Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
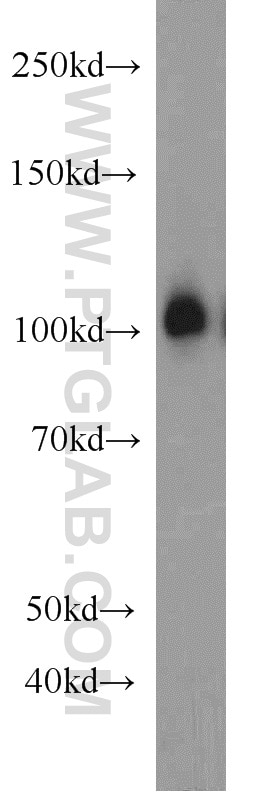
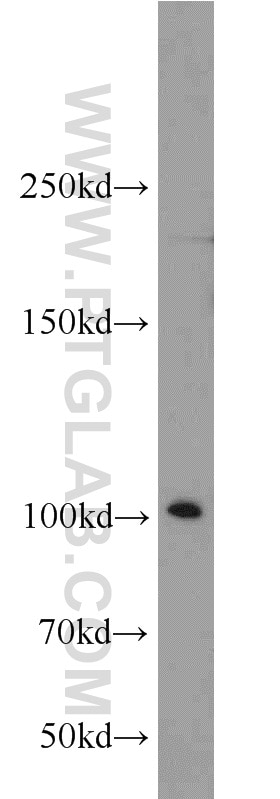
| Positive WB detected in | rat brain tissue, human brain tissue, mouse brain tissue |
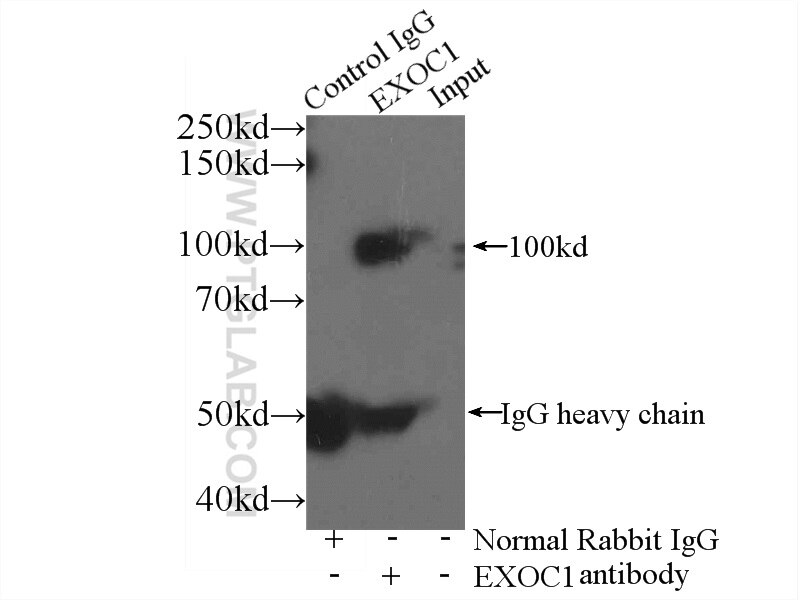
| Positive IP detected in | mouse brain tissue |
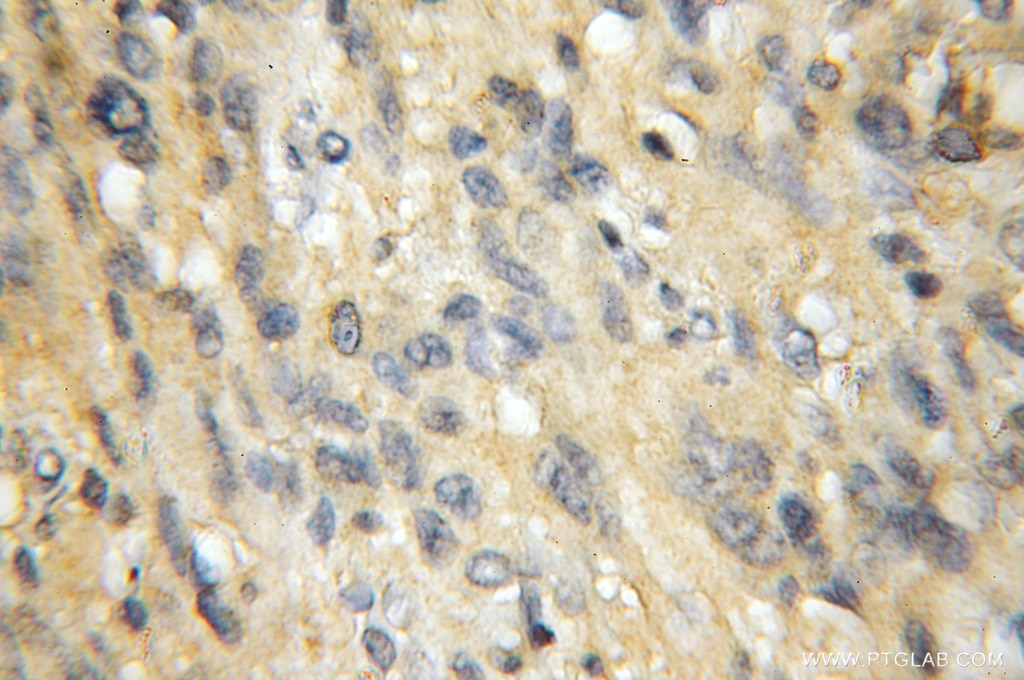
| Positive IHC detected in | human gliomas tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
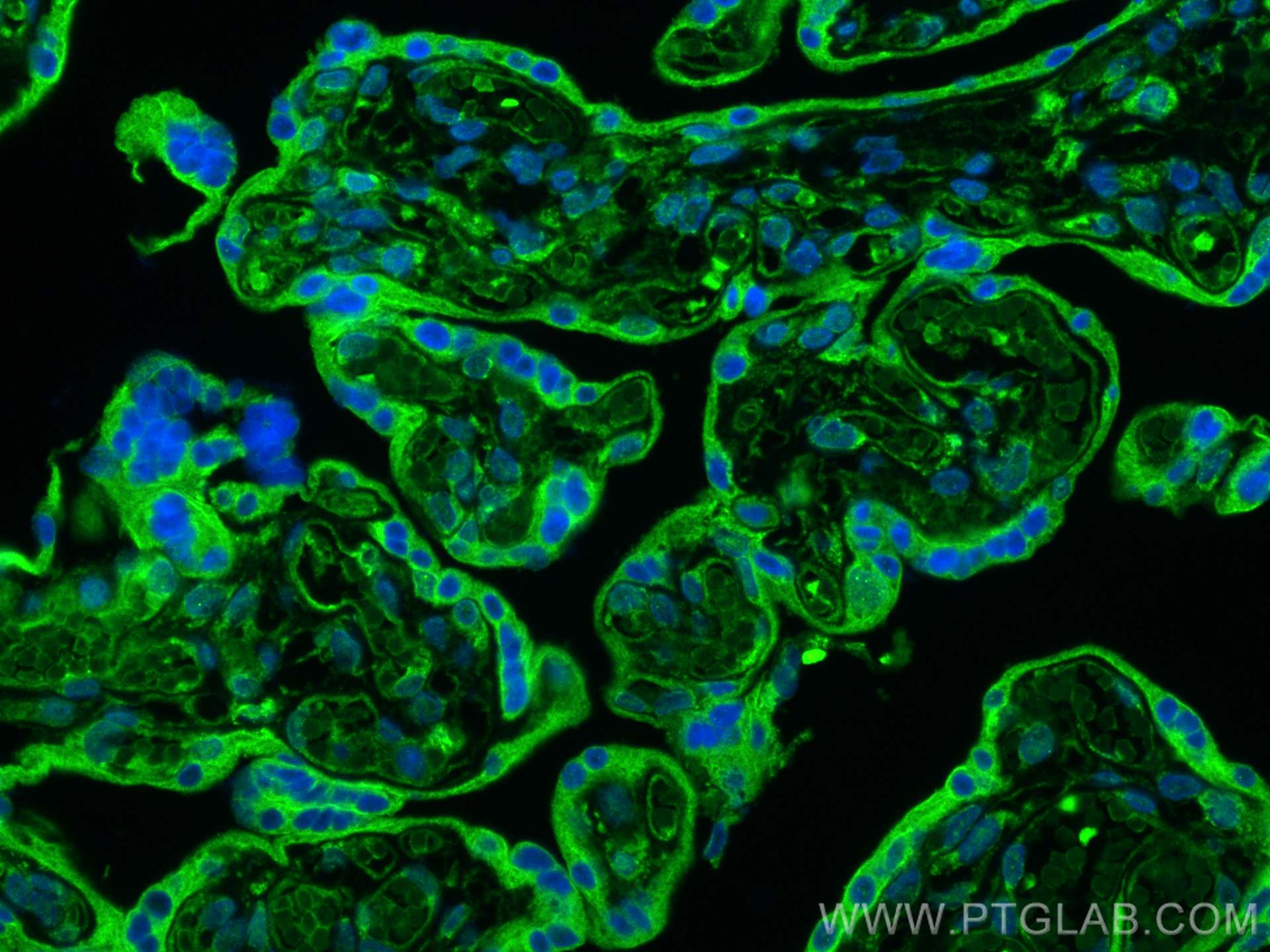
| Positive IF-P detected in | human placenta tissue |
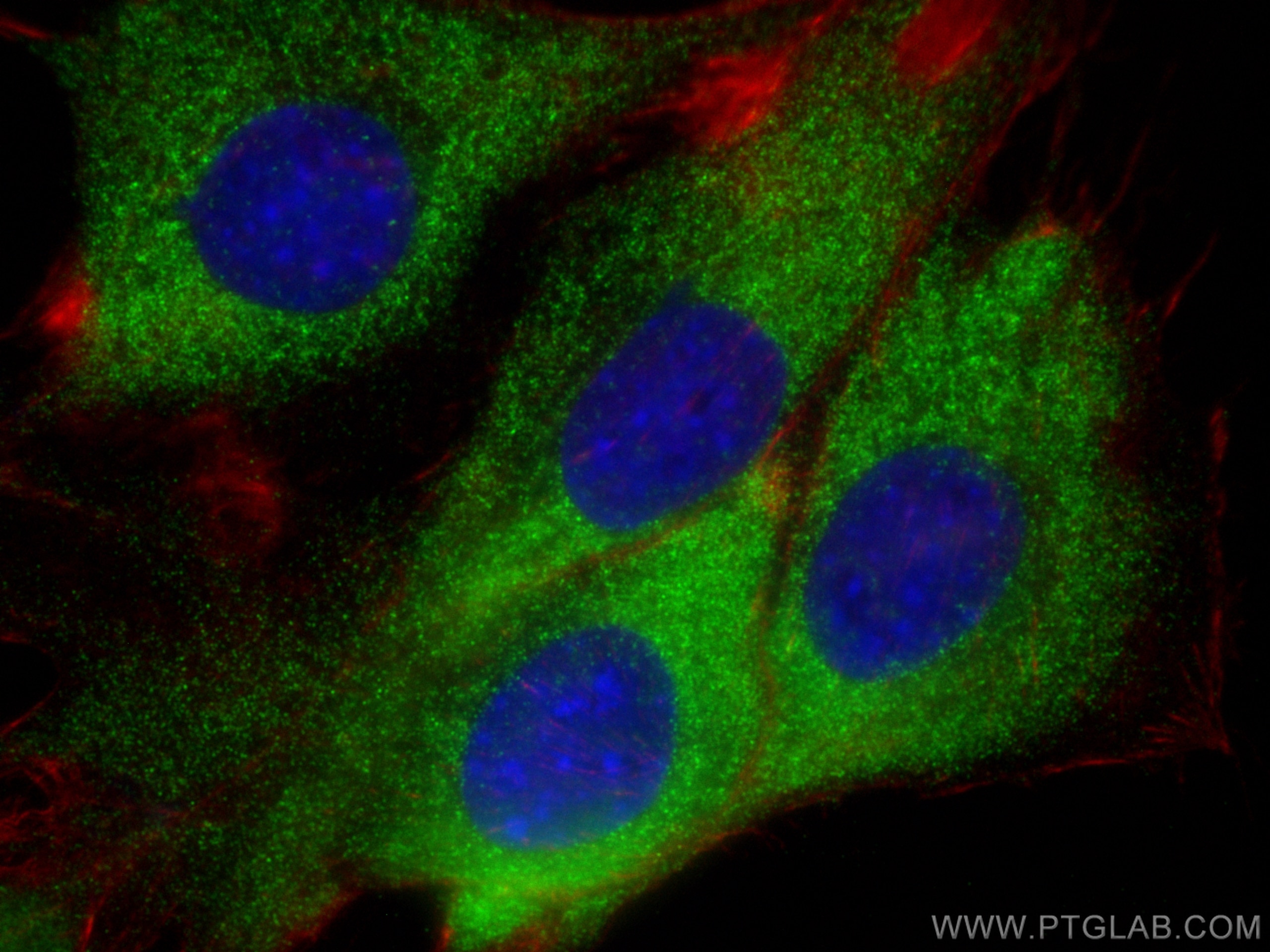
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | C2C12 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:20-1:200 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)-P | IF-P : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 3 publications below |
| WB | See 10 publications below |
| IF | See 9 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
