Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
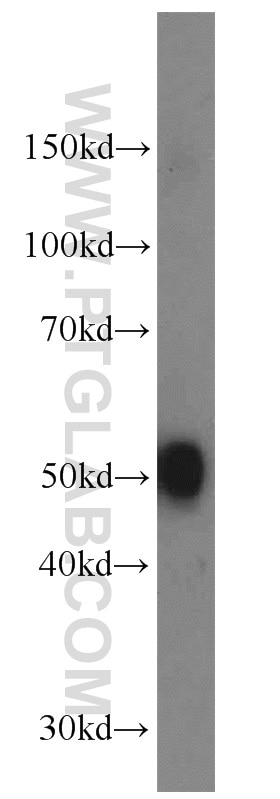
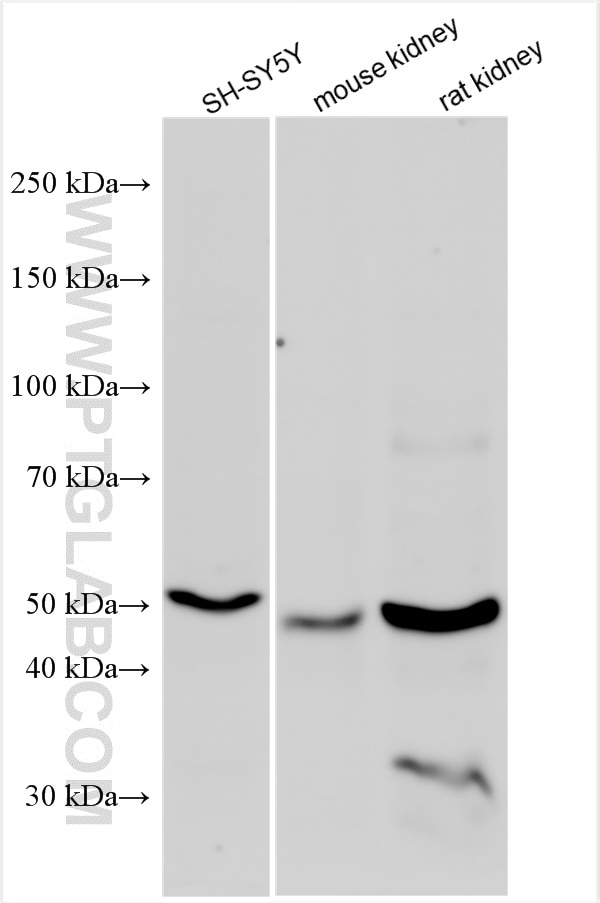
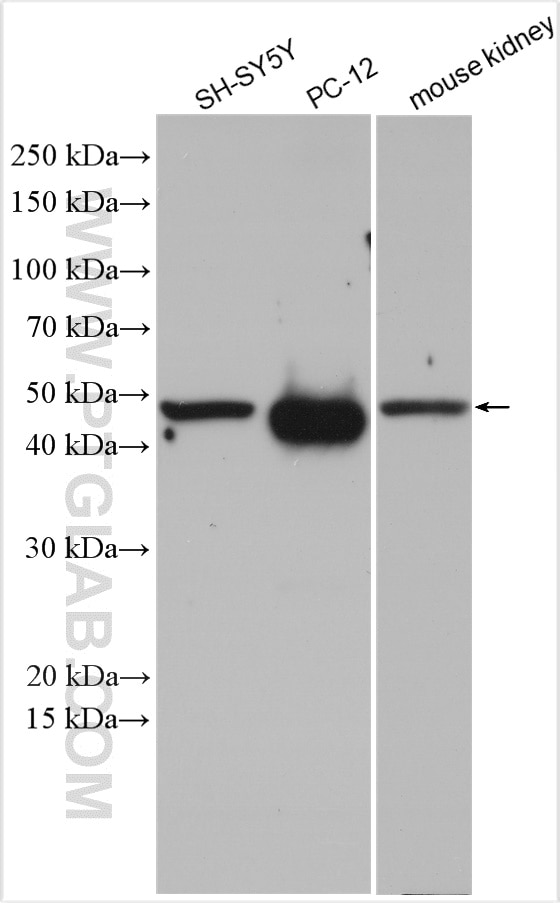
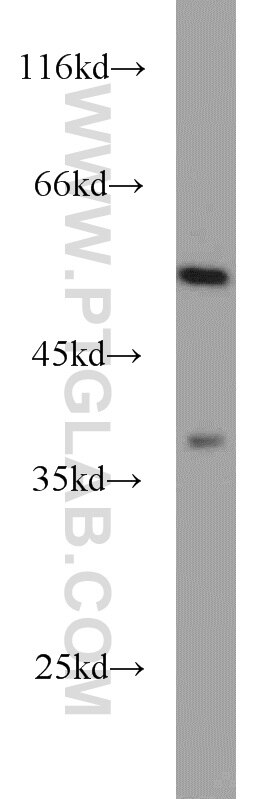
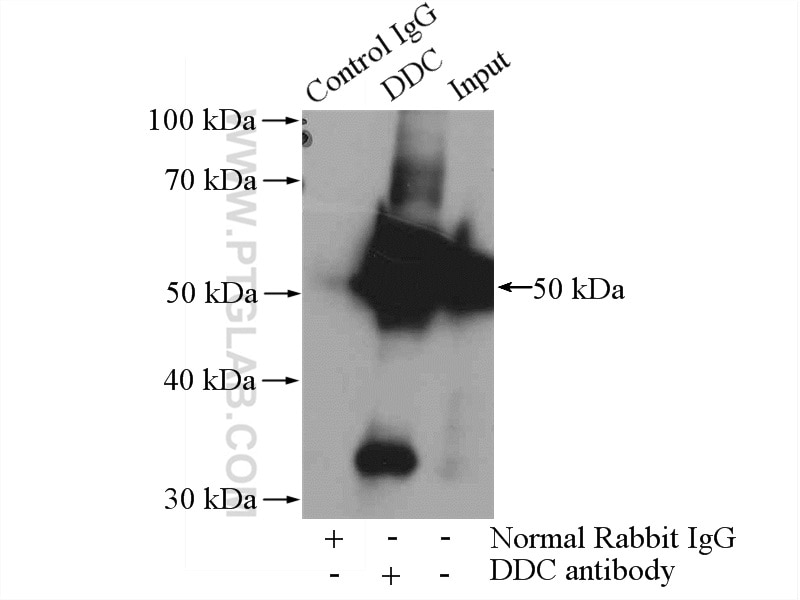
| Positive WB detected in | SH-SY5Y cells, mouse kidney tissue, mouse brain tissue, rat kidney tissue, PC-12 cells |
| Positive IP detected in | mouse brain tissue |
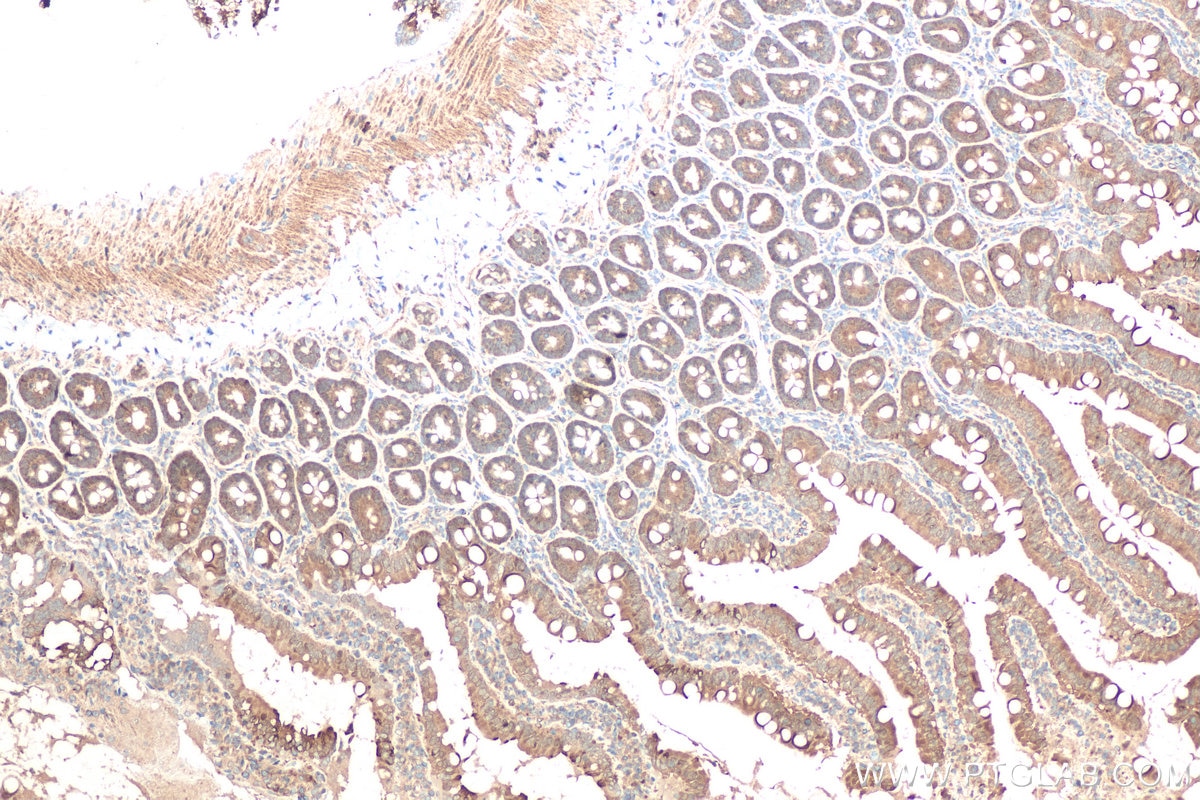
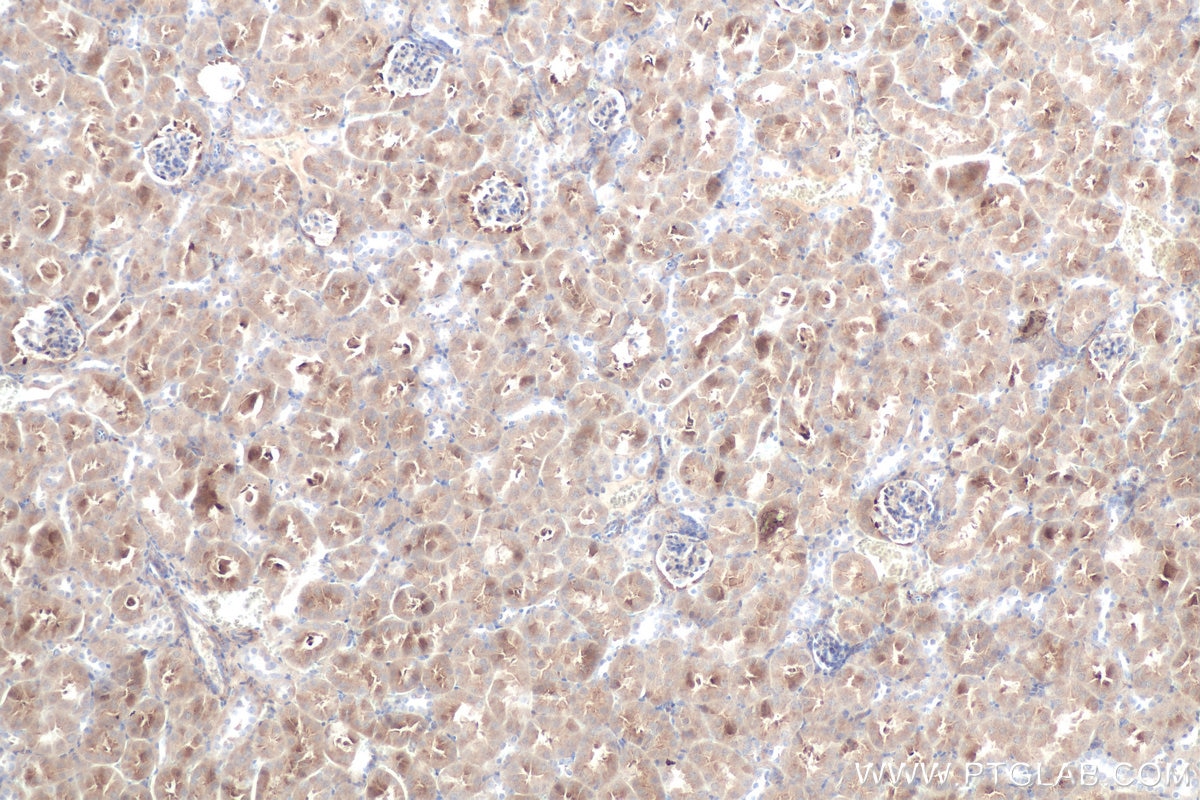
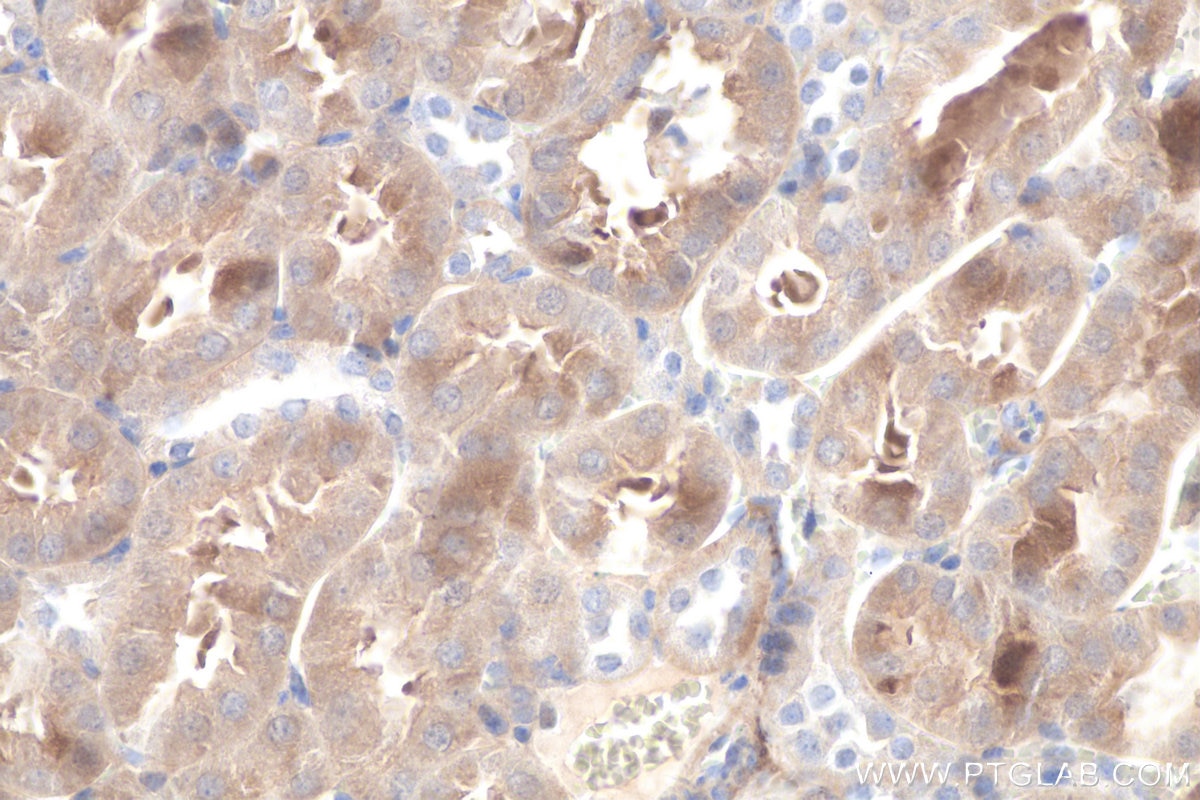
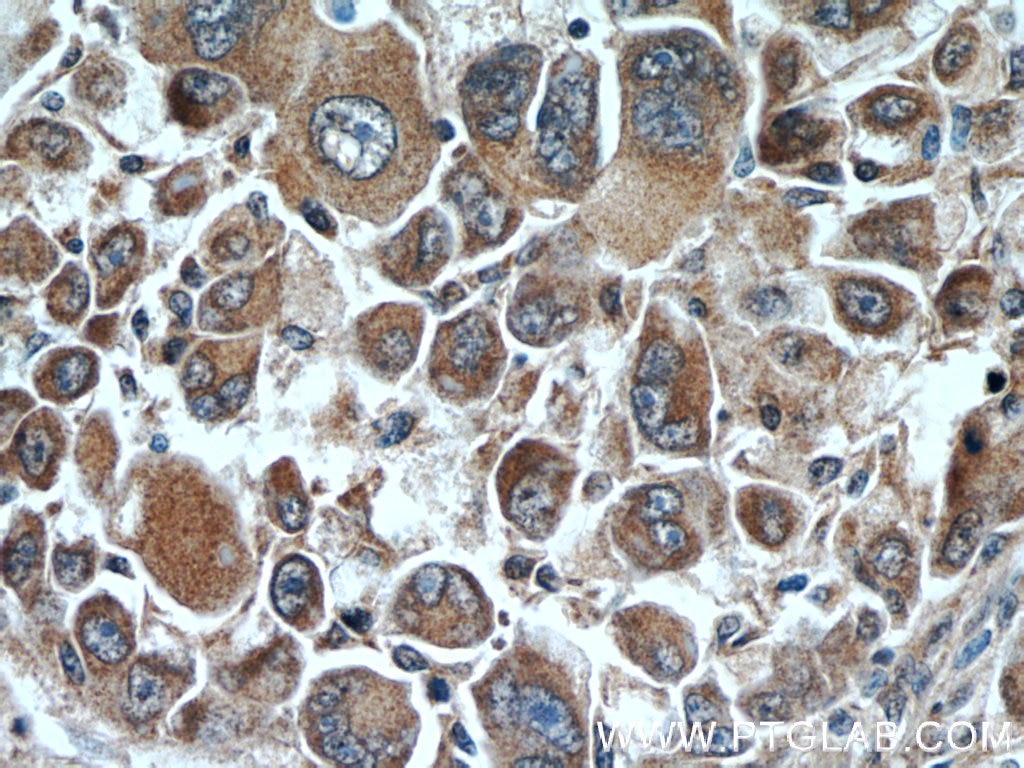
