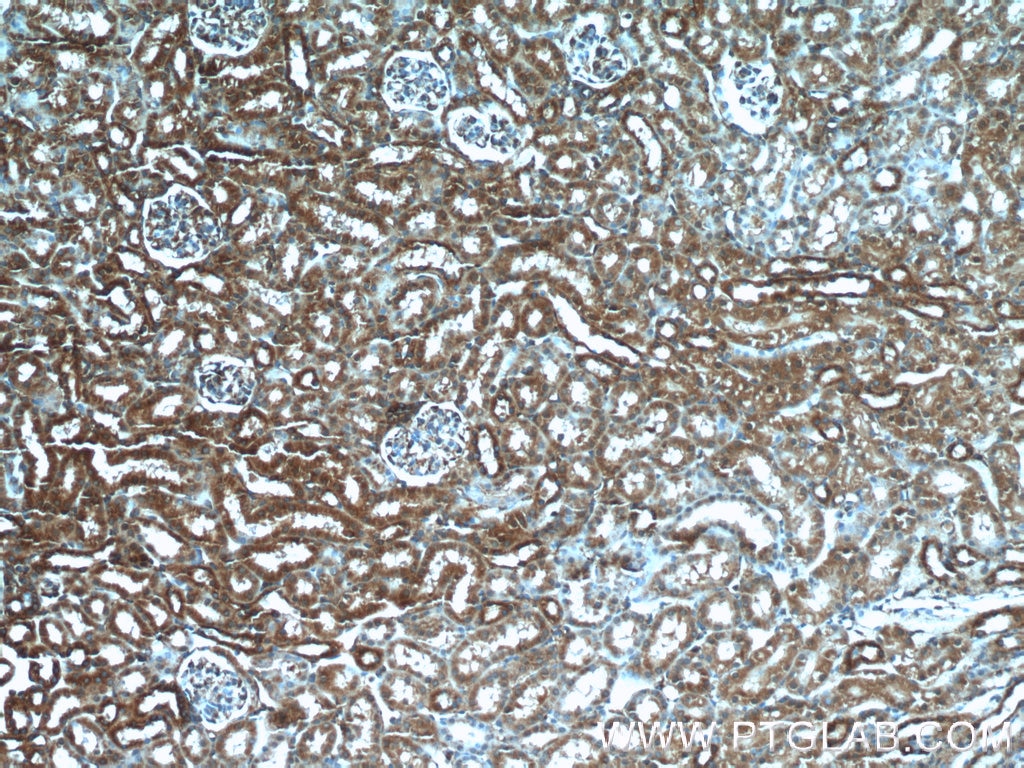
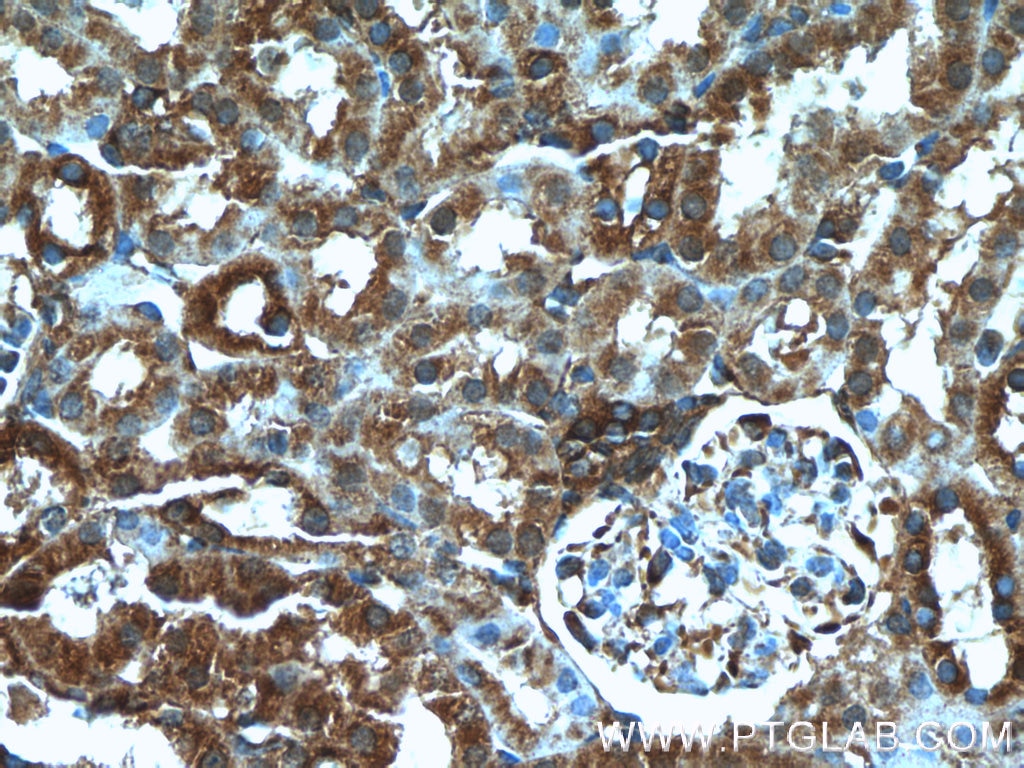
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
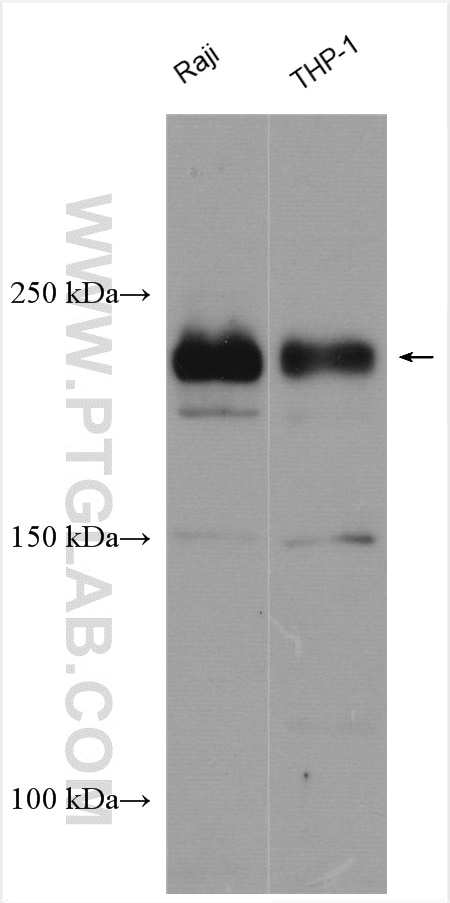
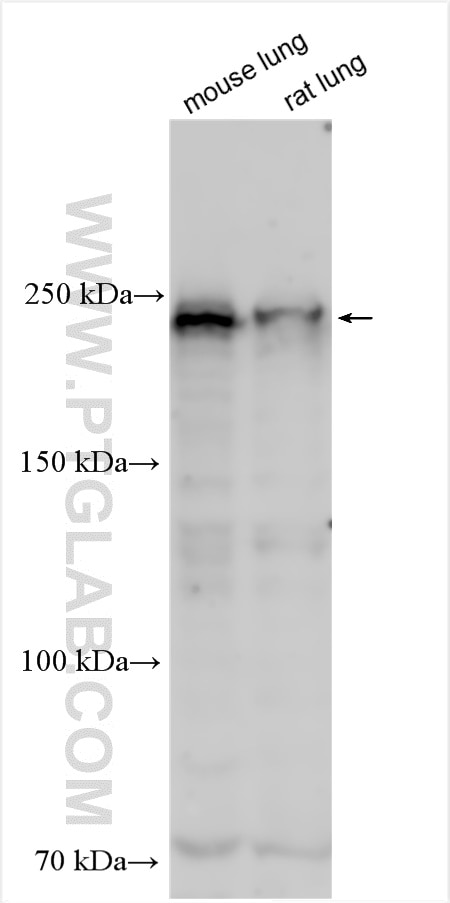
| Positive WB detected in | Raji cells, rat lung tissue, THP-1 cells |
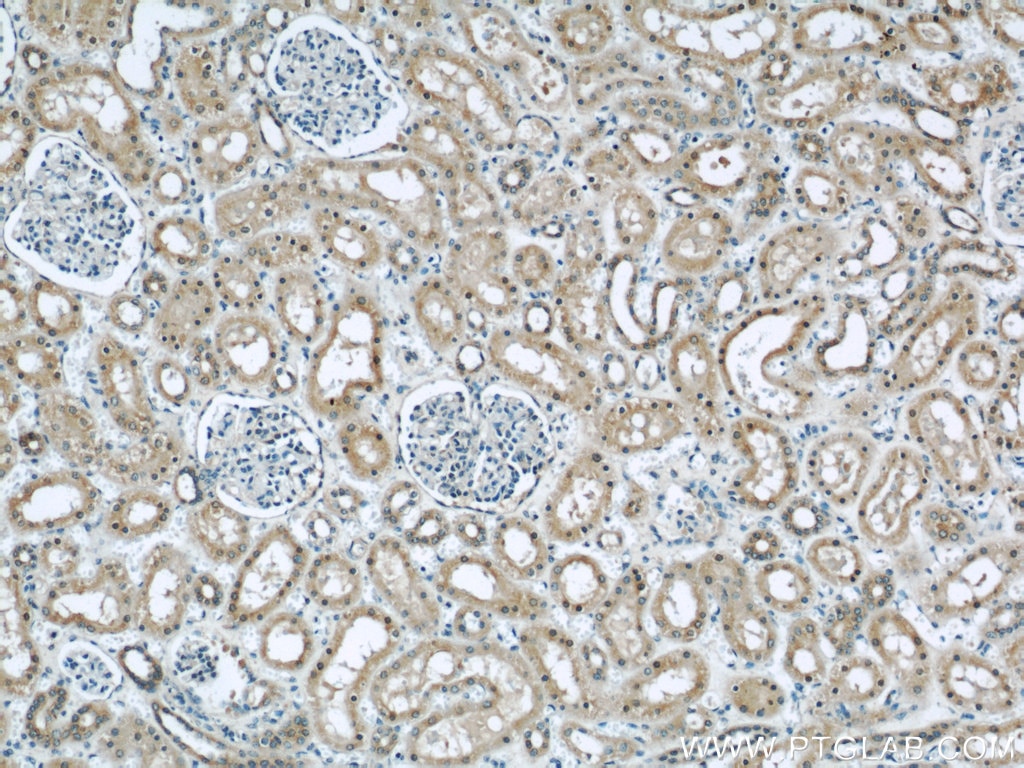
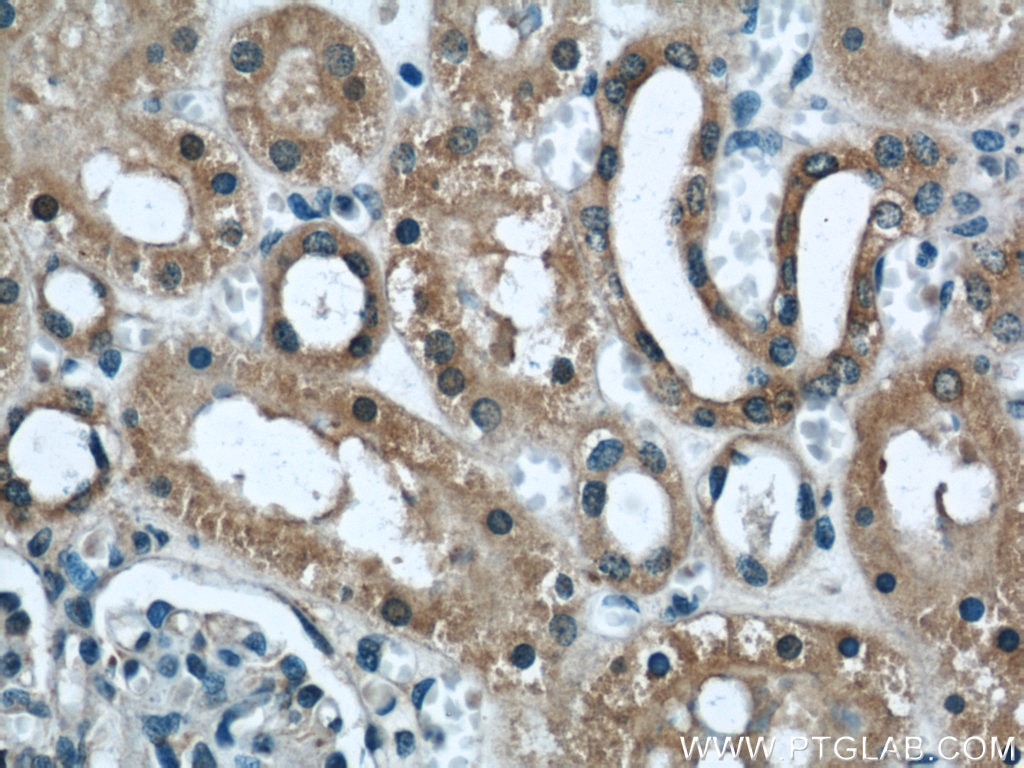
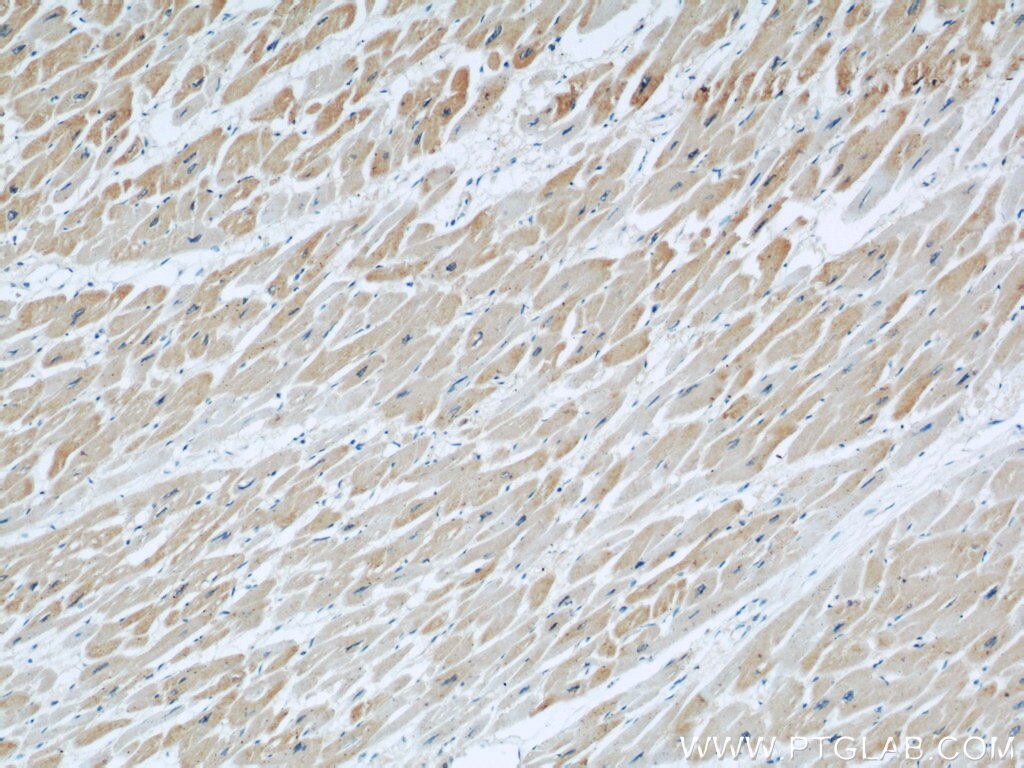
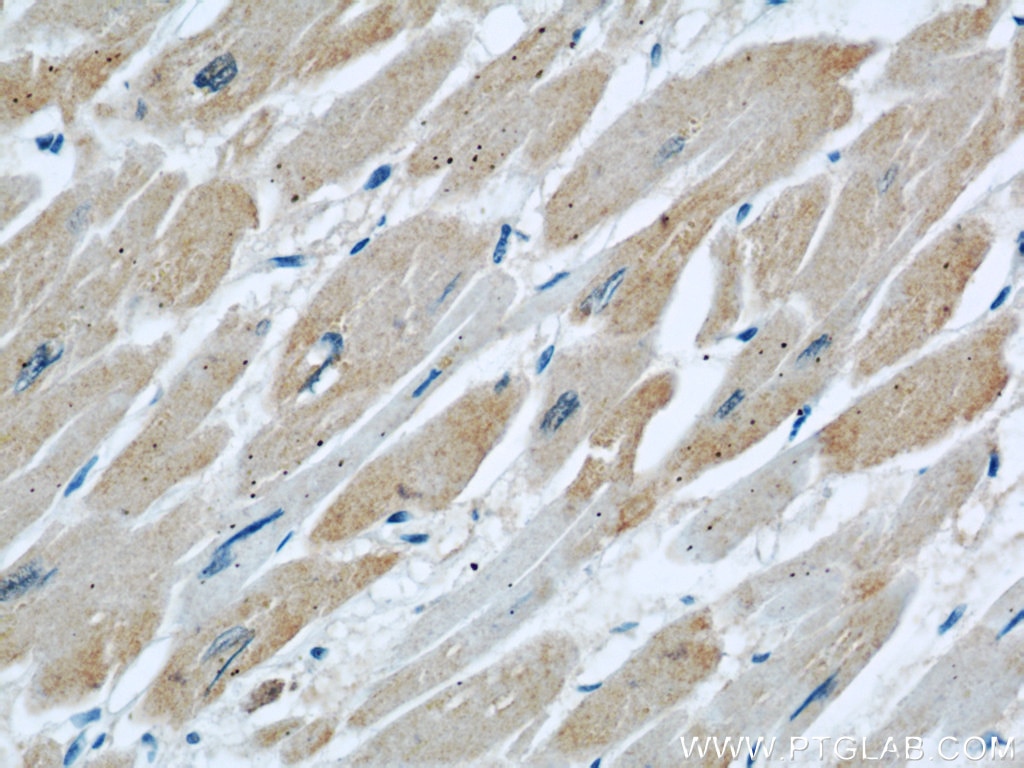
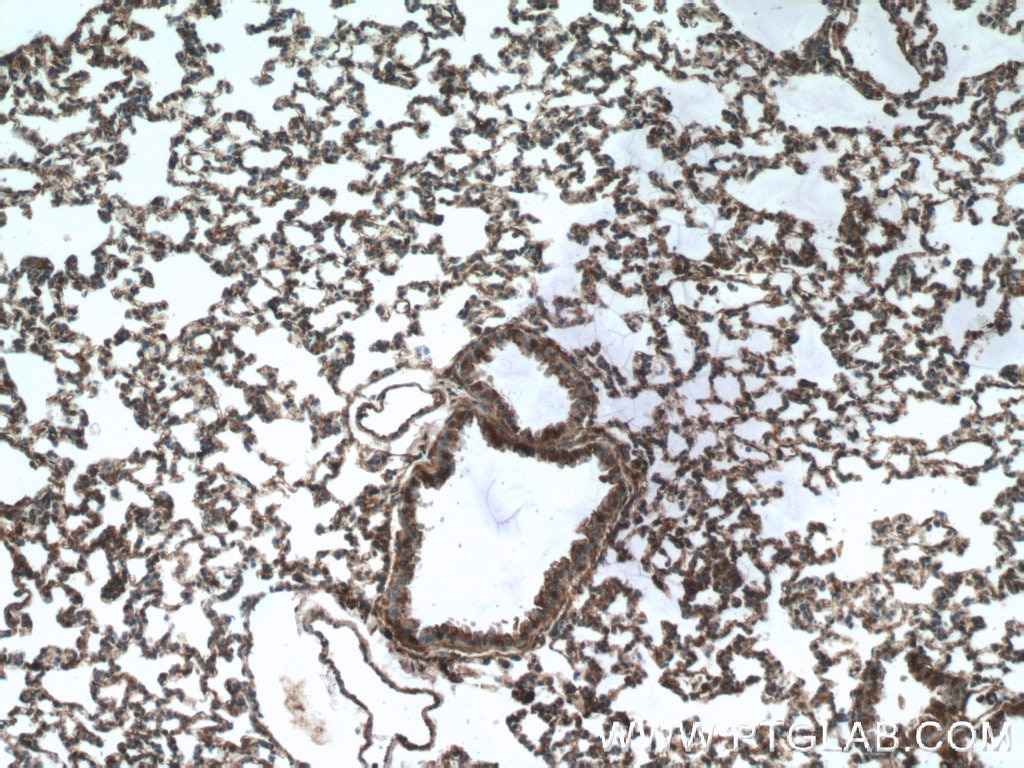
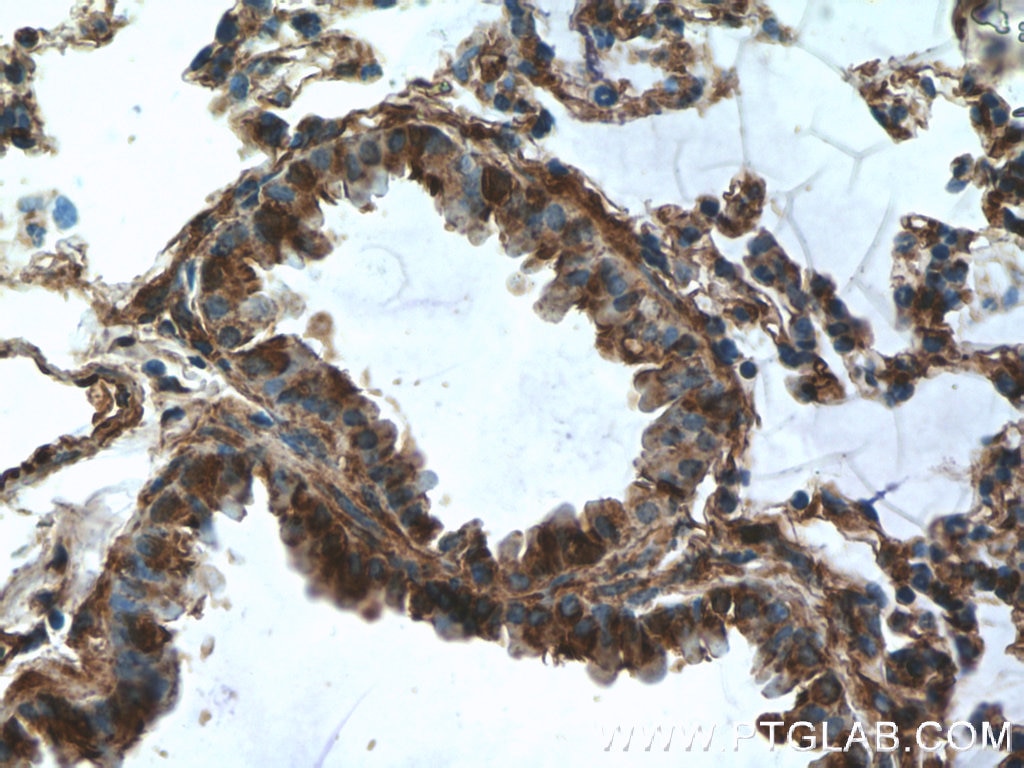
| Positive IHC detected in | human kidney tissue, human heart tissue, mouse kidney tissue, mouse lung tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 4 publications below |
