Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
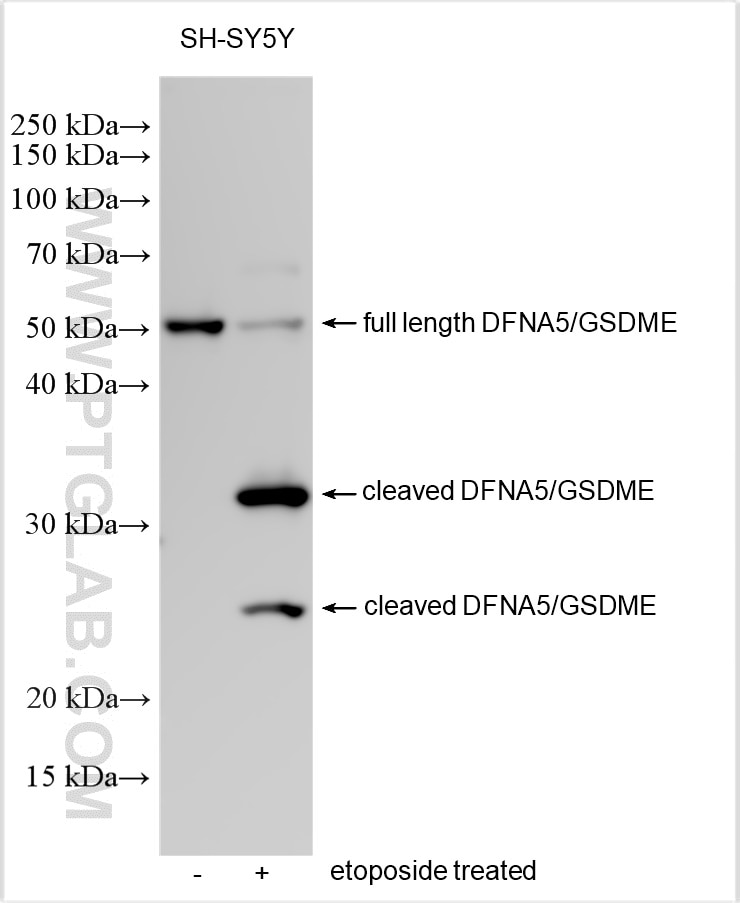
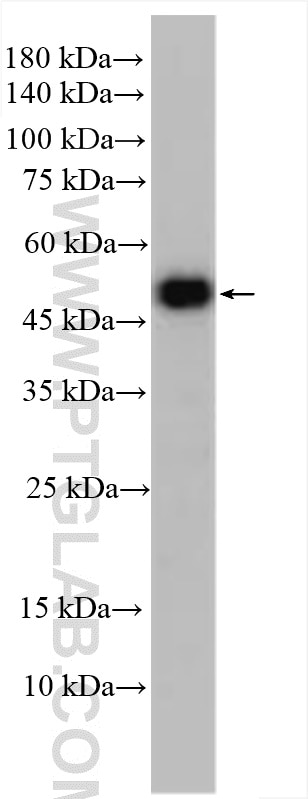
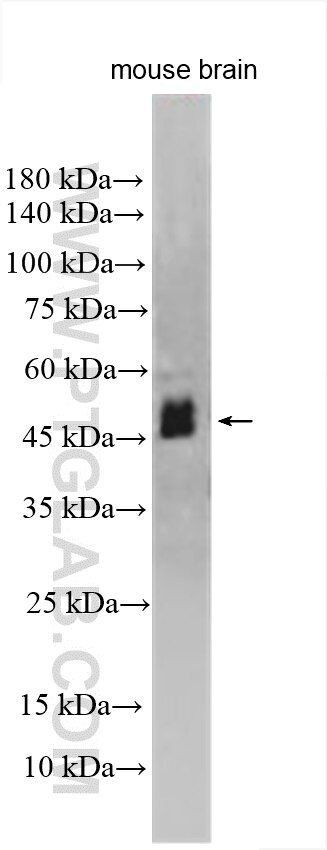
| Positive WB detected in | SH-SY5Y cells, A549 cells, mouse brain tissue |
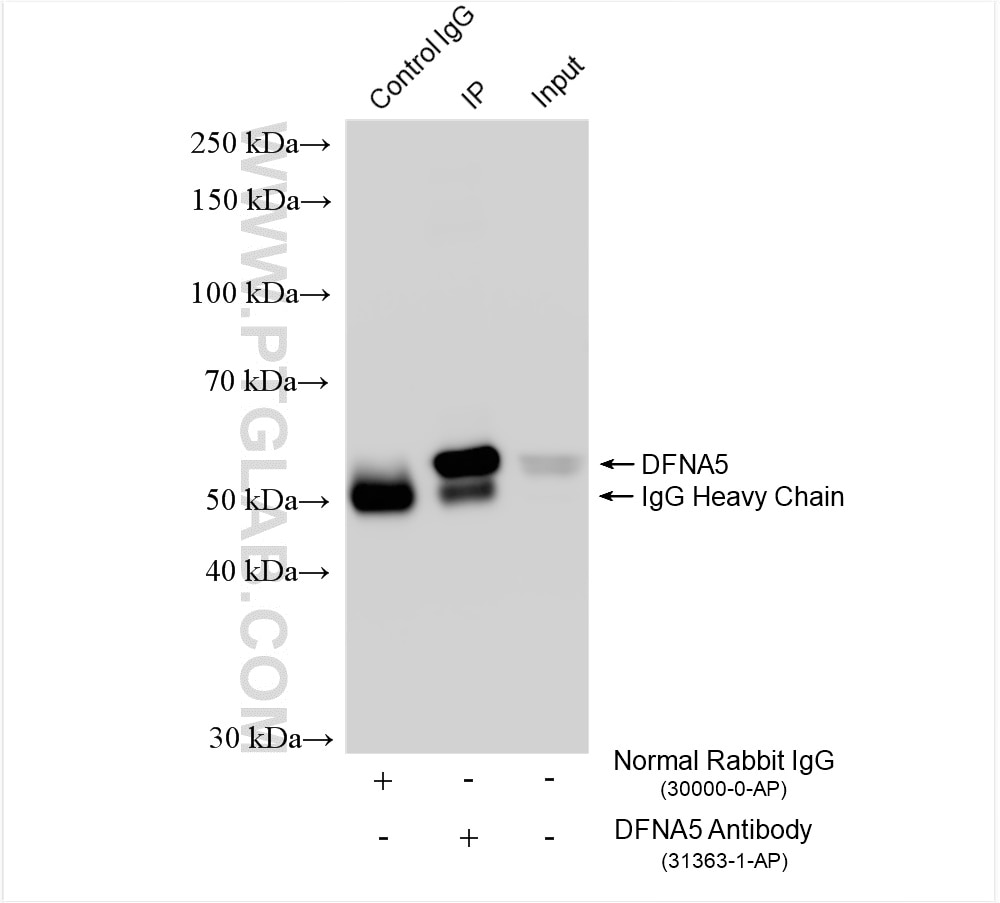
| Positive IP detected in | SH-SY5Y cells |
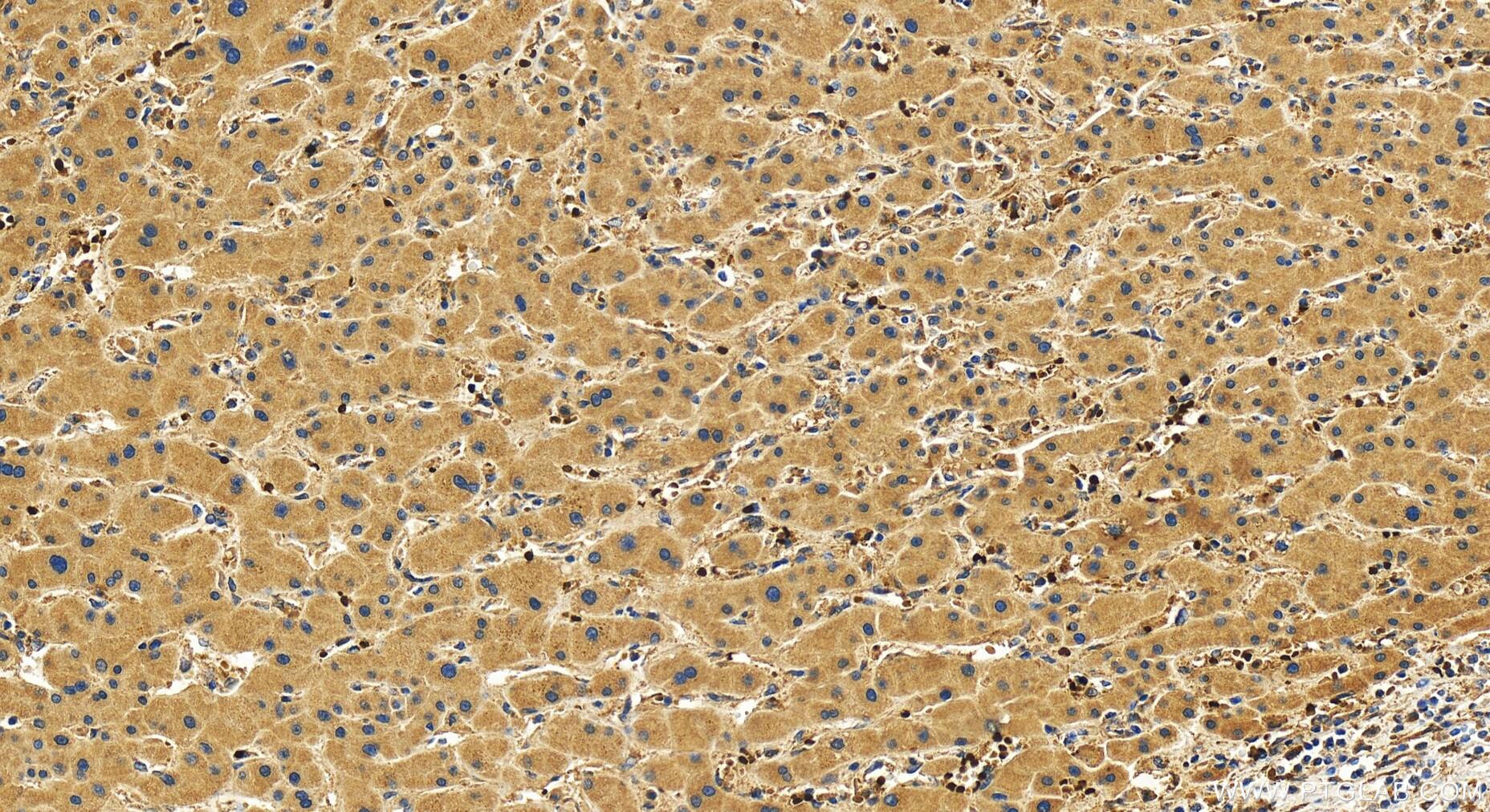
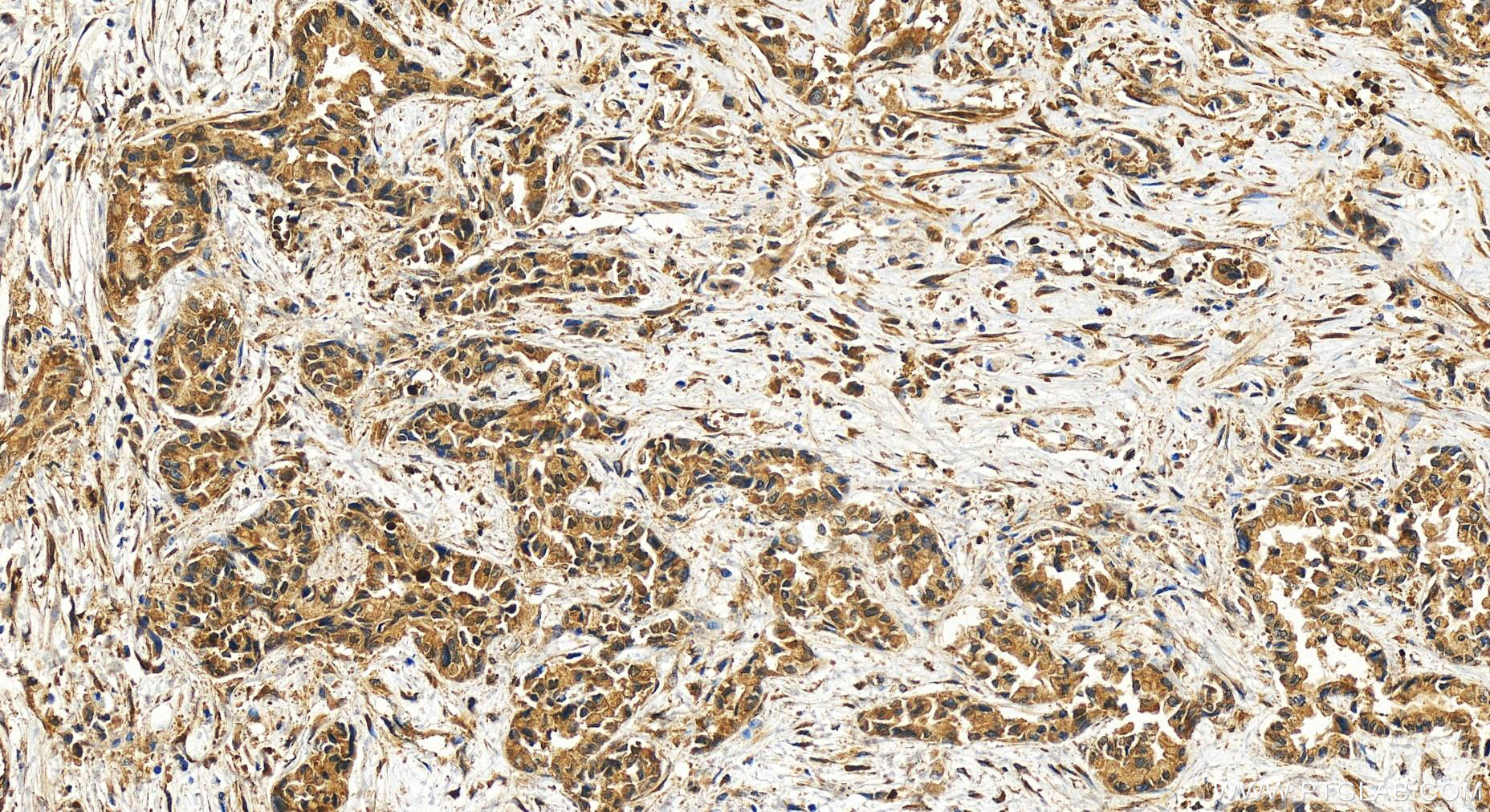
