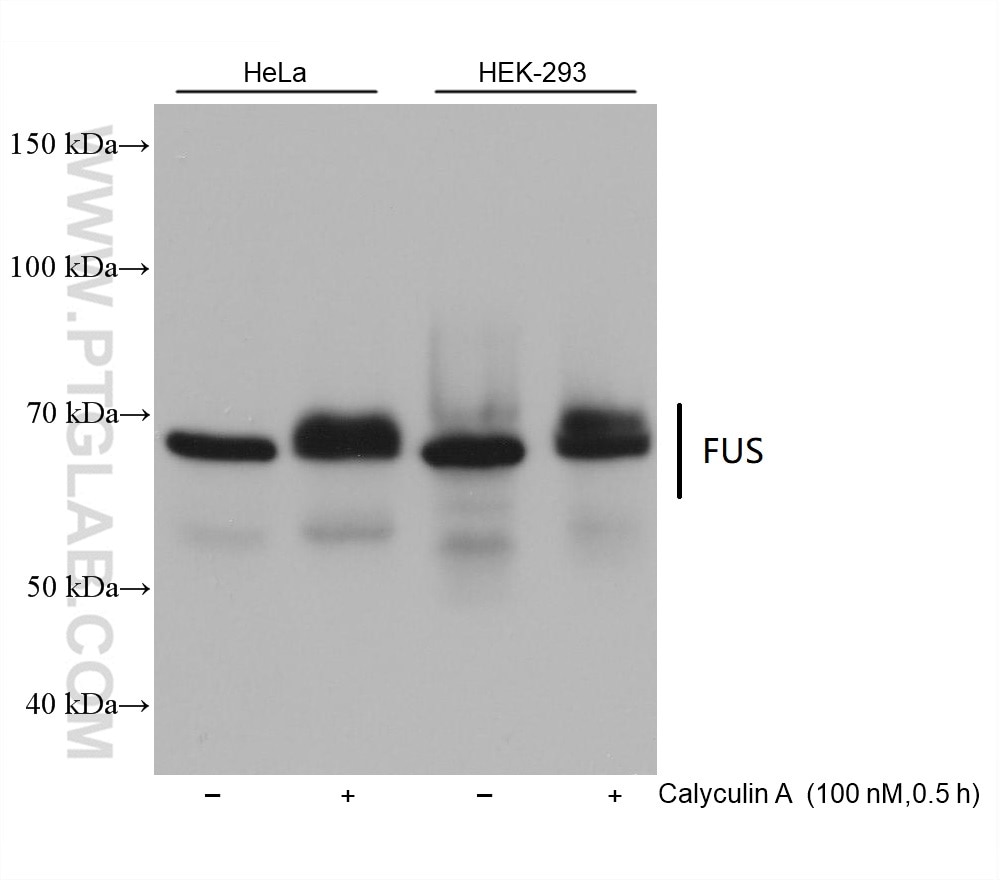
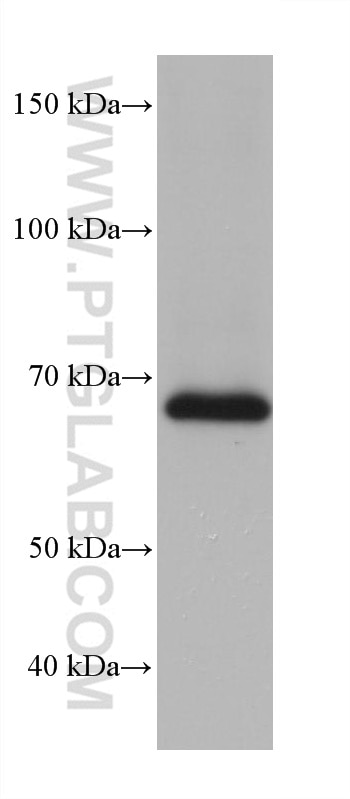
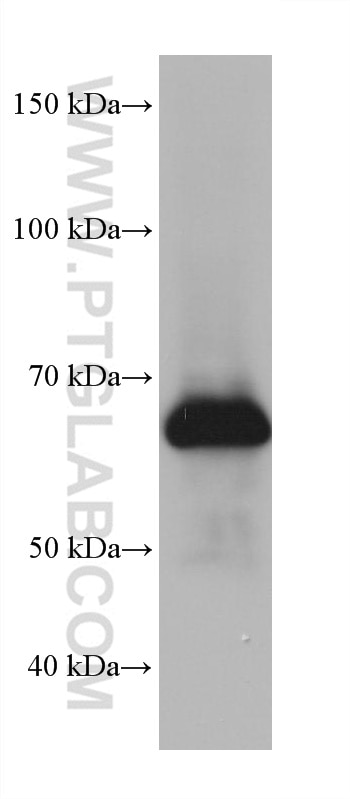
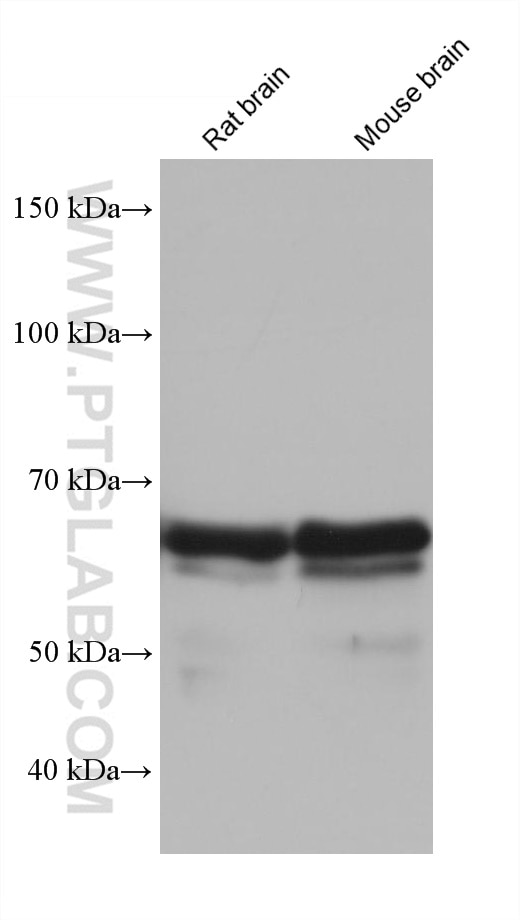
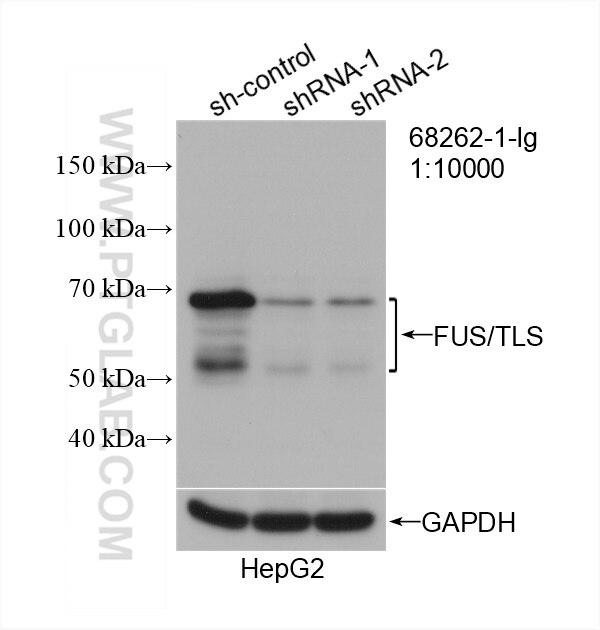
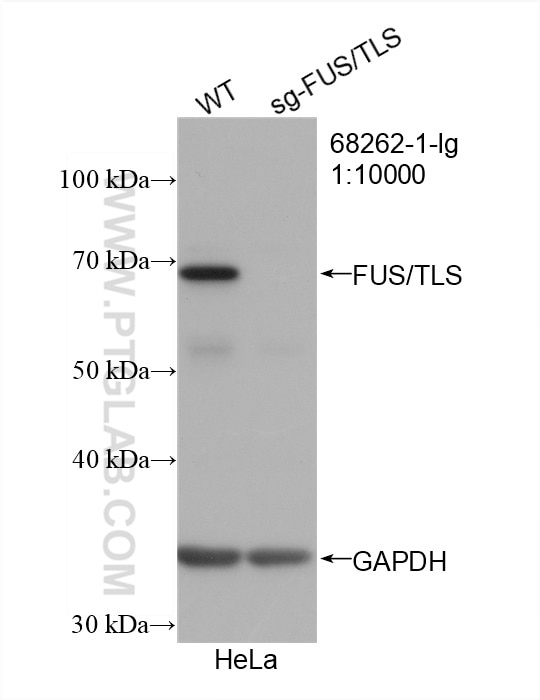
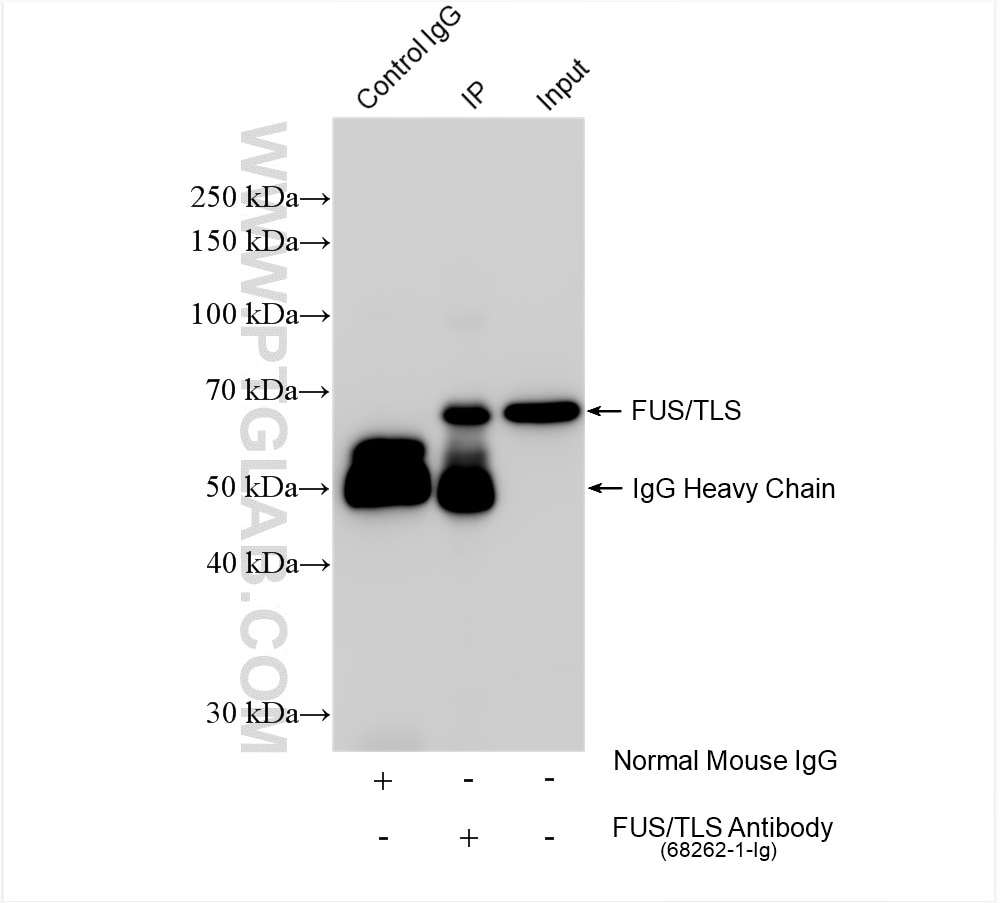
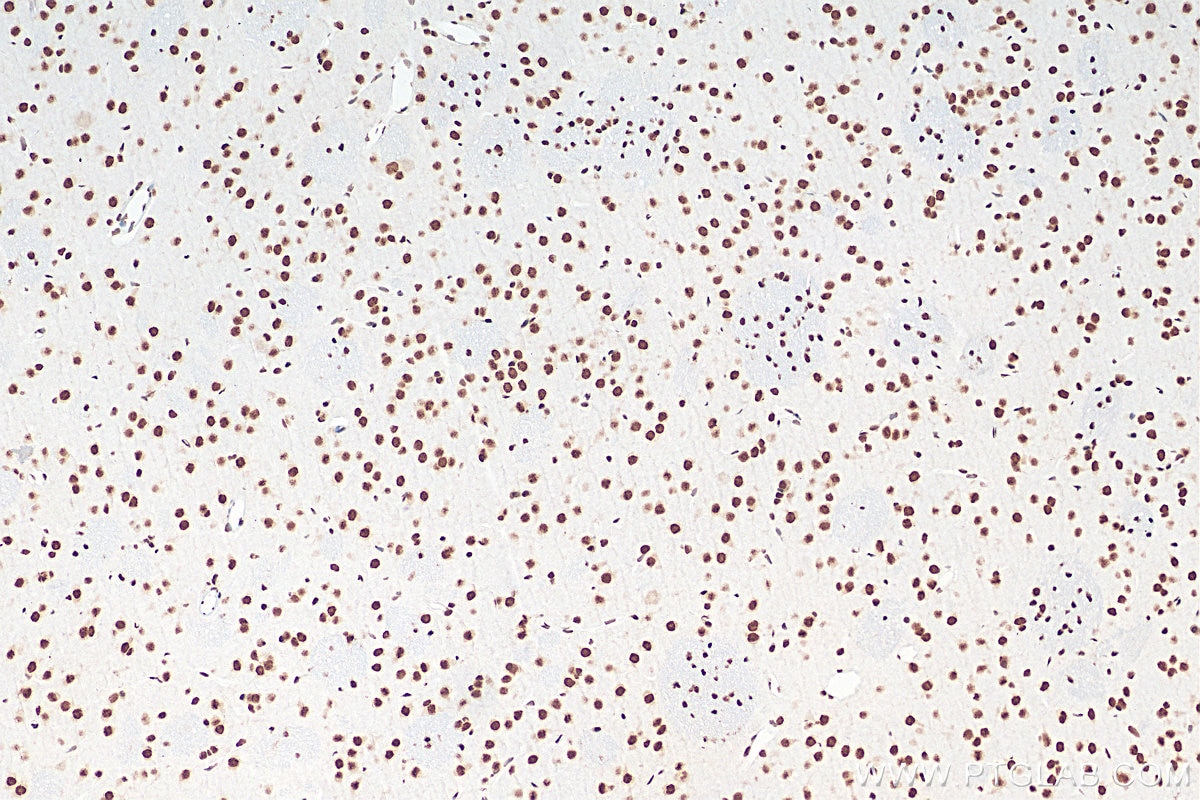
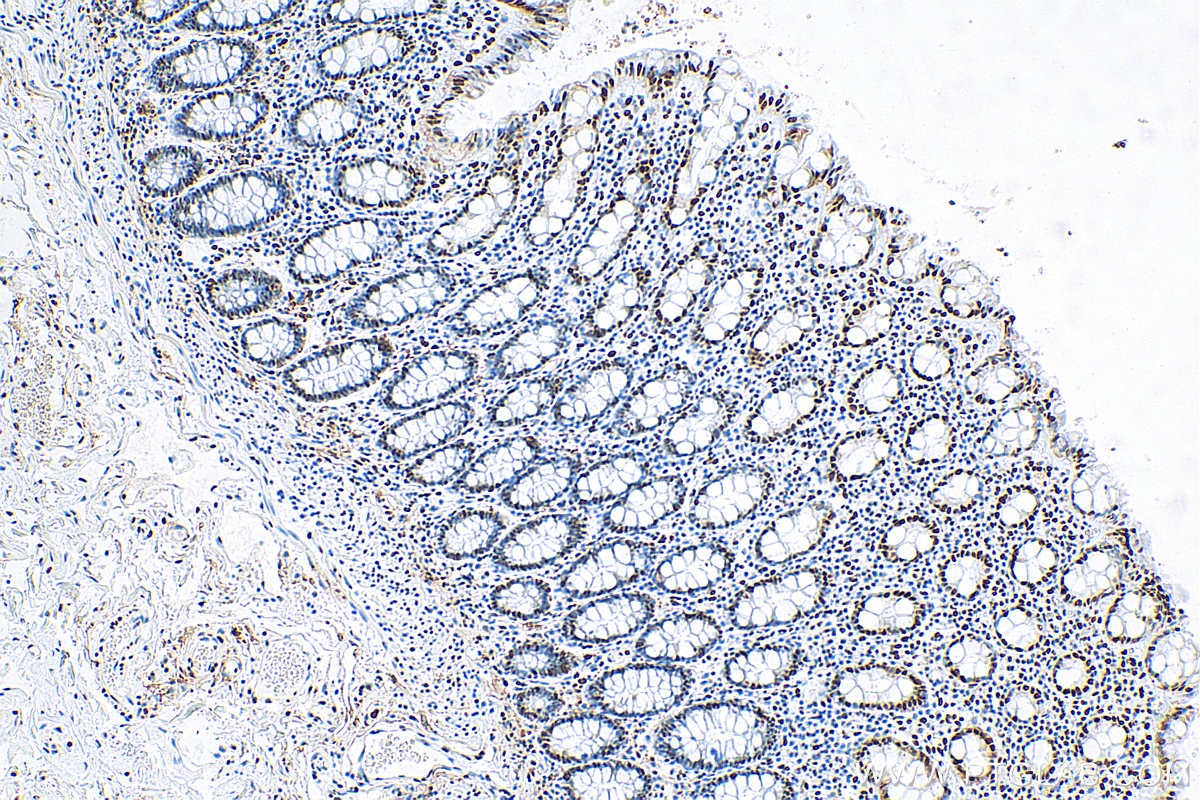
