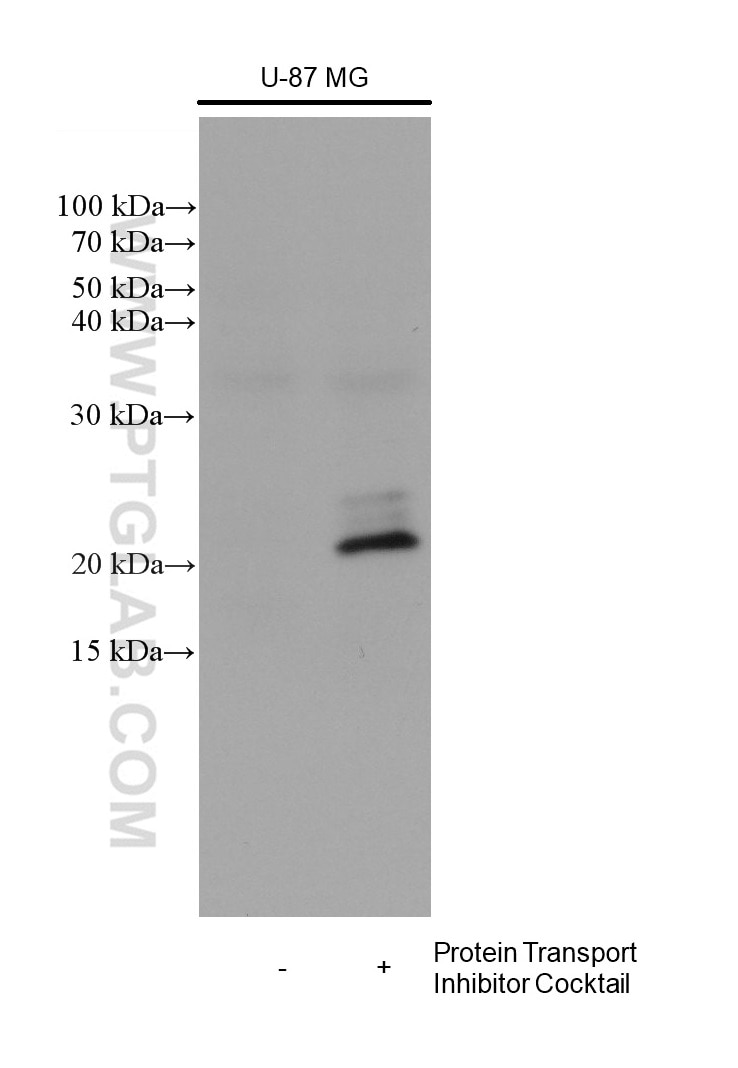
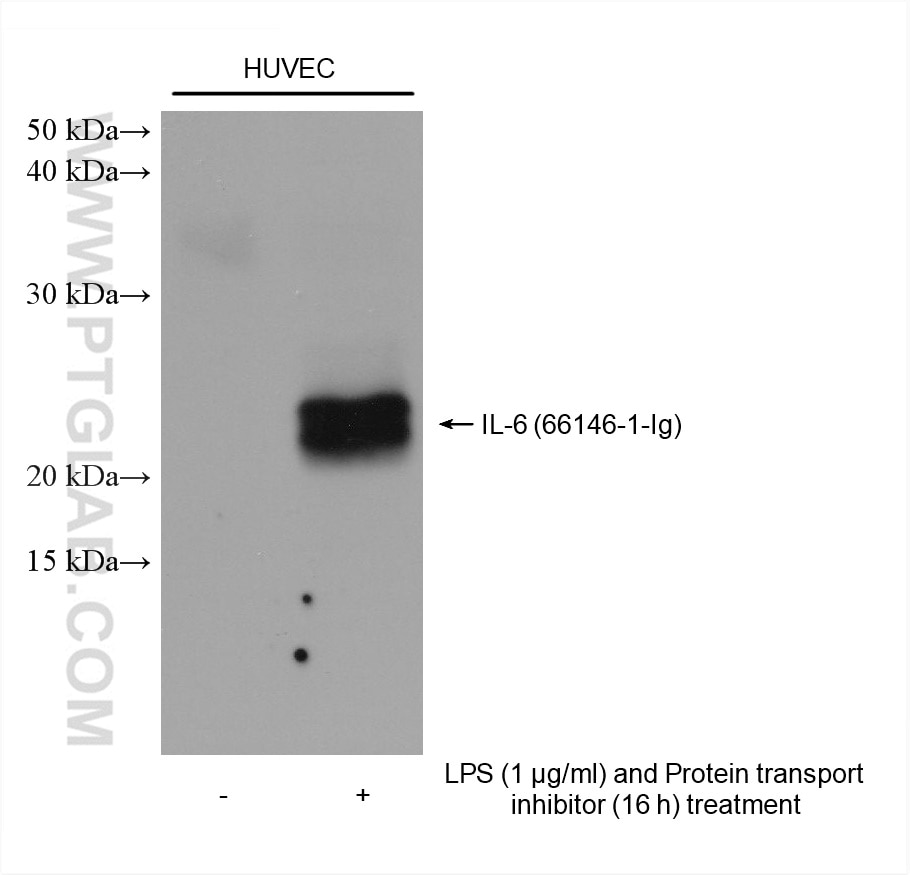
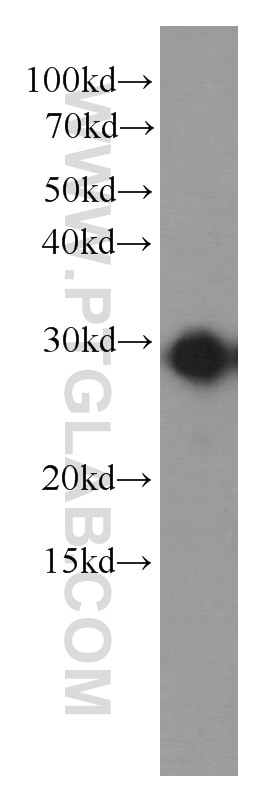
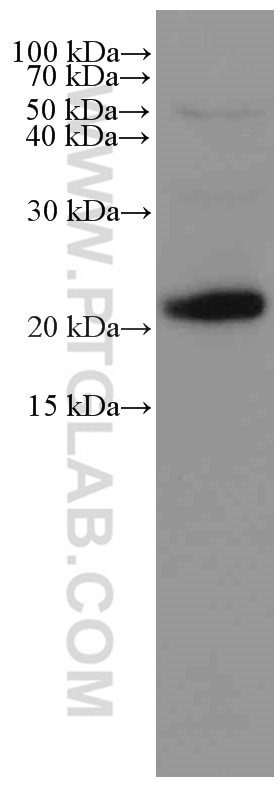
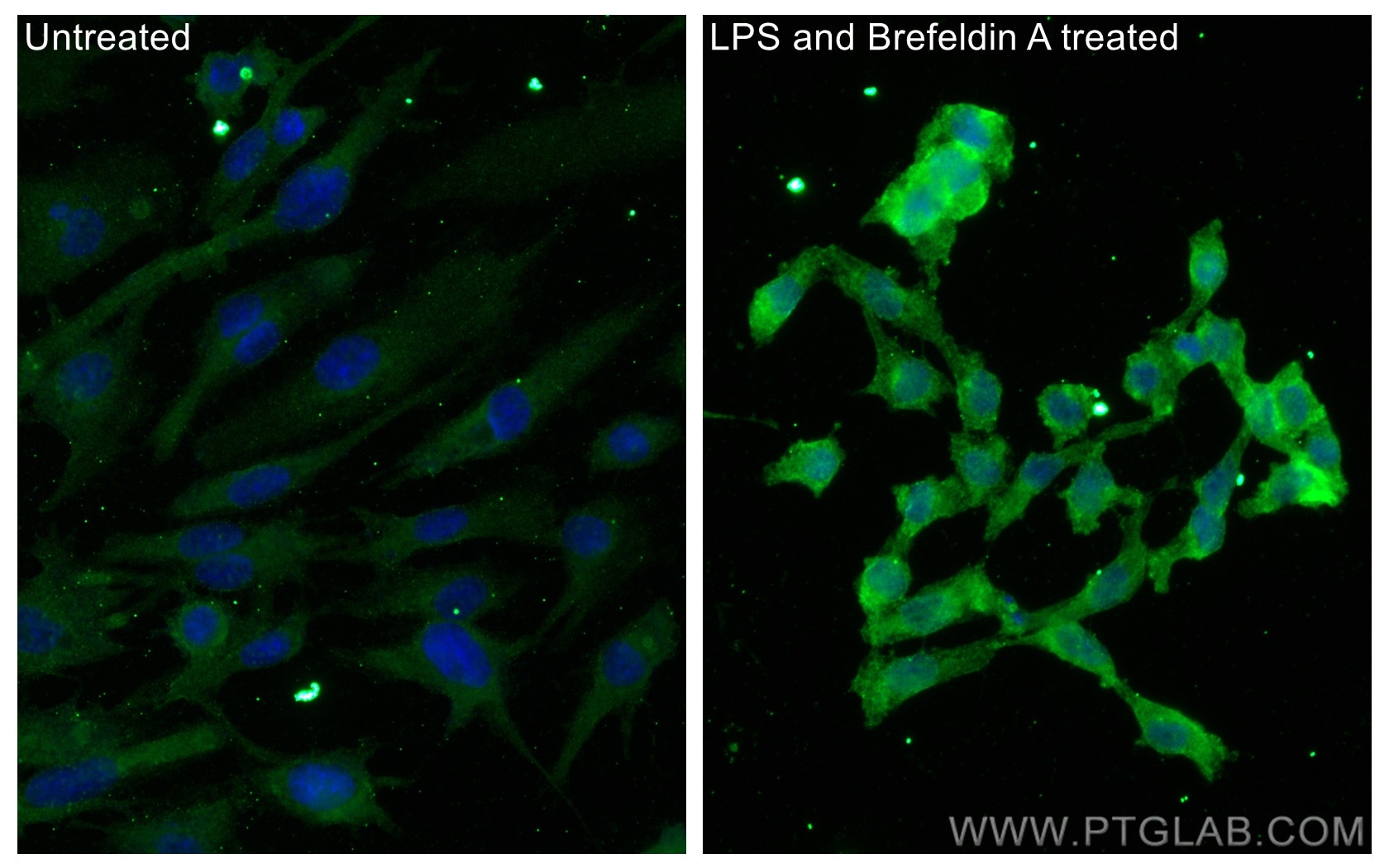
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
66146-1-PBS targets IL-6 in WB, IF/ICC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag10646 Product name: Recombinant human IL-6 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-212 aa of BC015511 Sequence: MNSFSTSAFGPVAFSLGLLLVLPAAFPAPVPPGEDSKDVAAPHRQPLTSSERIDKQIRYILDGISALRKETCNKSNMCESSKEALAENNLNLPKMAEKDGCFQSGFNEETCLVKIITGLLEFEVYLEYLQNRFESSEEQARAVQMSTKVLIQFLQKKAKNLDAITTPDPTTNASLLTKLQAQNQWLQDMTTHLILRSFKEFLQSSLRALRQM 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | interleukin 6 (interferon, beta 2) |
| Calculated molecular weight | 212 aa, 24 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 24 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC015511 |
| Gene Symbol | IL6 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3569 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000136244 |
| RRID | AB_2881543 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P05231 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is an interleukin that acts as both a pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokine. IL-6 protein is secreted by a variety of cell types including T cells and macrophages as phosphorylated and variably glycosylated molecule. IL-6 plays an essential role in the final differentiation of B-cells into Ig-secreting cells involved in lymphocyte and monocyte differentiation. It induces myeloma and plasmacytoma growth and induces nerve cells differentiation Acts on B-cells, T-cells, hepatocytes, hematopoietic progenitor cells and cells of the CNS. IL-6 is also considered a myokine, a cytokine produced from muscle, and is elevated in response to muscle contraction. IL-6 has been shown to interact with interleukin-6 receptor and glycoprotein 130. Additionally, IL-6 is involved in hematopoiesis, bone metabolism, and cancer progression, and has been defined an essential role in directing transition from innate to acquired immunity.