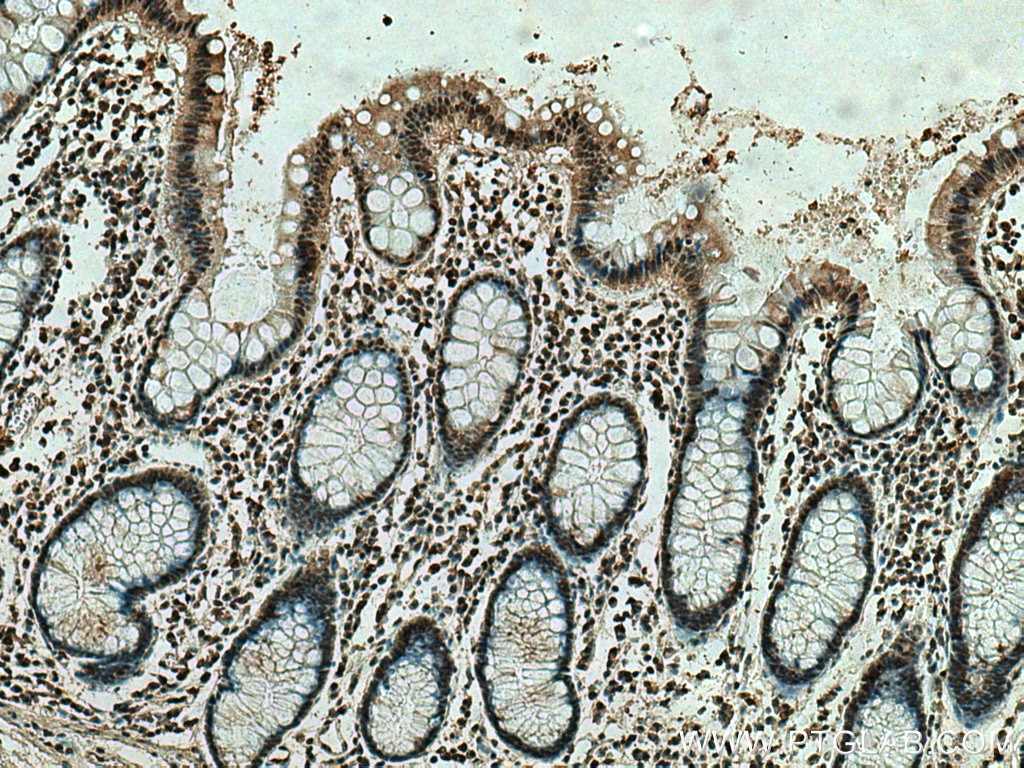
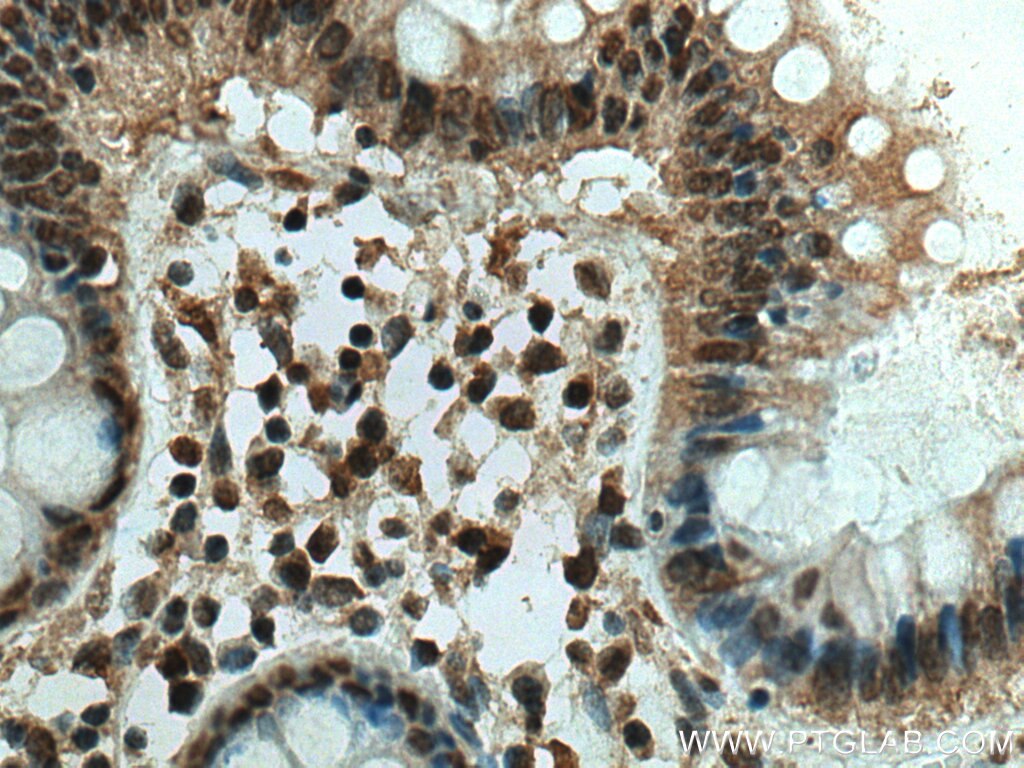
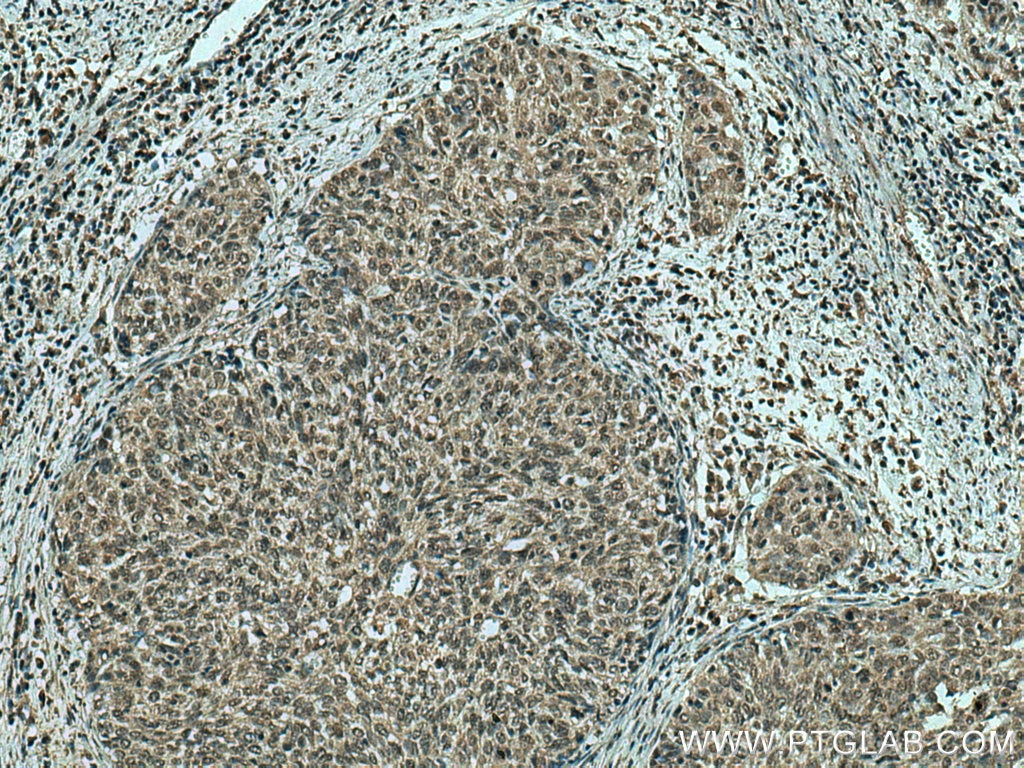
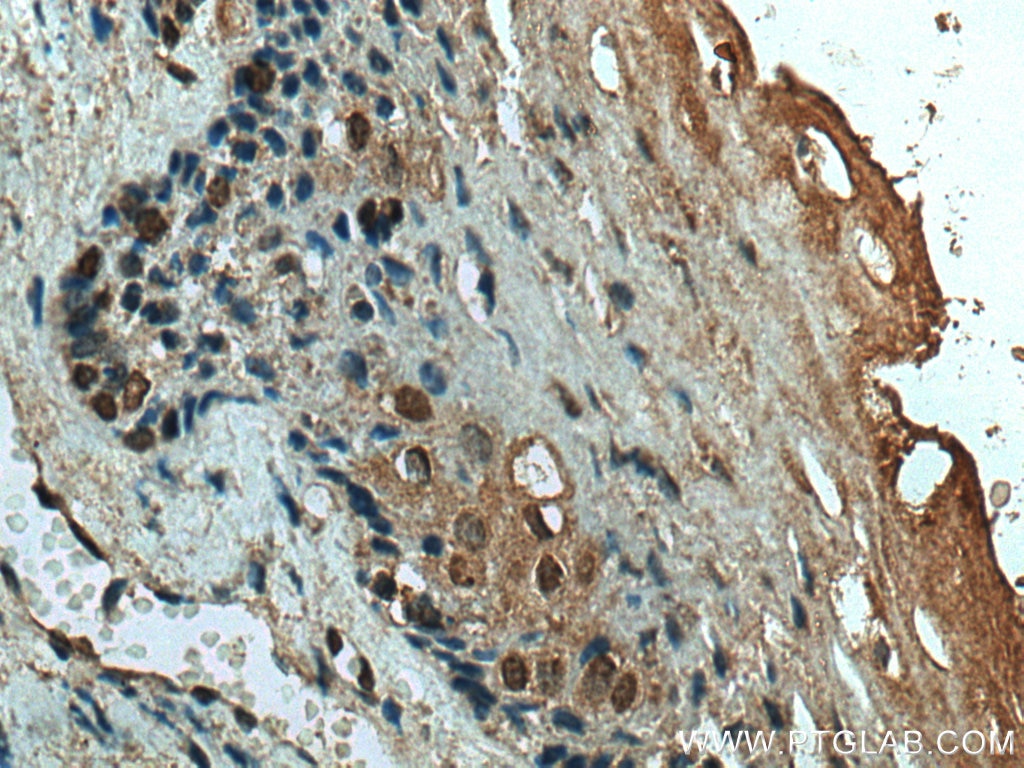
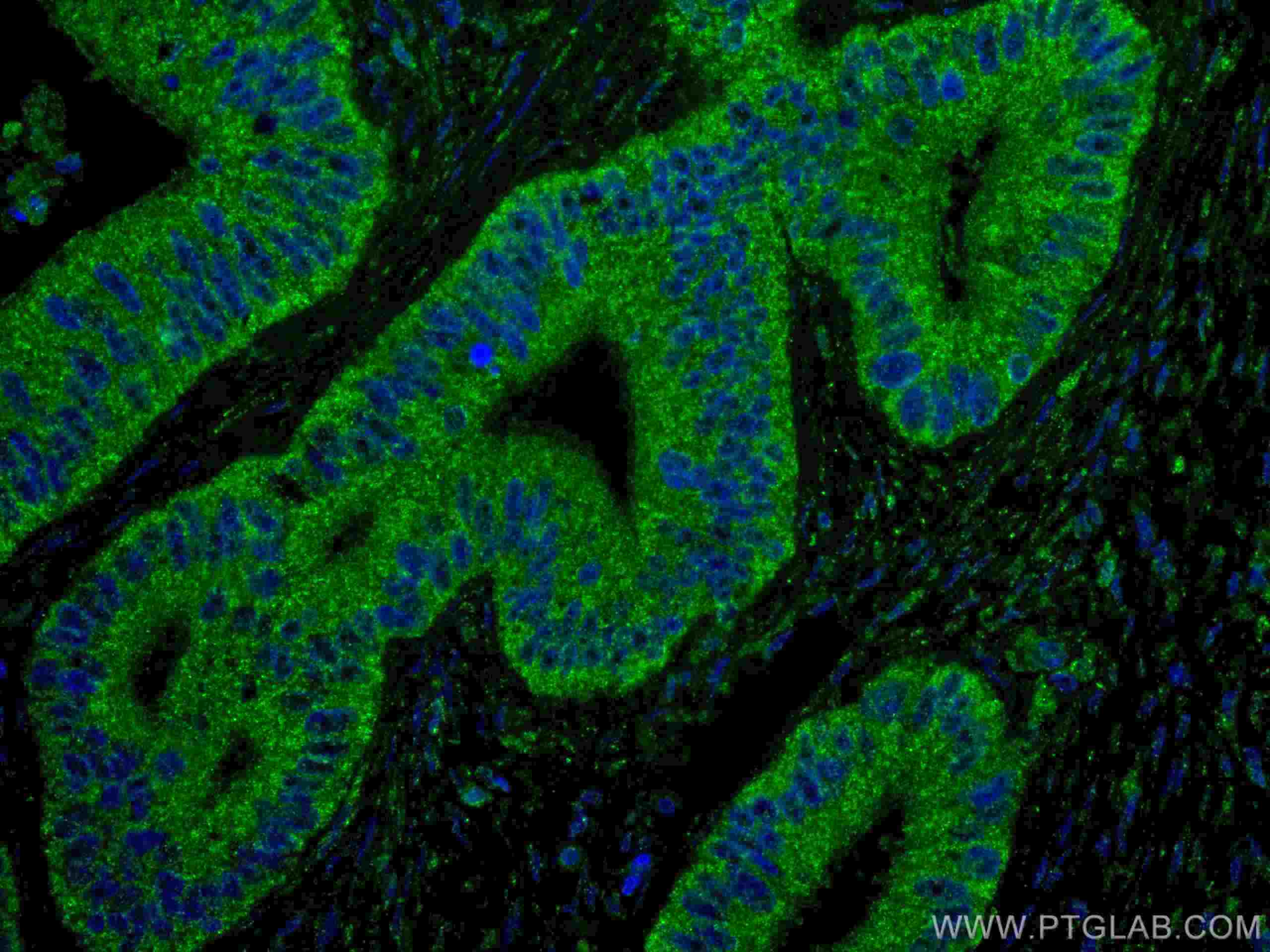
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
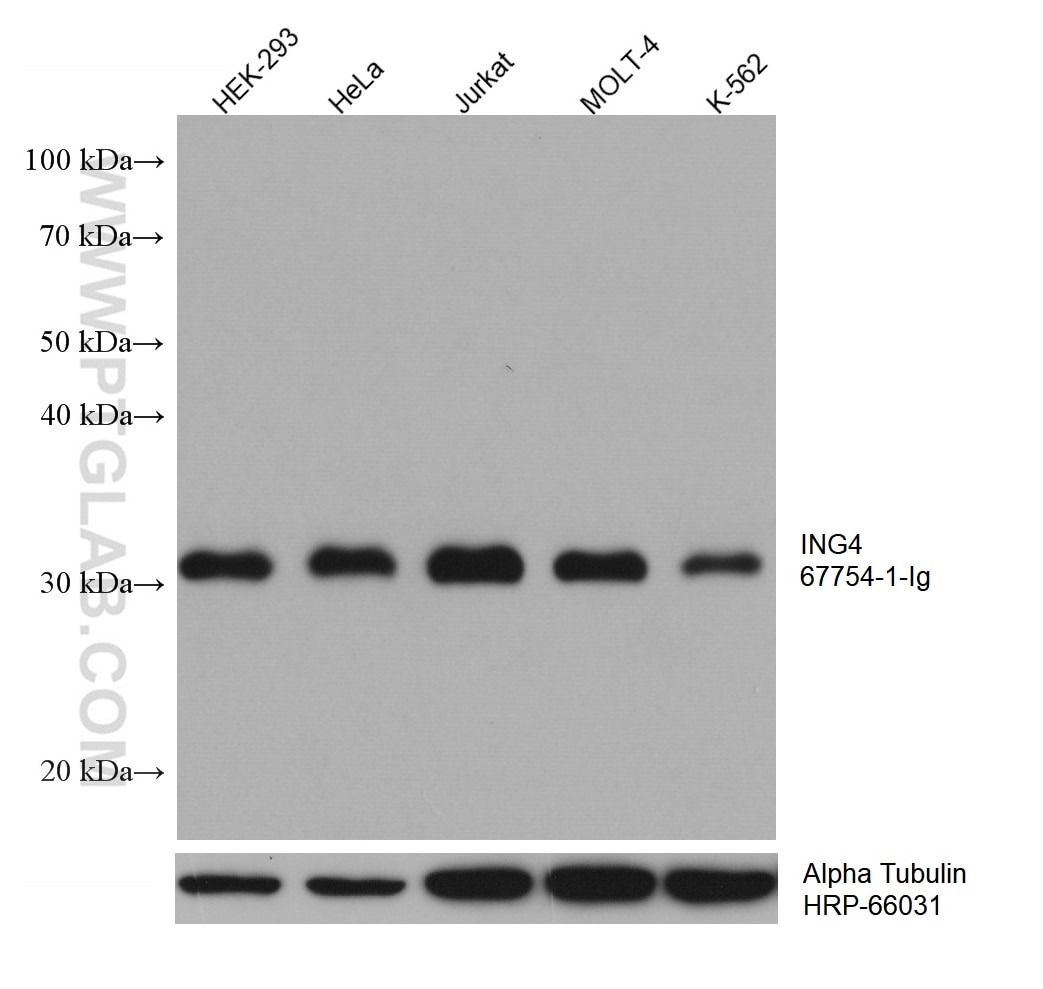
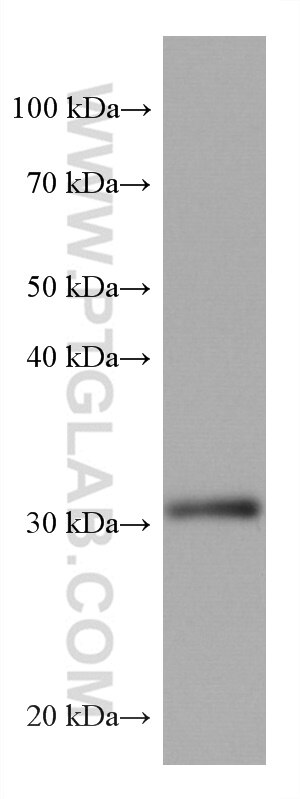
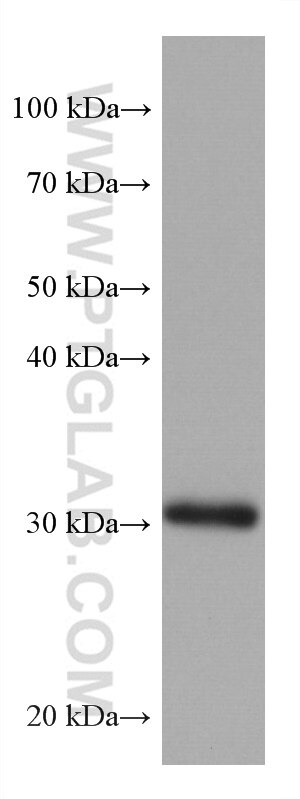
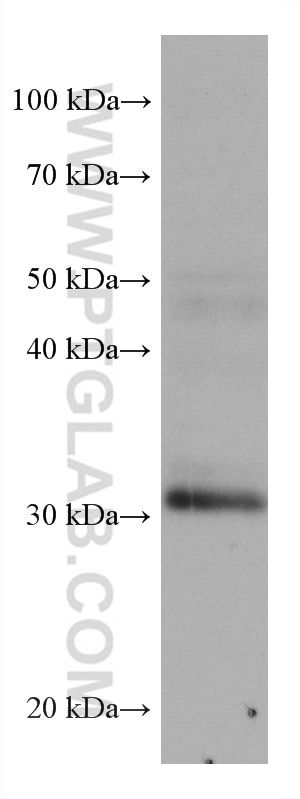
67754-1-PBS targets ING4 in