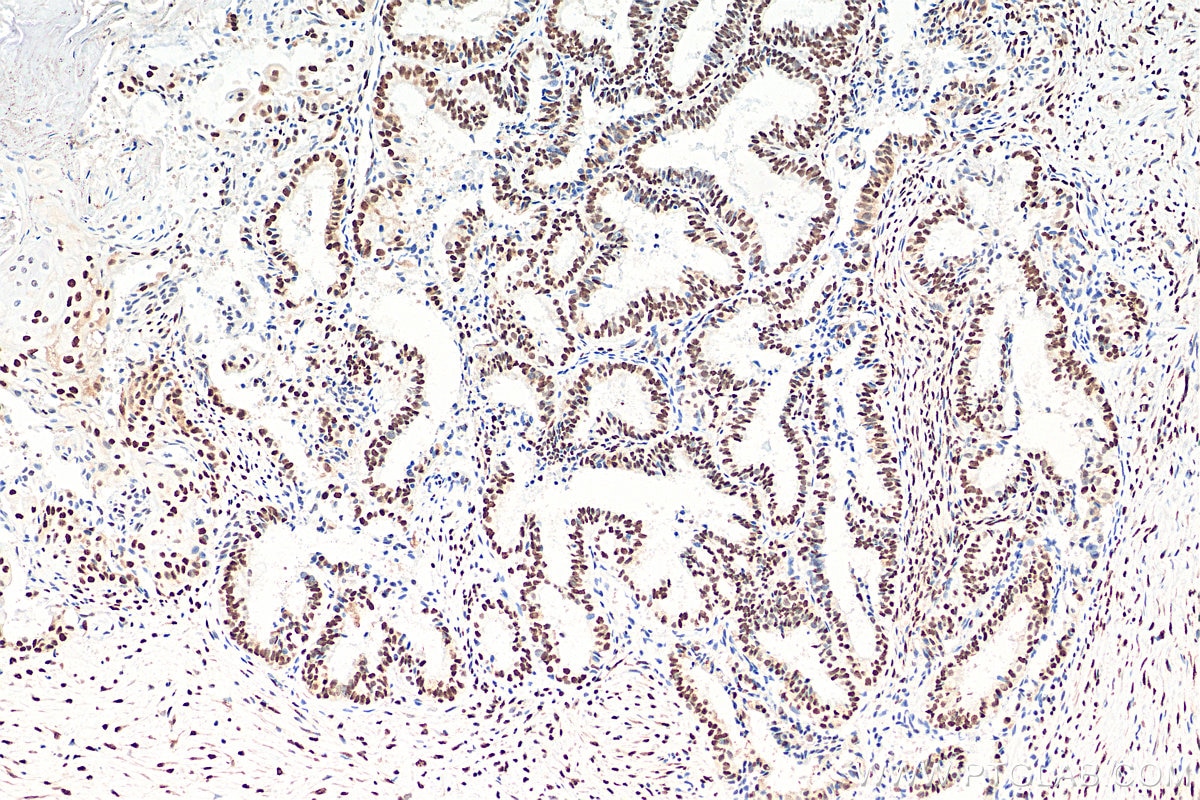
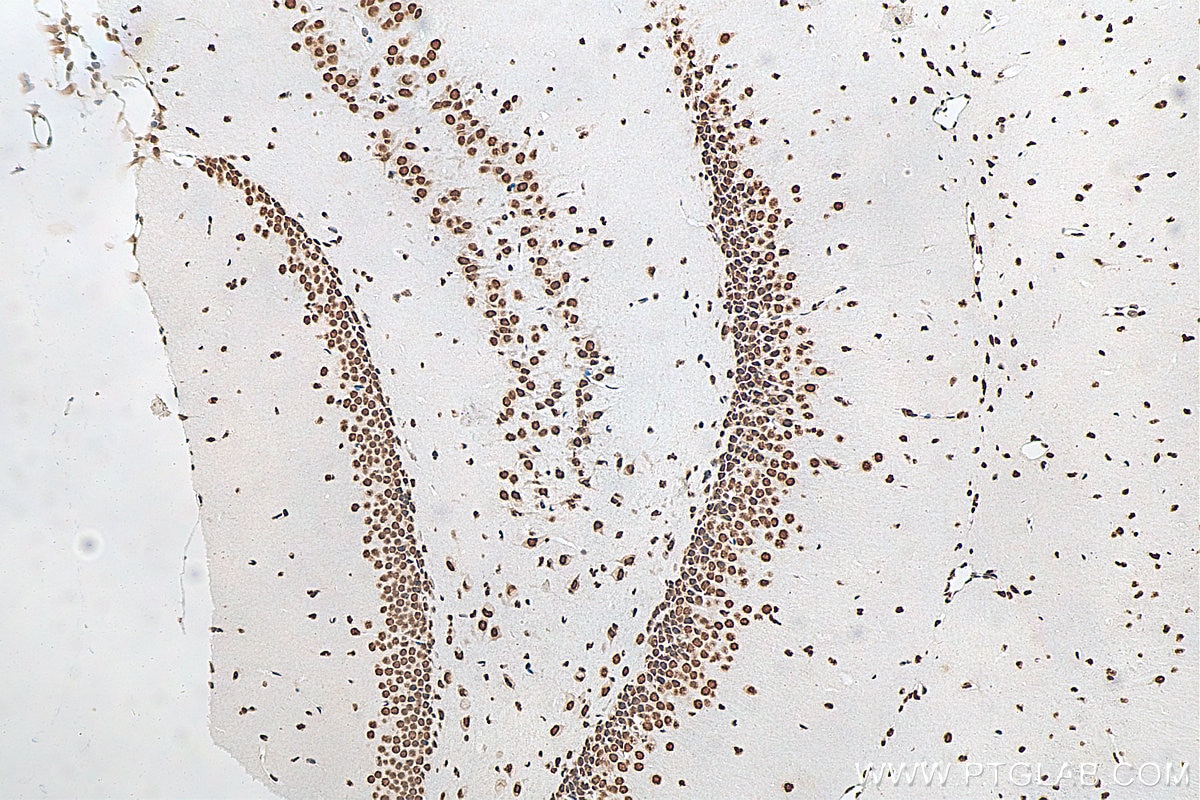
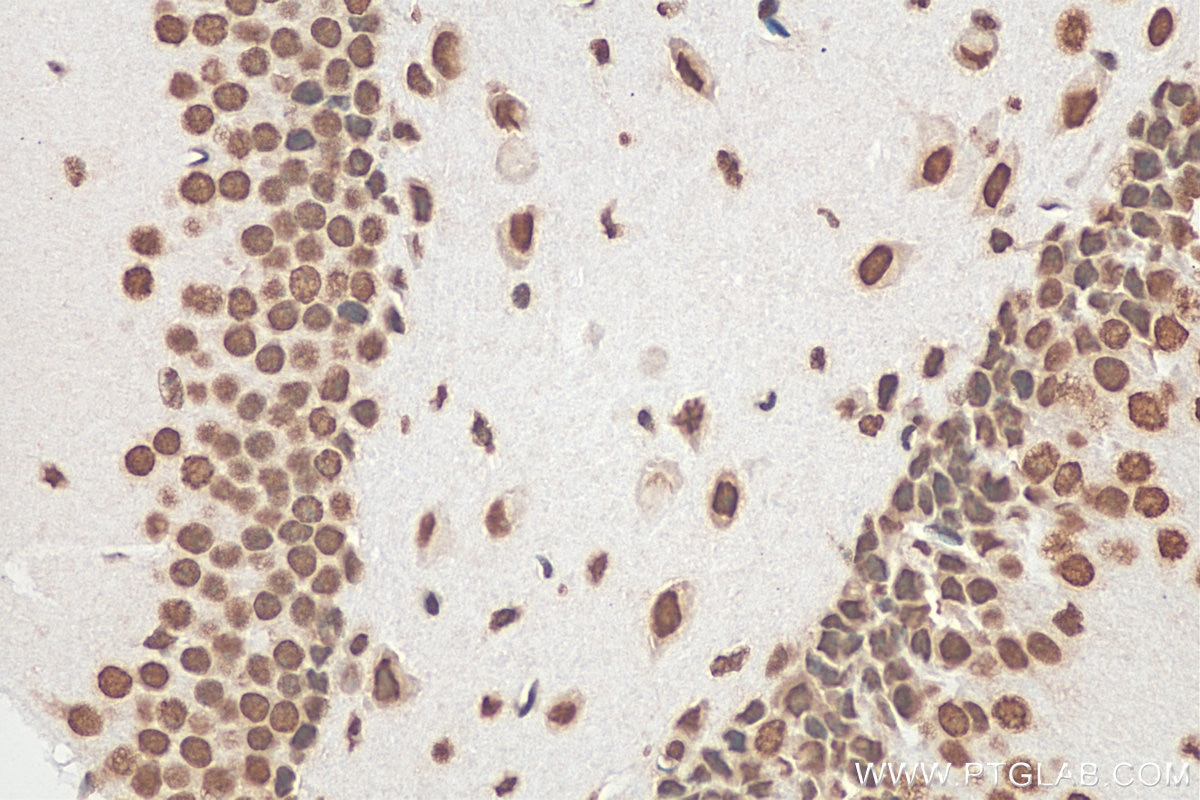
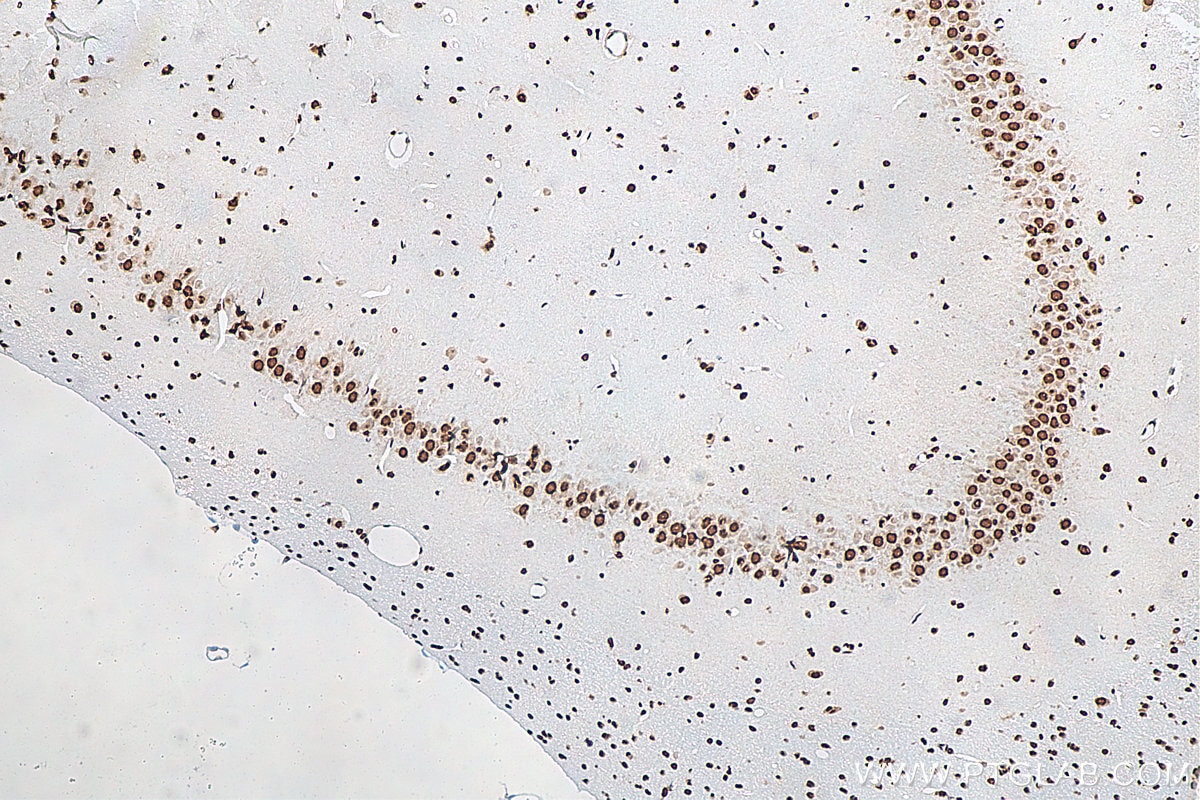
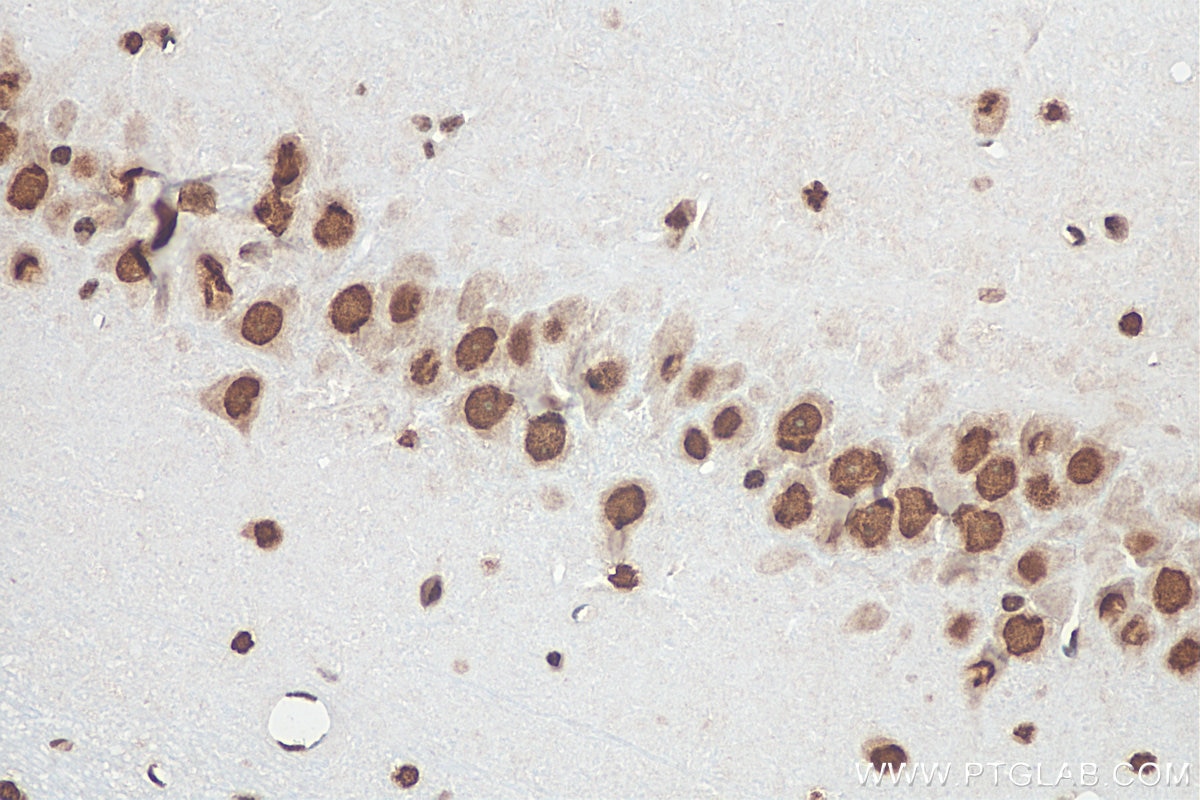
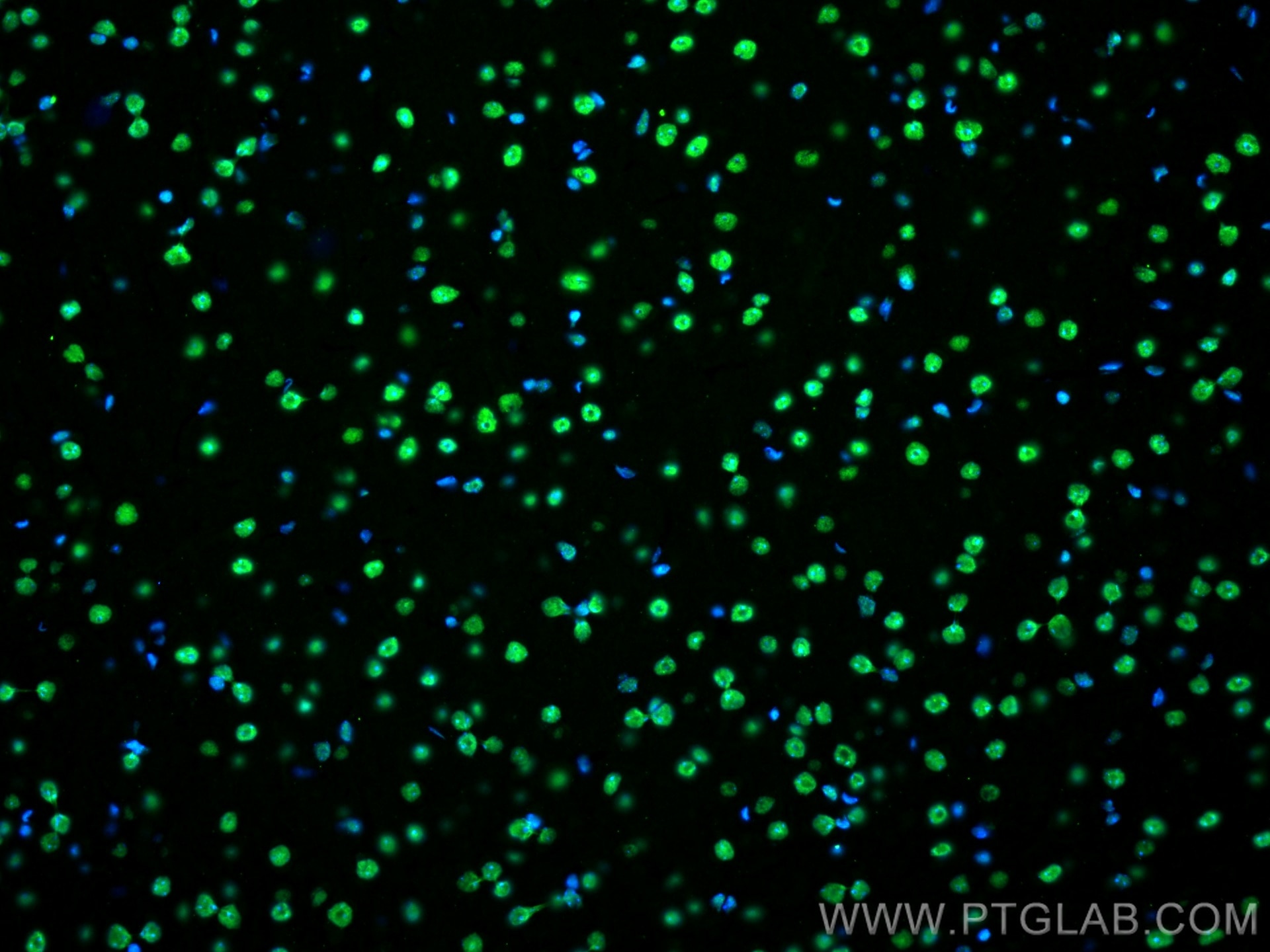
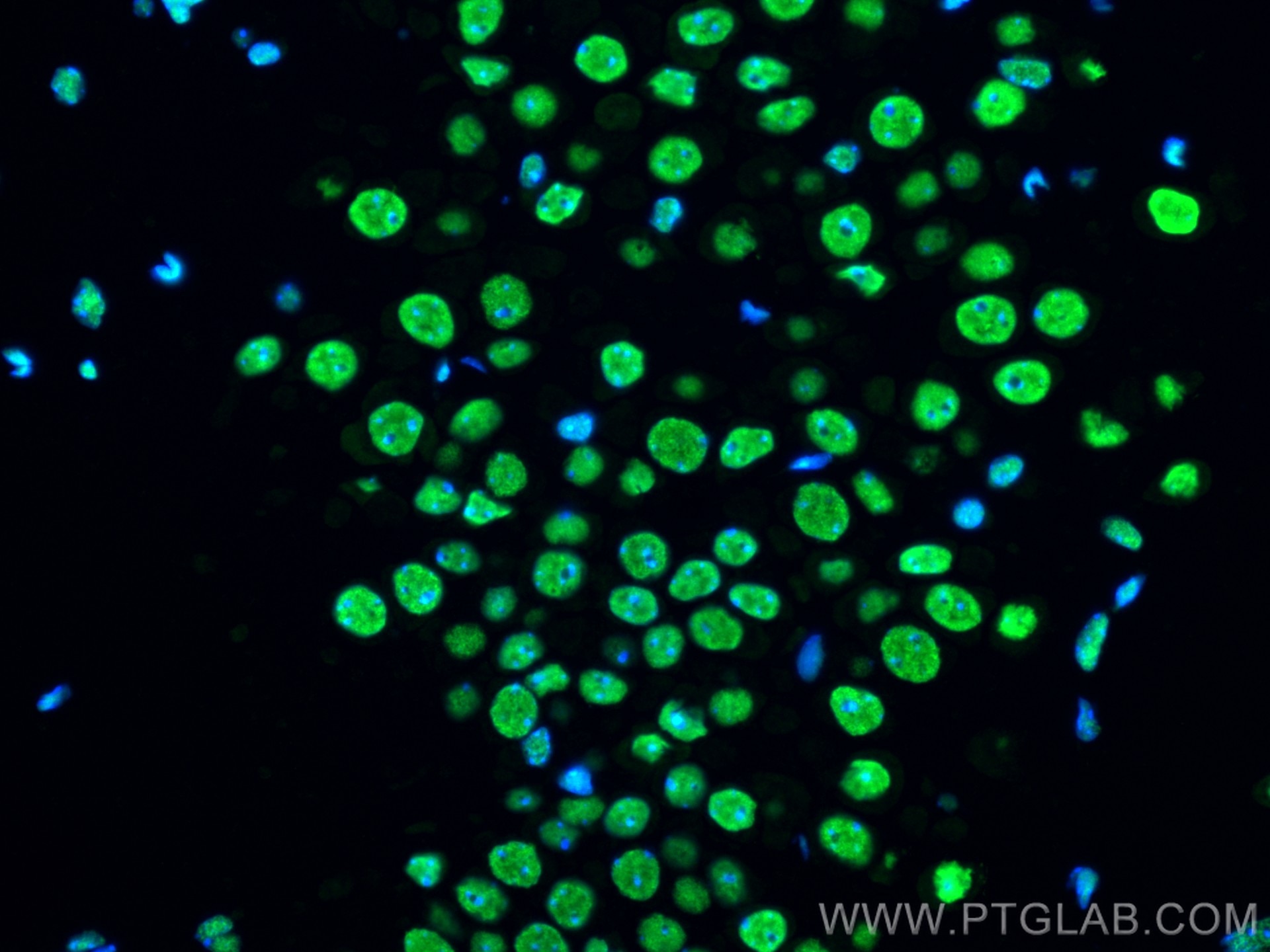
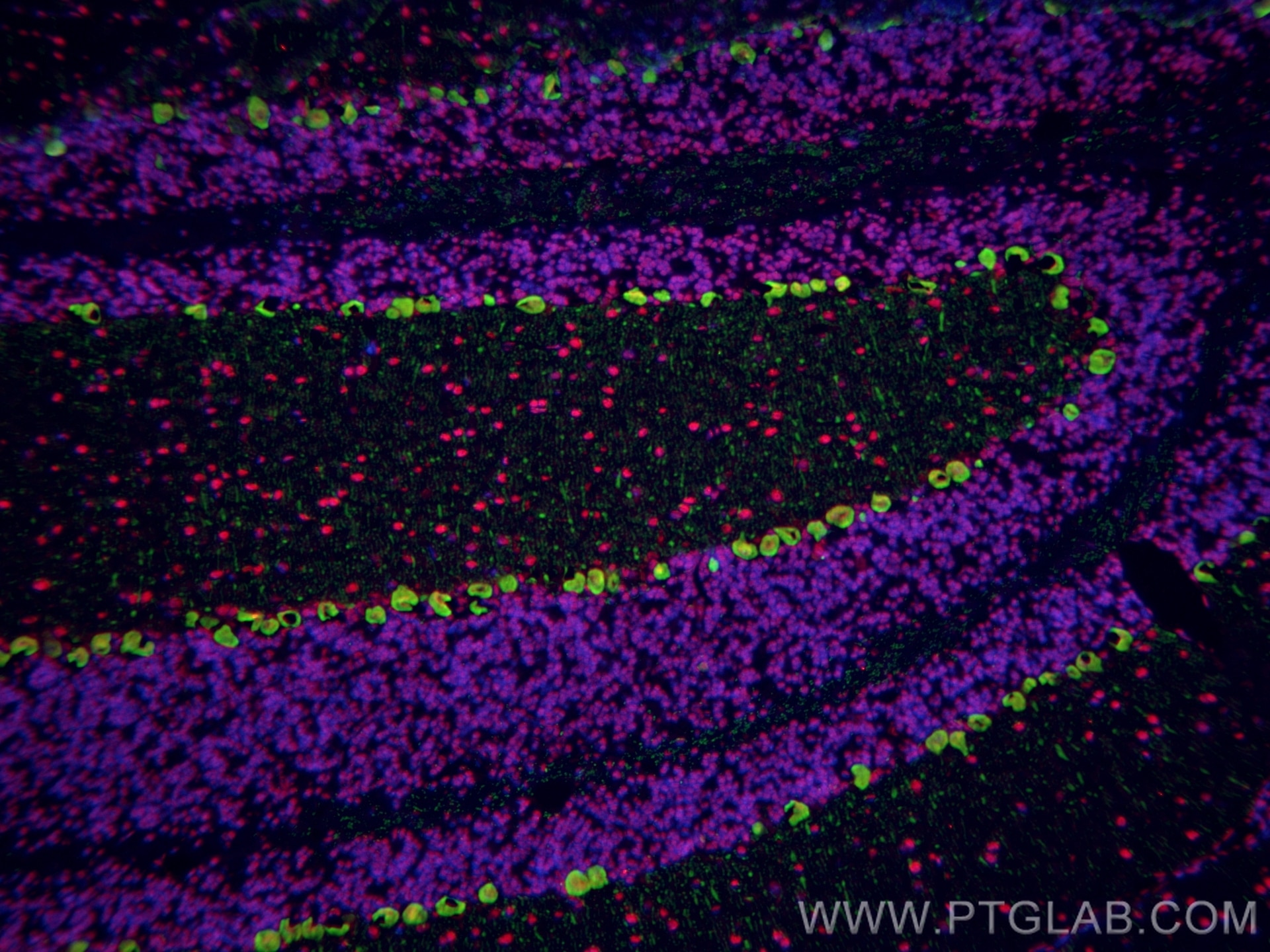