| Positive IHC detected in | human intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
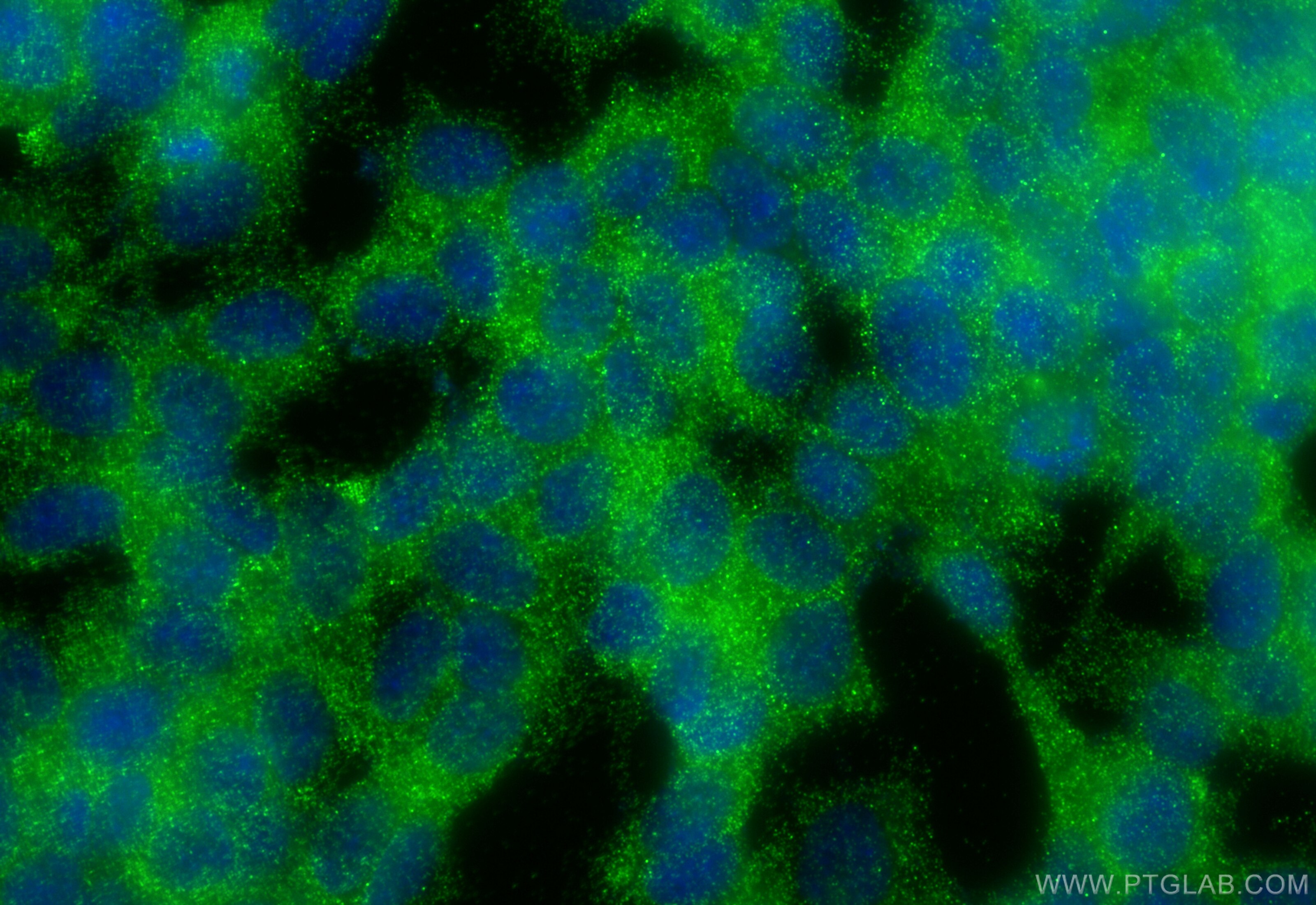
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | SH-SY5Y cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
31363-1-AP targets DFNA5/GSDME in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | DFNA5/GSDME fusion protein Ag35186 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | deafness, autosomal dominant 5 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 496 aa, 55 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 55 kDa, 35 kDa, 25 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC019689 |
| Gene Symbol | DFNA5 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 1687 |
| RRID | AB_3669957 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity Purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O60443 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
DFNA5 (deafness, autosomal dominant 5), also known as GSDME or ICERE-1, is a 496 amino acid protein that is expressed in cochlea tissue, as well as in placenta, brain, heart, liver, lung and pancreas. Defects in the gene encoding DFNA5 are the cause of non-syndromic sensorineural deafness autosomal dominant type 5 (DFNA5), a form of sensorineural hearing loss that results from damage to one of various structures that receive sound information in the brain. GSDME produced two GSDME fragments with MW of 35 kDa and 25 kDa.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for DFNA5/GSDME antibody 31363-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for DFNA5/GSDME antibody 31363-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for DFNA5/GSDME antibody 31363-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for DFNA5/GSDME antibody 31363-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |