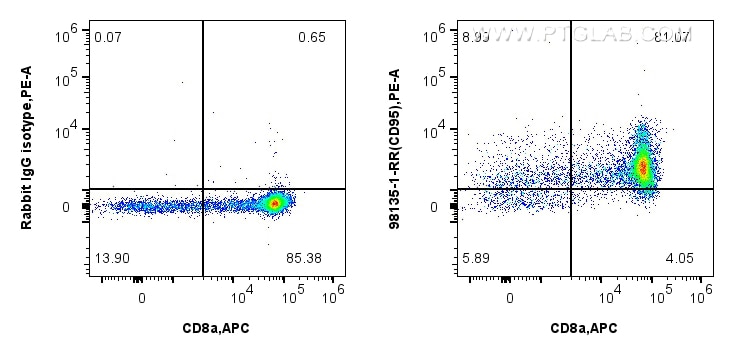
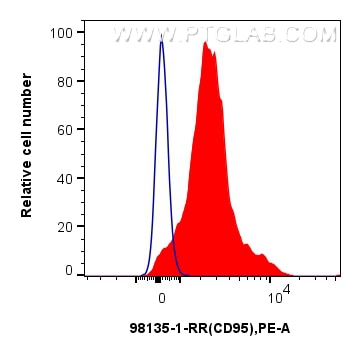
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| This reagent has been tested for flow cytometric analysis. It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
98135-1-PBS targets Fas/CD95 in FC applications and shows reactivity with mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | FusionProtein 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | Fas (TNF receptor superfamily member 6) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 37kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_007987.2 |
| Gene Symbol | Fas/CD95 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 14102 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | P25446 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Fas (CD95/APO-1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein belonging to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily. It can mediate apoptosis by ligation with an agonistic anti-Fas antibody or Fas ligand. Stimulation of Fas results in the aggregation of its intracellular death domains, leading to the formation of the death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). FAS-mediated apoptosis may have a role in the induction of peripheral tolerance, in the antigen-stimulated suicide of mature T-cells, or both. The molecular mass of native Fas is 38 kDa, the high molecular weight form (40-55 kDa) of Fas is due to glycosylation.