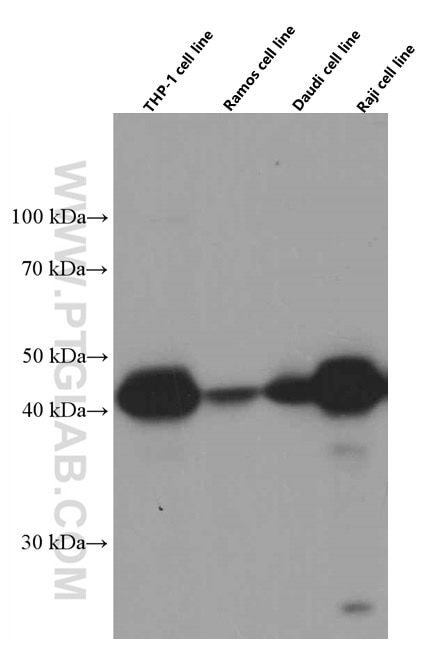
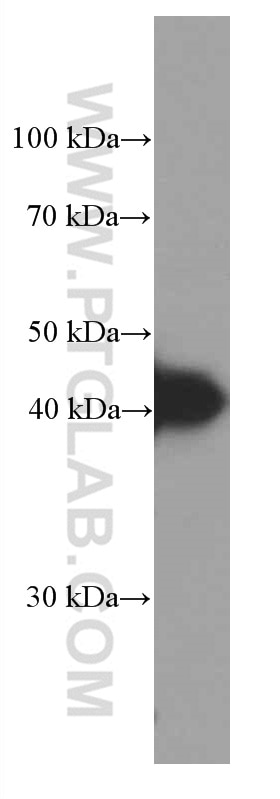
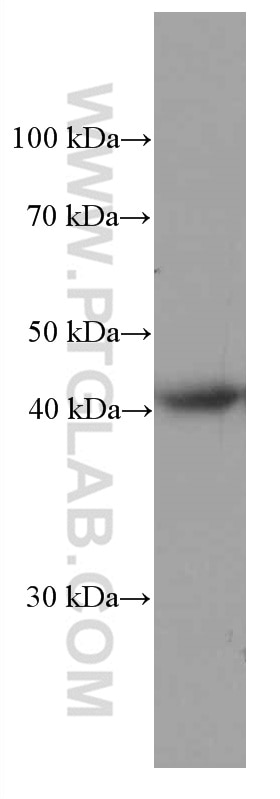
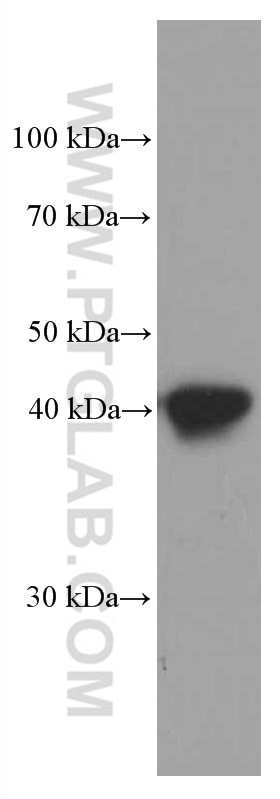
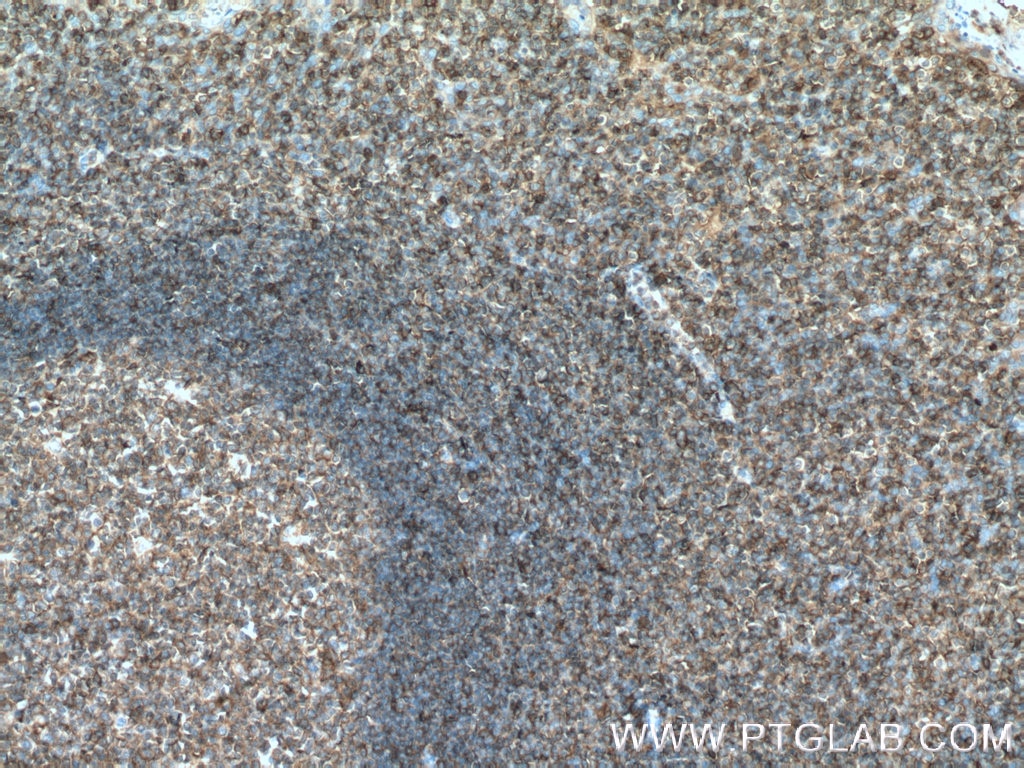
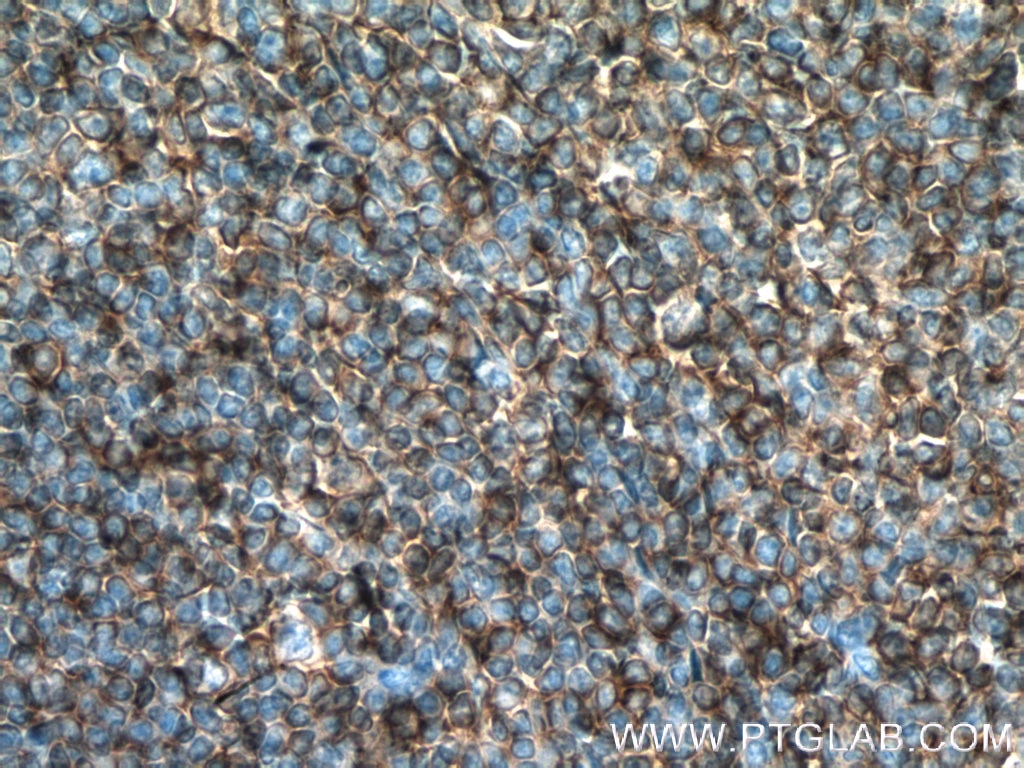
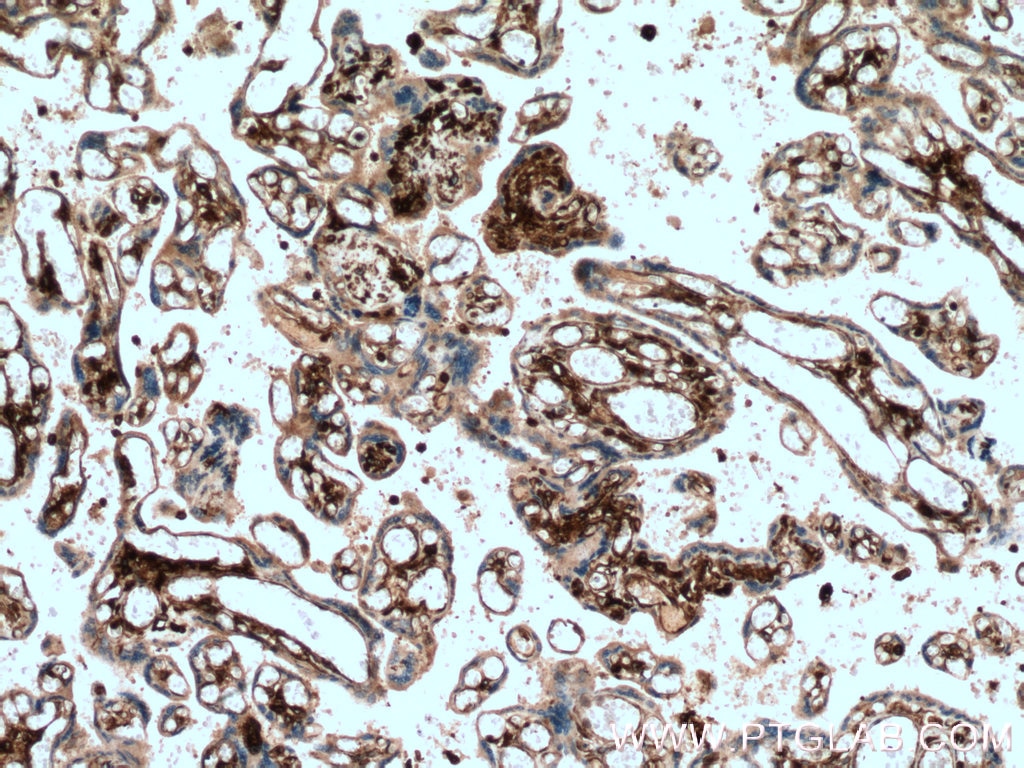
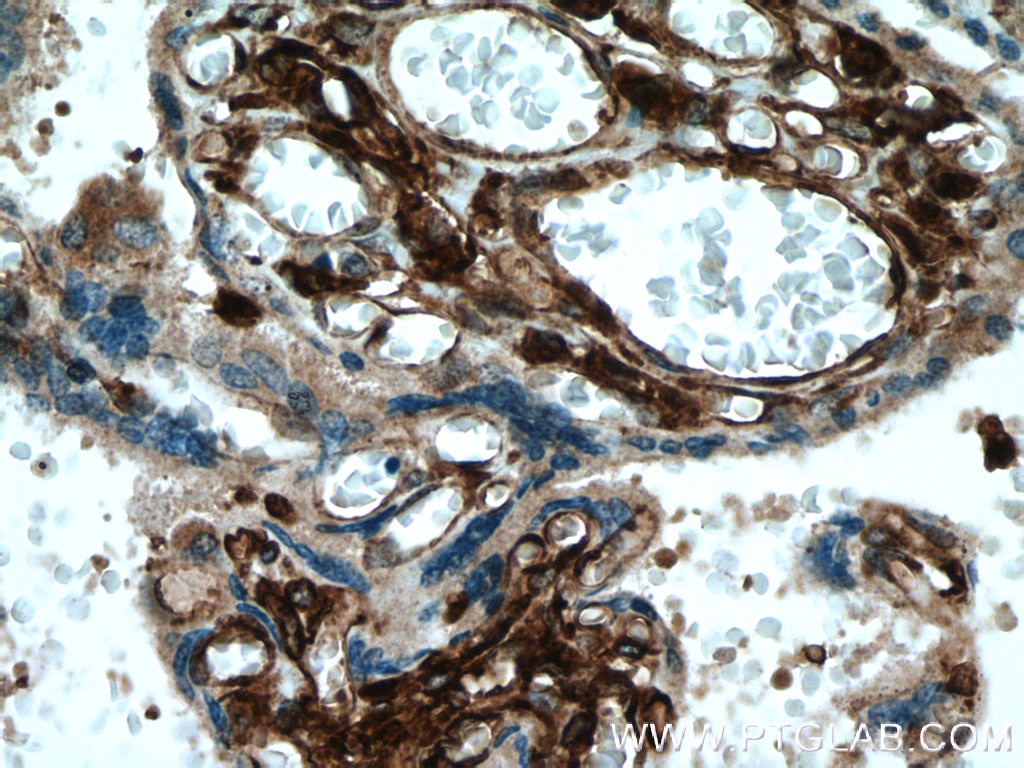
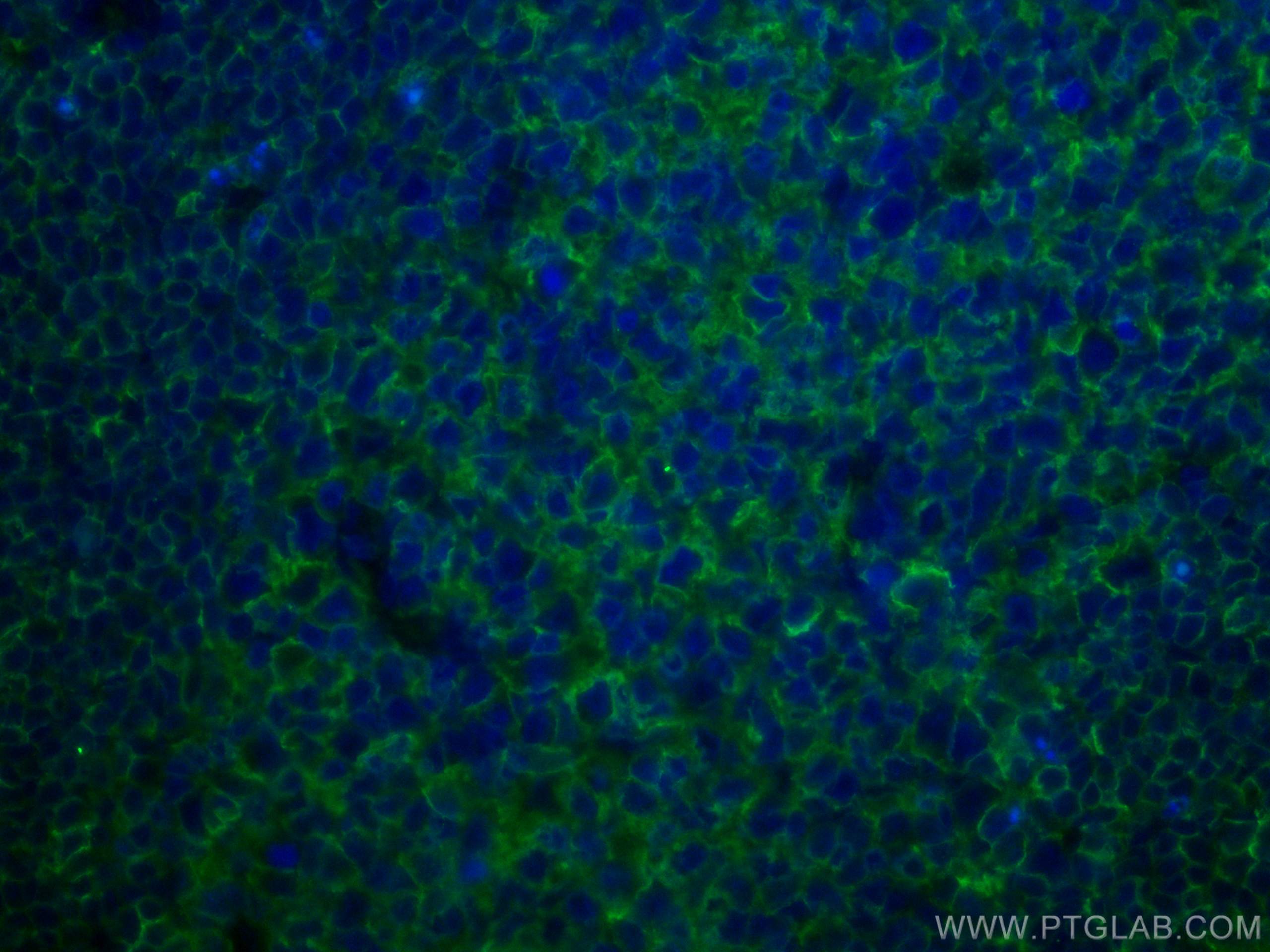
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
66530-1-PBS targets HLA-E in WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | HLA-E fusion protein Ag6724 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | major histocompatibility complex, class I, E |
| Calculated molecular weight | 40 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 40 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC002578 |
| Gene Symbol | HLA-E |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3133 |
| RRID | AB_2881893 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P13747 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Human major histocompatibility complex (MHC) antigens, also referred to as human leukocyte antigens (HLA), are encoded by genes located on the short arm of chromosome 6 (6p21.3). There are two classes of HLA antigens: class I and class II. This class I molecules are membrane glycoproteins composed of a heavy (alpha) chain which is encoded by a HLA class I gene, and β2-microglobulin light (beta) chain. The most extensively characterized members of the HLA class I gene family are the genes encoding the major transplantation antigenes, HLA-A, B and C. HLA-E is a non-classical MHC class I molecule. HLA-E is frequently overexpressed in tumor diseases, transplants and virus-infected cells and represents an immunomodulatory molecule by binding to the receptors CD94/NKG2A, -B and -C on NK and T cells. Due to its immune suppressive features HLA-E expression might represent an important mechanism of tumors to escape immune surveillance.(PMID: 667938; 3375250; 2249951; 27589686)