11690-1-AP targets EXOC1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | EXOC1 fusion protein Ag2303 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | exocyst complex component 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 894 aa, 102 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 102 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC020650 |
| Gene Symbol | EXOC1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 55763 |
| RRID | AB_2231500 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9NV70 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
EXOC1 (exocyst complex component 1), also known as SEC3, is a component of the exocyst complex which is essential for the targeting of exocytic vesicles to specific docking sites on the plasma membrane. The exocyst complex is an octameric complex that tethers vesicles at the plasma membrane, regulates polarized exocytosis, and recruits membranes and proteins required for nanotube formation.Recently it has been reported that exocyst complex proteins are likely a key effector of Nef-mediated enhancement of nanotube formation, and possibly microvesicle secretion, which suggests a new paradigm of exocyst involvement in polarized targeting for intercellular transfer of viral proteins and viruses.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for EXOC1 antibody 11690-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for EXOC1 antibody 11690-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for EXOC1 antibody 11690-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for EXOC1 antibody 11690-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Nat Nanotechnol Intercellular nanotubes mediate mitochondrial trafficking between cancer and immune cells.
| ||
J Cell Biol The exocyst controls lysosome secretion and antigen extraction at the immune synapse of B cells. | ||
Elife EXOC1 plays an integral role in spermatogonia pseudopod elongation and spermatocyte stable syncytium formation in mice. | ||
PLoS Pathog Shigella hijacks the exocyst to cluster macropinosomes for efficient vacuolar escape. | ||
Retrovirology Proteomic analysis of HIV-1 Nef cellular binding partners reveals a role for exocyst complex proteins in mediating enhancement of intercellular nanotube formation. |