Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
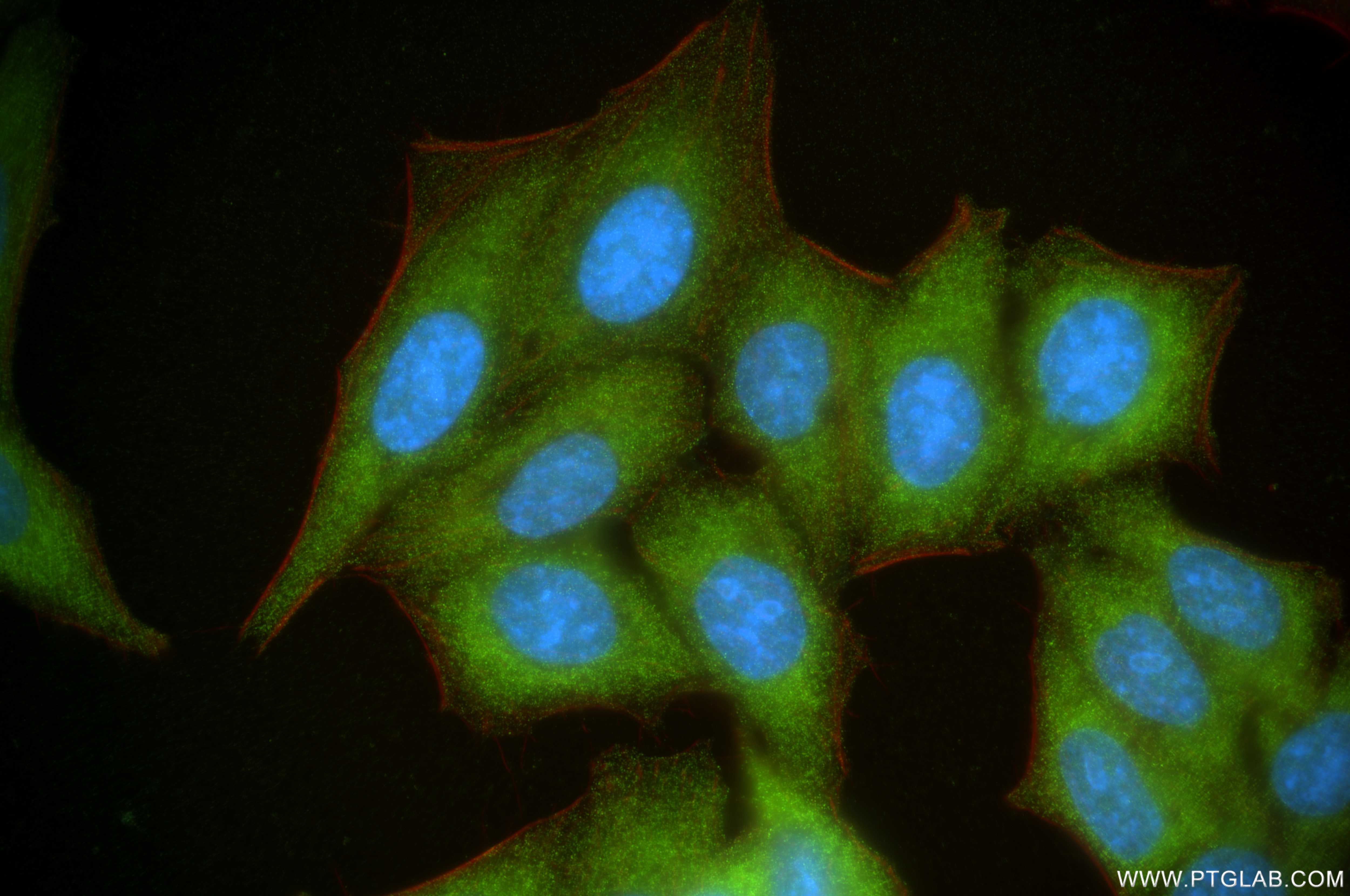
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:125-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
85094-1-RR targets HMMR-Specific in IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Peptide 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor (RHAMM) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 84 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_001142556 |
| Gene Symbol | HMMR |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3161 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purfication |
| UNIPROT ID | O75330 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
Hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor (HMMR), also termed CD168, was first described by Turley in murine cells . It is reported that HMMR has an extensive coiled-coil structure (CC) that contains multiple sites for interactive partners. Initially, HMMR was considered a novel hyaluronan-mediated motility receptor and a microtubule-associated spindle assembly factor. Full-length human RHAMM is an 85 kDa coiled-coil protein that occurs both in intracellular and extracellular compartments. It has highly restricted and tightly regulated expression in most normal tissues, but is one of a number of oncogenic proteins that are exported to the cell surface in response to tissue stress by unconventional transport mechanisms. (PMID: 36750558, PMID: 30249497)
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| IF protocol for HMMR-Specific antibody 85094-1-RR | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |