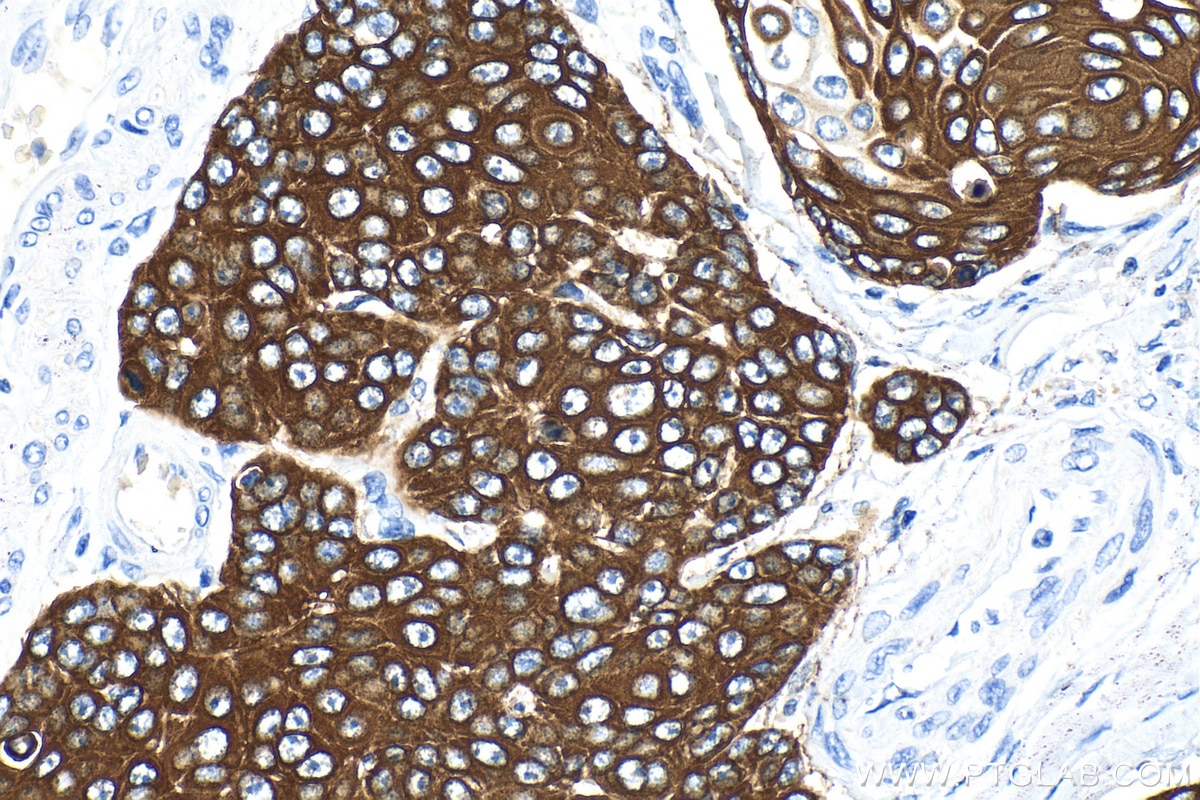
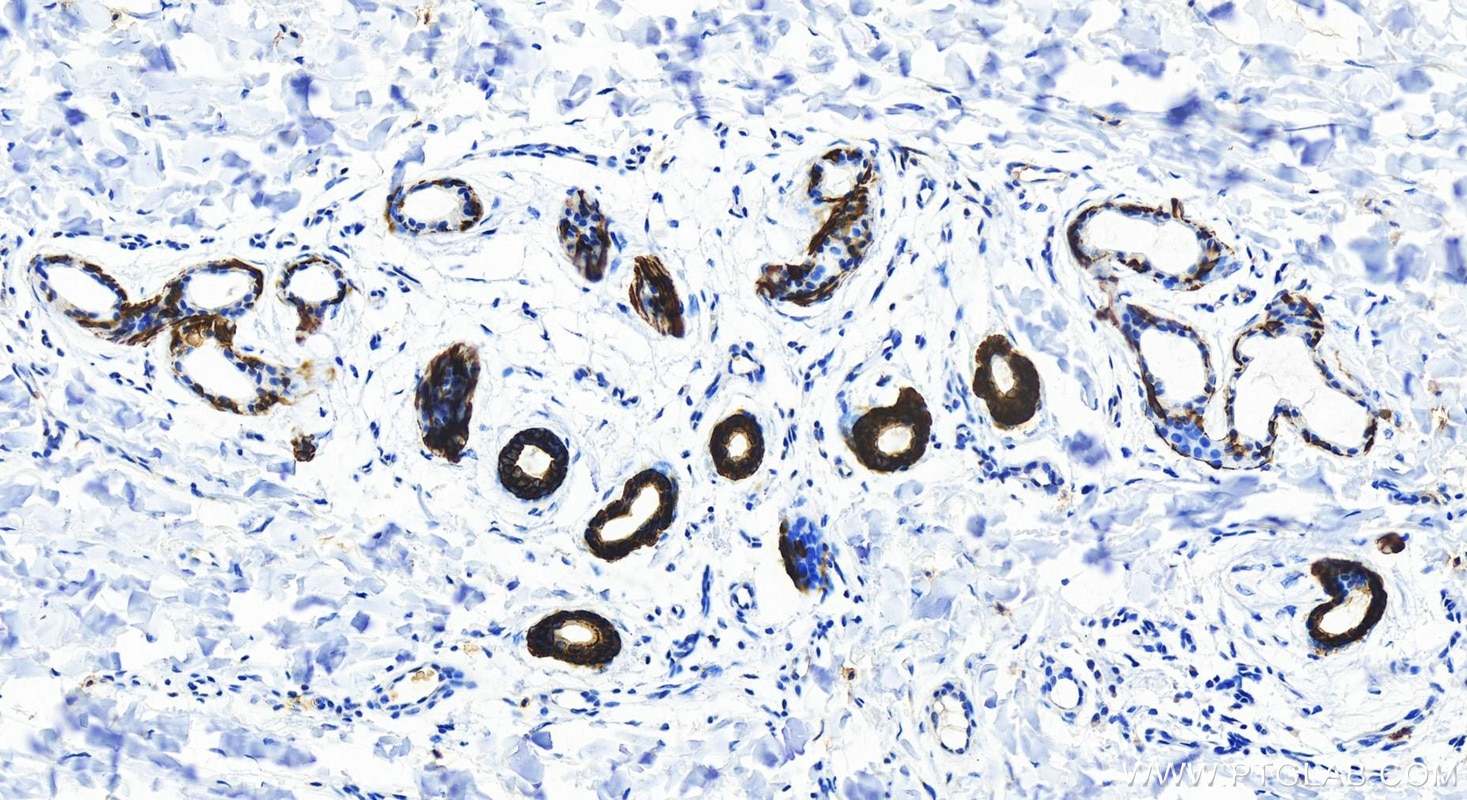
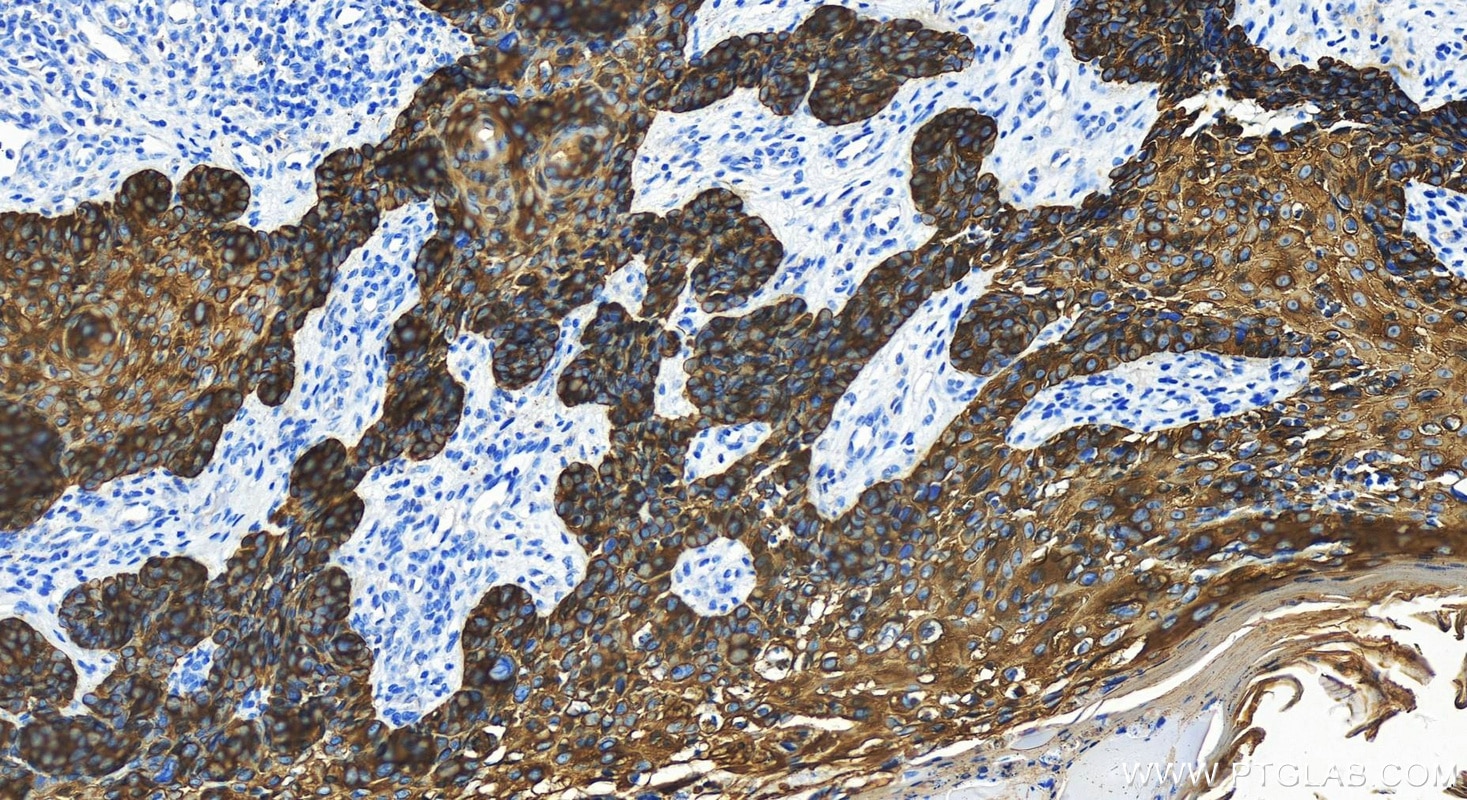
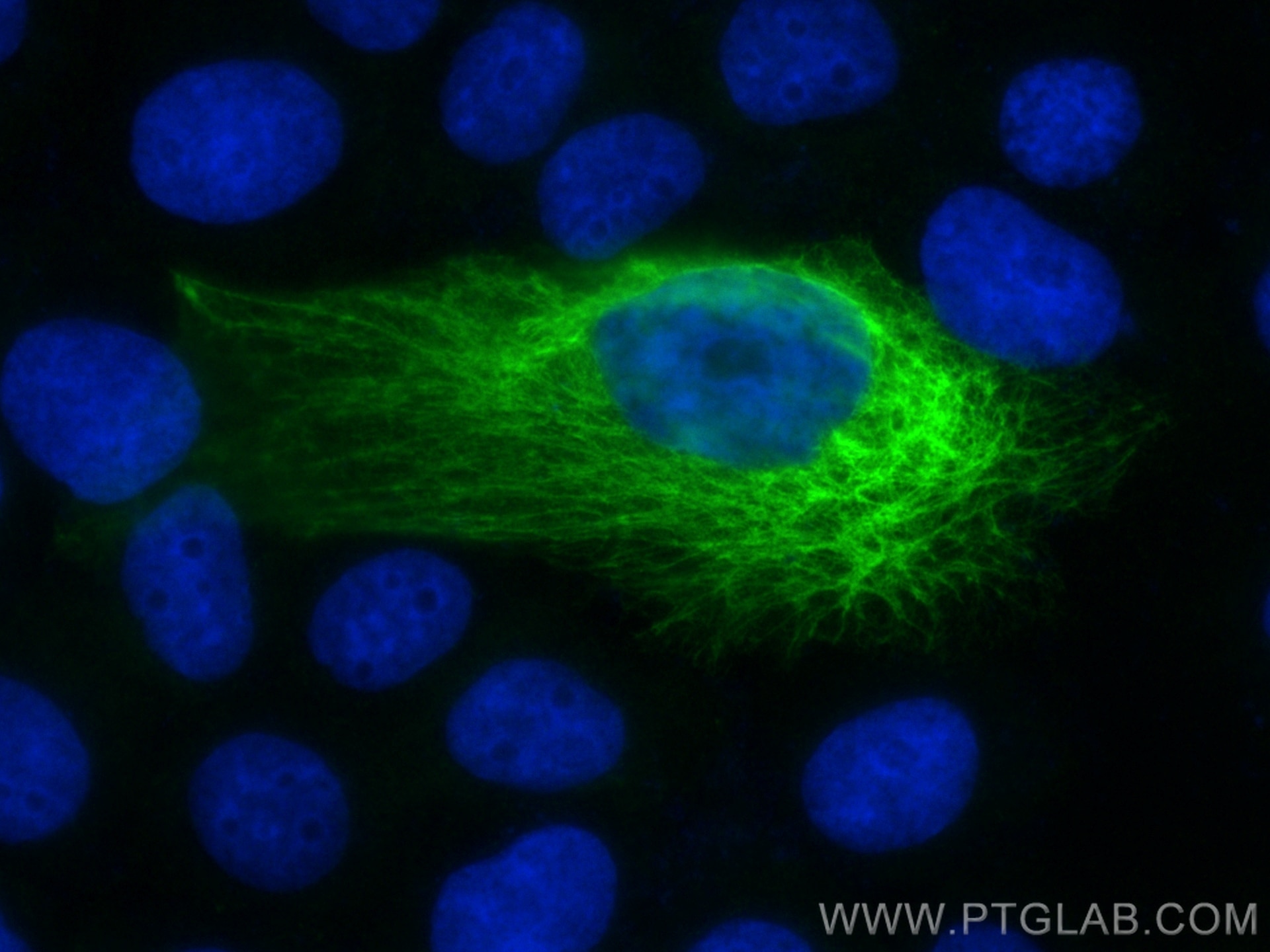
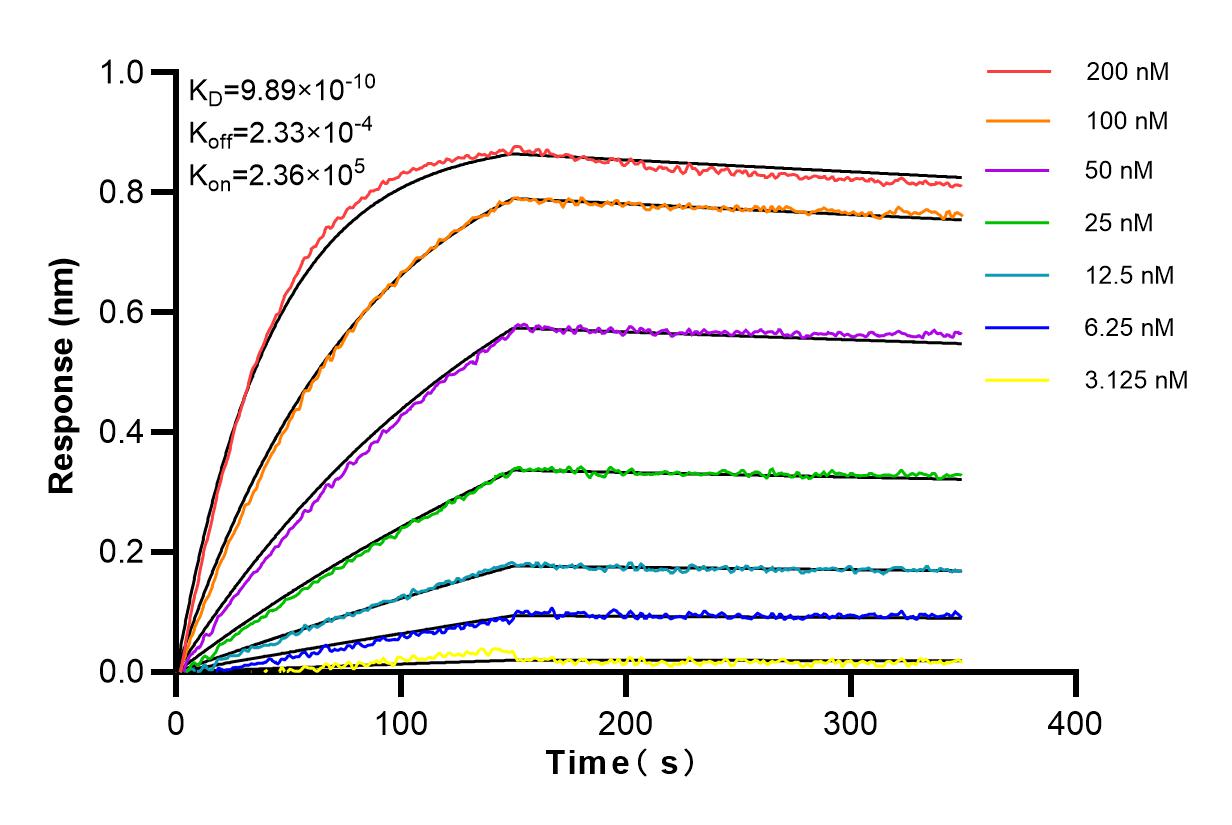
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
82824-1-PBS targets Cytokeratin 14 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Cytokeratin 14 fusion protein Ag17559 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | keratin 14 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 472 aa, 52 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 52 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC002690 |
| Gene Symbol | Cytokeratin 14 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3861 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P02533 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Cytokeratin 14, one of about 20 different cytokeratin isotypes of human cells, is the intermediate filament protein characteristic of epithelial cells. Cytokeratin 14 is expressed in the basal compartment of all stratified squamous epithelia. In various kinds of human tumors, the appearance and increasing expression of Cytokeratin 14 were strikingly associated with higher grade and stage of carcinoma, with varying degrees of unfavorable prognosis. In lung squamous cell carcinoma(LSCC), Cytokeratin 14 was expressed in the tumor cell nests showing stromal invasion with fibrosis and lymph node metastases, indicating that Cytokeratin 14 involved in proliferation and metastasis of LSCC. Cytokeratin 14 expression is sometimes used in diagnosis of myoepithelioma1 and intraductal vs. invasive ductal carcinoma of the breast.