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse kidney tissue, human liver cancer tissue, rat kidney tissue, rat small intestine tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
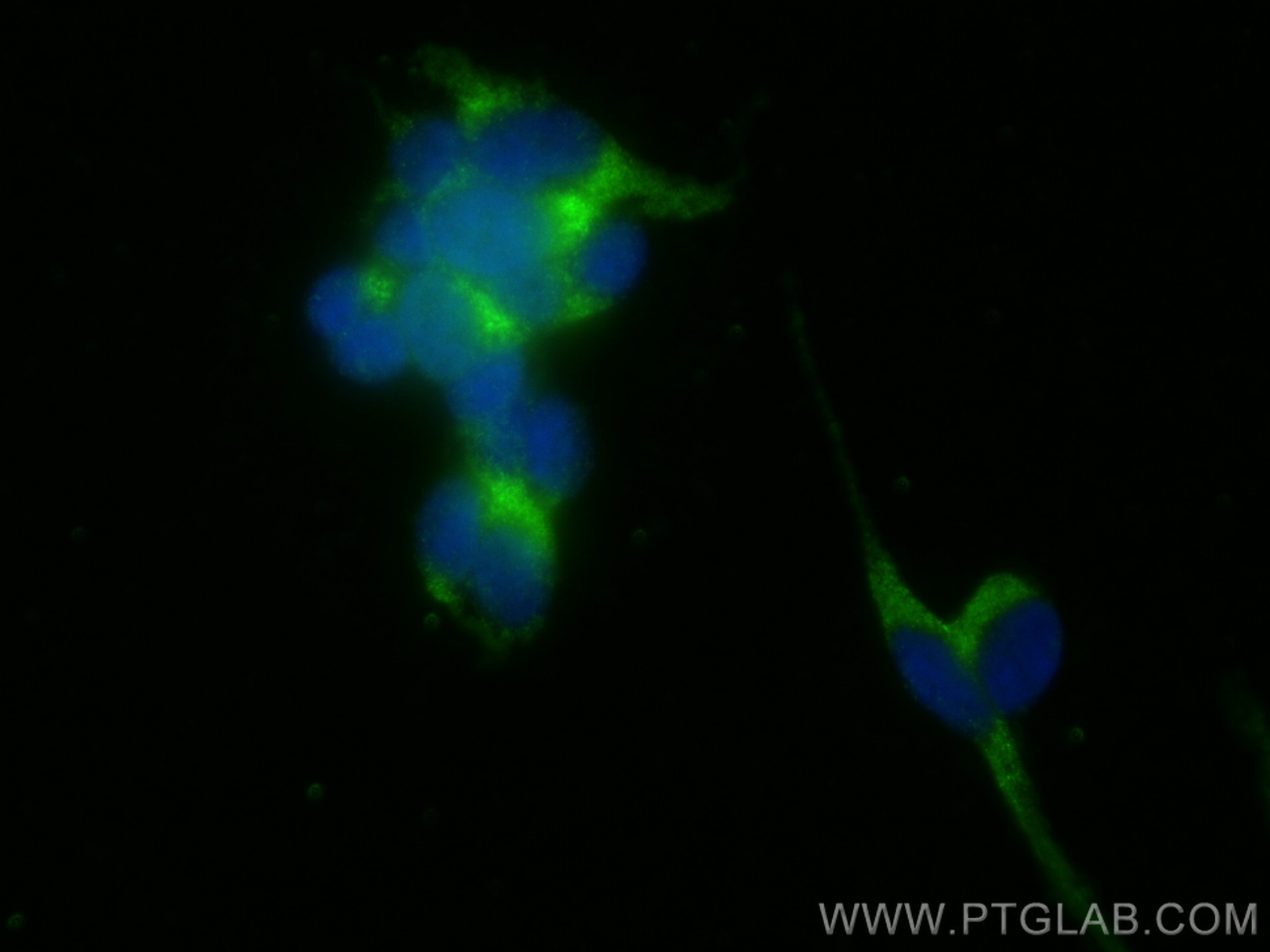
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | SH-SY5Y cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:3000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 6 publications below |
| IHC | See 7 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
10166-1-AP targets DOPA decarboxylase/DDC in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag0219 Product name: Recombinant human DDC protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 121-389 aa of BC008366 Sequence: