Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
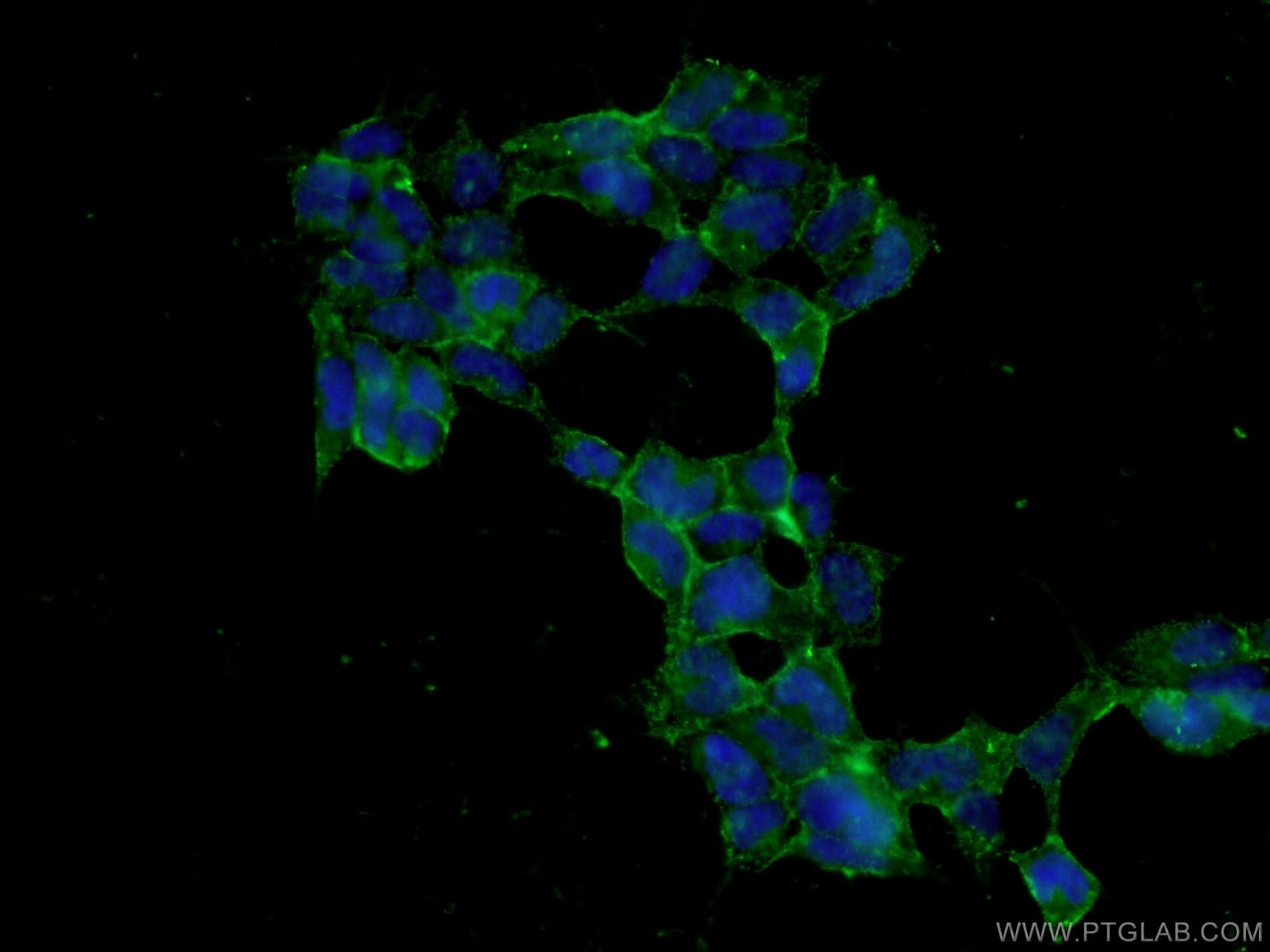
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HEK-293 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:500-1:2000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
27347-1-AP targets HEK 293 cells in WB, IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Cell Lysate 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | HEK 293 cells |
| Gene Symbol | |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | |
| RRID | AB_2880850 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Human Embryonic Kidney 293 cells, also often referred to as HEK 293, 293 cells, or less precisely as HEK cells are a specific cell line originally derived from human embryonic kidney cells grown in tissue culture. HEK 293 cells were generated in early 70s by transformation of cultures of normal human embryonic kidney cells with sheared adenovirus 5 DNA in Alex Van der Eb's laboratory in Leiden, Holland. This antibody is designed to detect the protein of the HEK293 cells.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for HEK 293 cells antibody 27347-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Int J Biol Macromol Western blotting analysis of proteins separated by agarose native gel electrophoresis. |