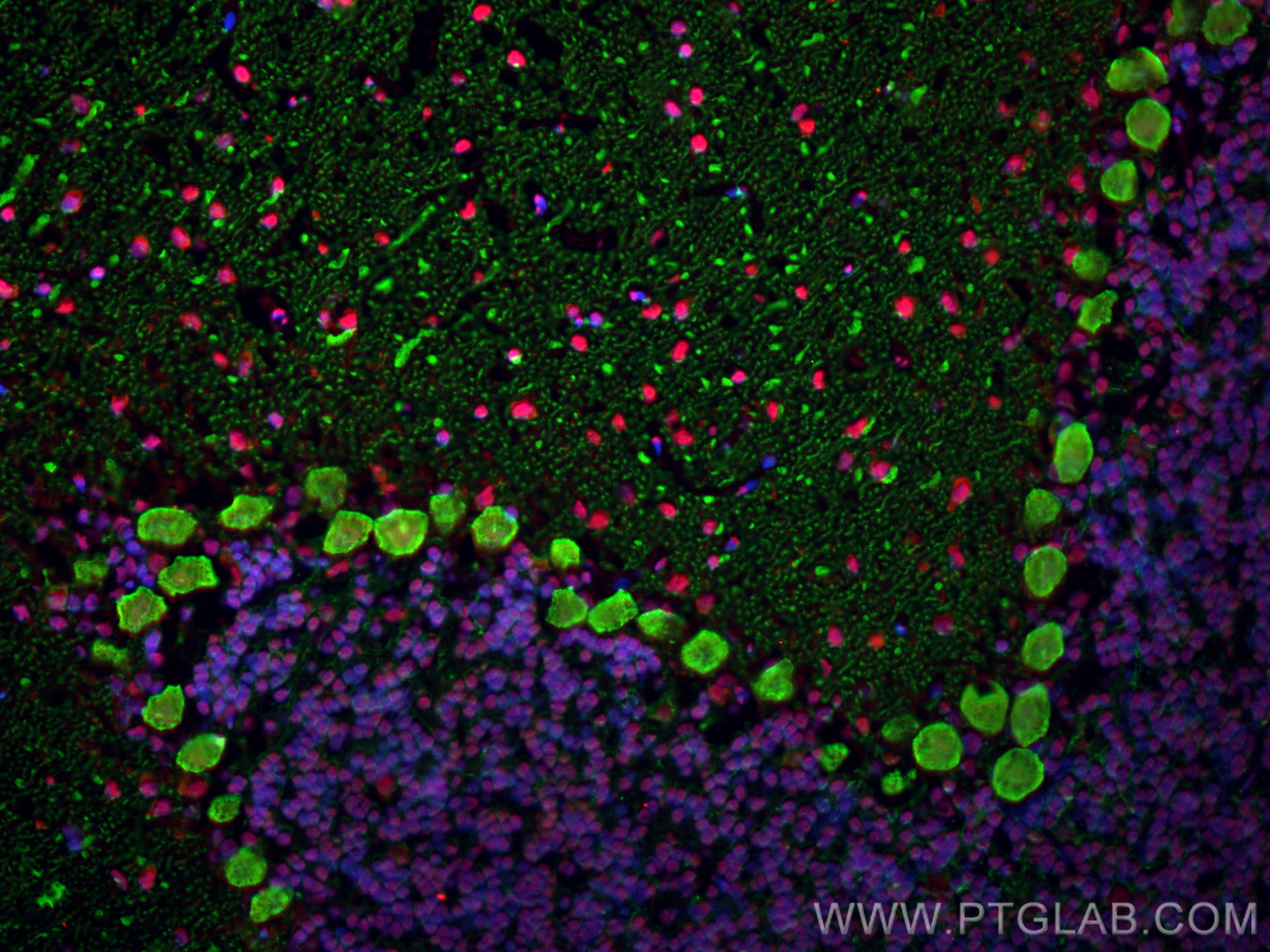
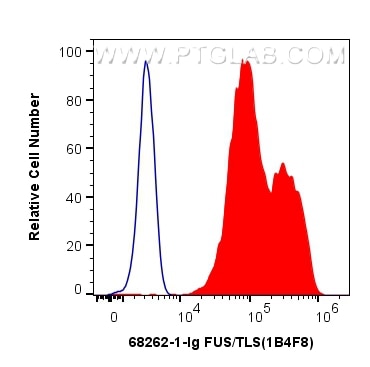
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
68262-1-PBS targets FUS/TLS in WB, IHC, IF-P, IF-Fro, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag2150 Product name: Recombinant human FUS/TLS protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 53-400 aa of BC026062 