WLGKMLELPKAFLNEKAGEGGGVIQGSASEATLVALLAARTKVIHRLQAASPELTQAAIMEKLVAYSSDQAHSSVERAGLIGGVKLKAIPSDGNFAMRASALQEALERDKAAGLIPFFMVATLGTTTCCSFDNLLEVGPICNKEDIWLHVDAAYAGSAFICPEFRHLLNGVEFADSFNFNPHKWLLVNFDCSAMWVKKRTDLTGAFRLDPTYLKHSHQDSGLITDYRHWQIPLGRRFRSLKMWFVFRMYGVKGLQAYIRKHVQLSHEFE 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | dopa decarboxylase (aromatic L-amino acid decarboxylase) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 54 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 48-50 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC008366 |
| Gene Symbol | DOPA decarboxylase |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1644 |
| RRID | AB_2088937 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P20711 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
DOPA decarboxylase (DDC), also known as aromatic l-amino acid decarboxylase, belongs to the pyridoxal-dependent aminotransferase superfamily (PMID: 38467937). DDC is an enzyme that converts levodopa into dopamine, the latter being severely depleted in LBD due to the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra (PMID: 28751068). DDC plays an important role in the dopaminergic system and participates in the uptake and decarboxylation of amine precursors in the peripheral tissues (PMID: 28100850). It is reported that DDC may be a novel and potential marker for the detection of peritoneal micrometastases of gastric cancer (PMID: 14760382).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for DOPA decarboxylase/DDC antibody 10166-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for DOPA decarboxylase/DDC antibody 10166-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for DOPA decarboxylase/DDC antibody 10166-1-AP | Download protocol |
| WB protocol for DOPA decarboxylase/DDC antibody 10166-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Signal Profile of 5-HT2A receptor involved in signaling cascades associated to intracellular inflammation and apoptosis in hepatocytes and its role in carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatotoxicity | ||
Dis Model Mech A Matrigel-based 3D construct of SH-SY5Y cells models the α-synuclein pathologies of Parkinson's disease. | ||
J Transl Med Retinal pigment epithelial cells secrete neurotrophic factors and synthesize dopamine: possible contribution to therapeutic effects of RPE cell transplantation in Parkinson's disease. | ||
Toxicol Appl Pharmacol Carbon tetrachloride induced mitochondrial division, respiratory chain damage, abnormal intracellular [H+] and apoptosis are due to the activation of 5-HT degradation system in hepatocytes. |