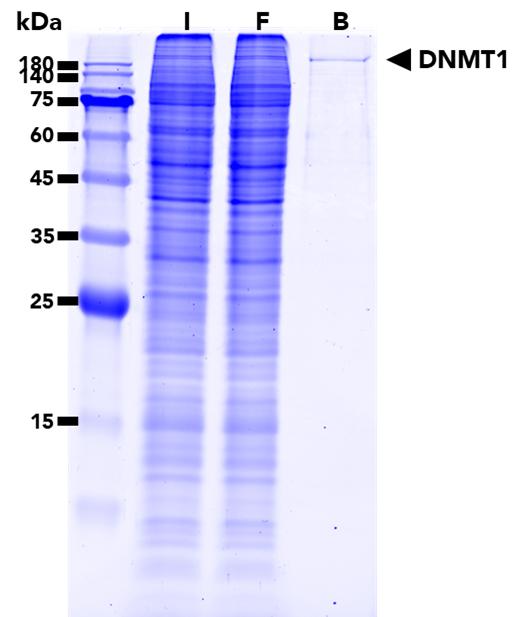
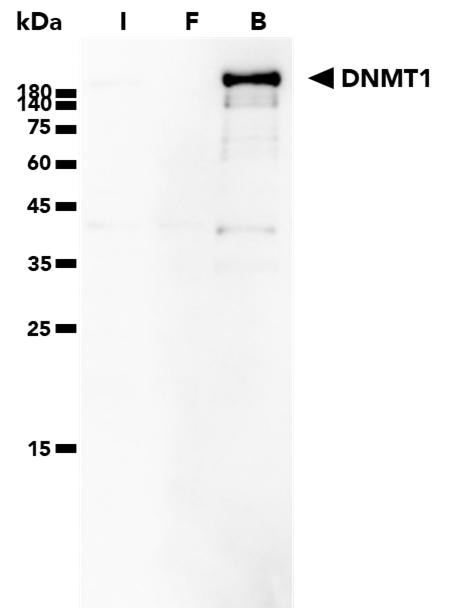
ChromoTek DNMT1-Trap Agarose, Kit for Immunoprecipitation
The DNMT1-Trap Agarose Kit is a ready-to-use reagent for the IP of DNMT1 proteins. It consists of an anti-DNMT1 Nanobody/VHH coupled to agarose beads, along with lysis, wash, and elution buffers to use in the IP process.
Cat no : dtak
Synonyms
Validation Data Gallery
Product Information
The DNMT1-Trap Agarose Kit is a ready-to-use reagent for the IP of DNMT1 proteins. It consists of an anti-DNMT1 Nanobody/VHH coupled to agarose beads, along with lysis, wash, and elution buffers to use in the IP process.
| Description | Immunoprecipitation of DNMT1 proteins with anti-DNMT1 Nanobody conjugated to agarose beads. • Fast, reliable & efficient one-step immunoprecipitation • Ready-to-use • No heavy & light antibody chains • Stable under harsh washing conditions • Suitable for downstream mass spec analysis |
| Applications | IP, Co-IP |
| Specificity/Target | DNMT1 |
| Binding Capacity | 2-3 ug of DNMT1 per 10 uL bead slurry |
| Conjugate | Agarose beads; ~90 um (cross-linked 4% agarose beads) |
| Elution buffer | 2x SDS-sample buffer (Lammli) |
| Type | Nanobody |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Host | Alpaca |
| Compatibility with mass spectrometry | The DNMT1-Trap is optimized for on-bead digestion. For the application note, please click here: On-bead digest protocol for mass spectrometry |
| RRID | AB_2631372 |
| Storage Buffer | 20% ethanol |
| Storage Condition | Shipped at ambient temperature. Upon receipt store at +4°C. Stable for one year. DO not freeze! |
Kit components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| DNMT1-Trap Agarose | 20 reactions (500 µl) |
| Lysis buffer | Optimized for cytoplasmic proteins and mammalian cell lysis |
| RIPA buffer | Optimized for nuclear/chromatin proteins and mammalian cell lysis |
| Wash buffer | Removal of unwanted proteins, peptides, etc. |
| Dilution buffer | Dilution of cell lysate |
| Elution buffer | For acidic elution |
Documentation
| SDS |
|---|
| SDS DNMT1-Trap Agarose Kit (PDF) |
| Protocol |
|---|
| Protocol DNMT1-Trap Agarose Kit (PDF) |
| Trouble shooting |
|---|
| Troubleshooting guide immunoprecipitation (IP) (PDF) |