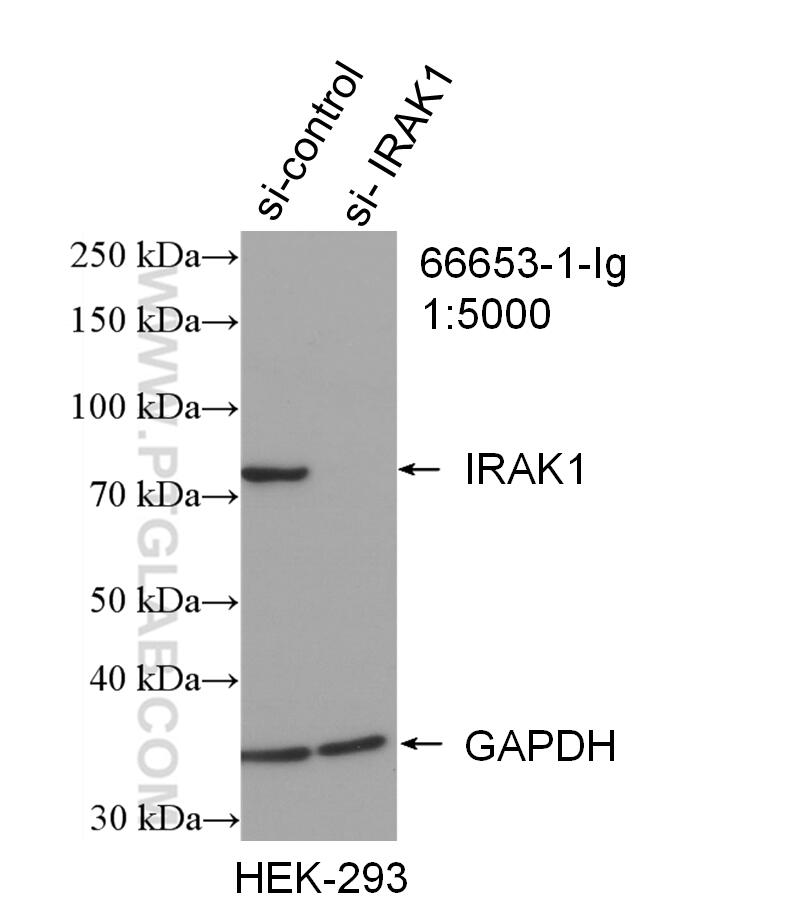
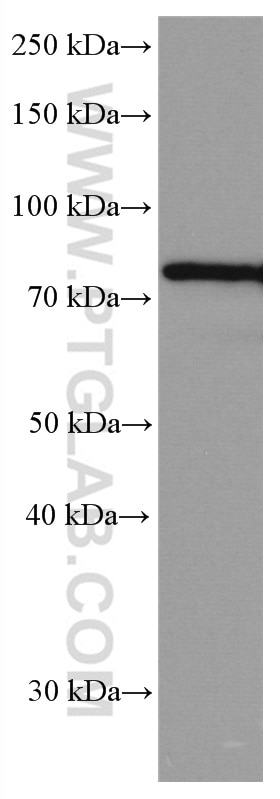
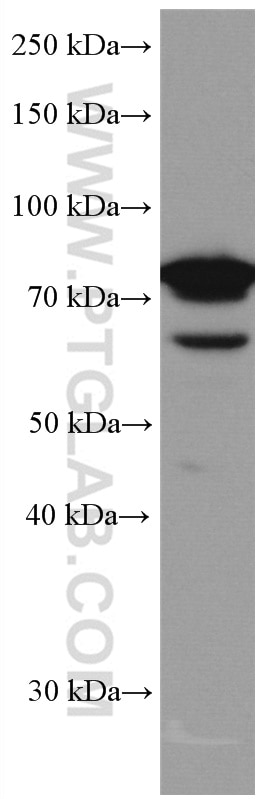
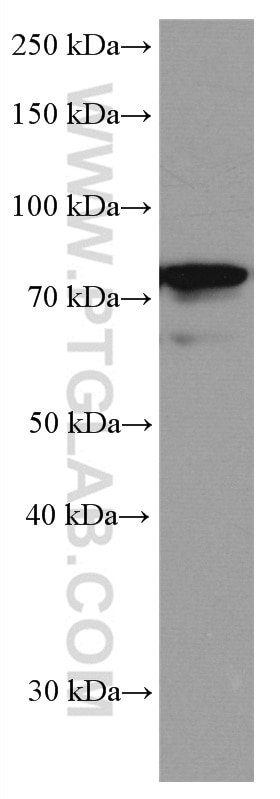
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
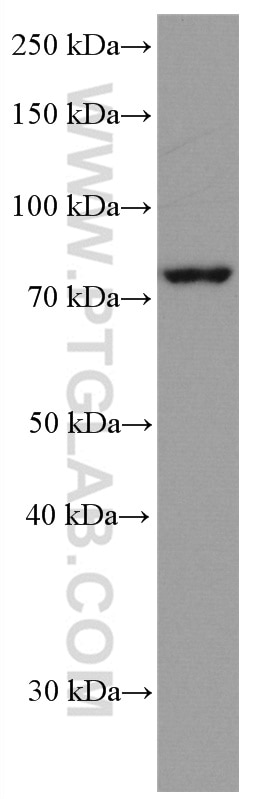
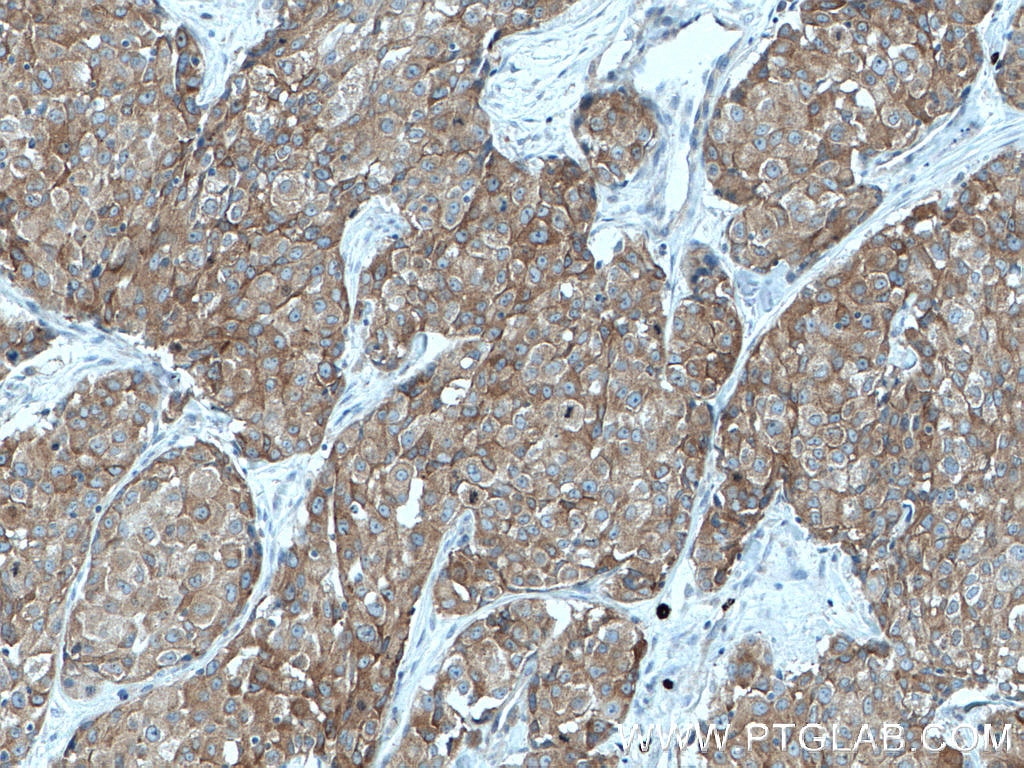
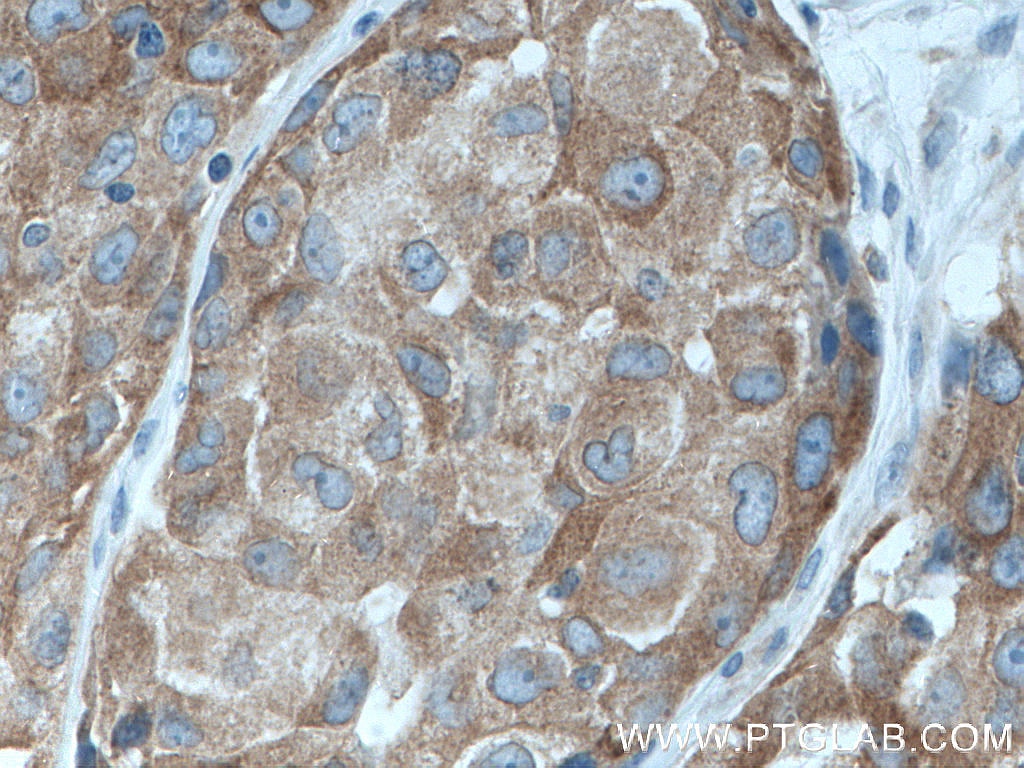
66653-1-PBS targets IRAK1 in WB, IHC, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | IRAK1 fusion protein Ag0728 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinase 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 77 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 80 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC014963 |
| Gene Symbol | IRAK1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 3654 |
| RRID | AB_2882010 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P51617 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Interleukin-1 receptor-associated kinases (IRAKs) are a unique family of death domain containing protein kinases that play a key role in initiating innate immune response against foreign pathogens. They are involved in Toll-like receptor (TLR) and interleukin-1 receptor (IL-1R) signaling pathways. IRAK1 is the first member of this kinase family. Upon ligand binding to TLR/IL-1R, IRAK1 is recruited by MYD88 to the receptor-signaling complex, the association leads to IRAK1 phosphorylation by IRAK4 and subsequent autophosphorylation and kinase activation. Hyper-phosphorylated IRAK1 then disengages from the receptor complex, and forms a cytosolic IRAK1-TRAF6 complex. TRAF6 then interacts with TAK and TAB, resulting in eventual activation of the NF-κB and MAPK pathways. Phosphorylated IRAK1 also undergoes ubiquitin-mediated degradation or sumoylation, which results in nuclear translocation and transcriptional activation of inflammatory target genes. (PMID: 17890055; 12620219)