Sequence: SSYSSYGQSQNTGYGTQSTPQGYGSTGGYGSSQSSQSSYGQQSSYPGYGQQPAPSSTSGSYGSSSQSSSYGQPQSGSYSQQPSYGGQQQSYGQQQSYNPPQGYGQQNQYNSSSGGGGGGGGGGNYGQDQSSMSSGGGSGGGYGNQDQSGGGGSGGYGQQDRGGRGRGGSGGGGGGGGGGYNRSSGGYEPRGRGGGRGGRGGMGGSDRGGFNKFGGPRDQGSRHDSEQDNSDNNTIFVQGLGENVTIESVADYFKQIGIIKTNKKTGQPMINLYTDRETGKLKGEATVSFDDPPSAKAAIDWFDGKEFSGNPIKVSFATRRADFNRGGGNGRGGRGRGGPMGRGGYGGG 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | fusion (involved in t(12;16) in malignant liposarcoma) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 75 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 53 kDa, 68-75 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC026062 |
| Gene Symbol | FUS/TLS |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2521 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P35637 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
FUS (also named TLS and POMp75) belongs to the RRM TET family. FUS may play a role in the maintenance of genomic integrity; it binds both single-stranded and double-stranded DNA and promotes ATP-independent annealing of complementary single-stranded DNAs and D-loop formation in superhelical double-stranded DNA. FUS is also an RNA-binding protein, and its links to neurodegenerative disease proffer the intriguing possibility that altered RNA metabolism or RNA processing may underlie or contribute to neuron degeneration[PMID: 22640227]. FUS may be a cause of angiomatoid fibrous histiocytoma (AFH) and is implicated in certain forms of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and frontotemporal dementias (FTDs) such as frontotemporal lobar dementia with ubiquitin inclusions (FTLD-U)(PMID: 22640227). Multiple phosphorylation on the N terminus of FUS caused that FUS was detected 68-75 kDa (PMID:24899704).