WB, IHC, IF-P, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human, pig, rabbit, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human, pig, rabbit, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag4610 Product name: Recombinant human ING4 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PET28a Tag: 6*His Domain: 1-249 aa of BC007781 Sequence: MAAGMYLEHYLDSIENLPFELQRNFQLMRDLDQRTEDLKAEIDKLATEYMSSARSLSSEEKLALLKQIQEAYGKCKEFGDDKVQLAMQTYEMVDKHIRRLDTDLARFEADLKEKQIESSDYDSSSSKGKKKGRTQKEKKAARARSKGKNSDEEAPKTAQKKLKLVRTSPEYGMPSVTFGSVHPSDVLDMPVDPNEPTYCLCHQVSYGEMIGCDNPDCSIEWFHFACVGLTTKPRGKWFCPRCSQERKKK 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | inhibitor of growth family, member 4 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 29 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 29 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC007781 |
| Gene Symbol | ING4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 51147 |
| RRID | AB_2918522 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9UNL4 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
ING4, also named as p29ING4, belongs to the ING family. It is a component of the HBO1 complex which has a histone H4-specific acetyltransferase activity, a reduced activity toward histone H3 and is responsible for the bulk of histone H4 acetylation in vivo. It may inhibit tumor progression by modulating the transcriptional output of signaling pathways which regulate cell proliferation. ING4 can suppress brain tumor angiogenesis through transcriptional repression of RELA/NFKB3 target genes when complexed with RELA. It may also specifically suppress loss of contact inhibition elicited by activated oncogenes such as MYC. Represses hypoxia inducible factor's (HIF) activity by interacting with HIF prolyl hydroxylase 2 (EGLN1). ING4 is a tumor suppressor gene that interacts with NFkB and represses its transcriptional activity. Several lines of evidence suggest that the tumor suppressor gene ING4, NFkB and its target genes matrix metalloproteases MMP-2, MMP-9 and u-PA are critically involved in tumor invasion.