| WB | See 7 publications below |
| IF | See 2 publications below |
| IP | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
11622-1-AP targets DOCK8 in WB, IHC, IF, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | DOCK8 fusion protein Ag2040 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | dedicator of cytokinesis 8 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 2031 aa, 231 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 230-239 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC019102 |
| Gene Symbol | DOCK8 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 81704 |
| RRID | AB_10216360 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q8NF50 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Background
Dedicator of Cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) is a protein that regulates the actin cytoskeleton, with particular importance in immune cells and a key role in innate and adaptive immune responses.
What is the molecular weight of DOCK8?
231 kDa. DOCK8 is a protein composed of 2031 amino acids and is a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF).
What is the function of DOCK8?
DOCK8 is a member of the DOCK family of proteins, which have a unique DRH2 domain enabling them to act as GEFs and so controlling a range of cellular processes in various signaling pathways (PMID: 12432077). The specific target of DOCK8 is Cell division control protein 42 homolog (Cdc42), a small GTPase that is involved in regulation of the cell cycle and forms a complex. DOCK8 also acts as a scaffold molecule in this complex that initiates actin polymerization via the Wiskott-Aldrich Syndrome protein (WASp) (PubMed: 28028151, PubMed: 22461490).
What diseases are associated with DOCK8?
The role of DOCK8 in immunity was first identified with the study of DOCK8-deficient patients who presented with combined immunodeficiency (PMID: 19776401; PMID: 20004785). The subsequent study of DOCK8 in immune cells such as T cells, natural killer (NK) cells, and B cells has revealed how it regulates their normal function. This includes the regulation of immune synapse formation, immune cell trafficking, regulation of dendritic cell polarization, and cytokine production (PMID: 28366940).
DOCK8 deficiency is caused by a number of different mutations in the gene. It leads to the autosomal recessive form of the immunodeficiency disease Hyper-IgE syndrome, or Job's syndrome. The symptoms of DOCK8 deficiency include eczema, high levels of serum IgE, hypereosinophilia, and recurrent respiratory and skin infections as a result of impaired immune cell function.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for DOCK8 antibody 11622-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for DOCK8 antibody 11622-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Immunol Heme drives hemolysis-induced susceptibility to infection via disruption of phagocyte functions.
| ||
Cell Death Differ CCL2 regulation of MST1-mTOR-STAT1 signaling axis controls BCR signaling and B-cell differentiation. | ||
Diabetes Dedicator of Cytokinesis 5 Regulates Keratinocyte Function and Promotes Diabetic Wound Healing. | ||
Oncotarget CD147 promotes Src-dependent activation of Rac1 signaling through STAT3/DOCK8 during the motility of hepatocellular carcinoma cells.
| ||
iScience DOCK8-expressing T follicular helper cells newly generated beyond self-organized criticality cause systemic lupus erythematosus.
| ||
MedComm (2020) Ultra-high static magnetic fields cause immunosuppression through disrupting B-cell peripheral differentiation and negatively regulating BCR signaling |