Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
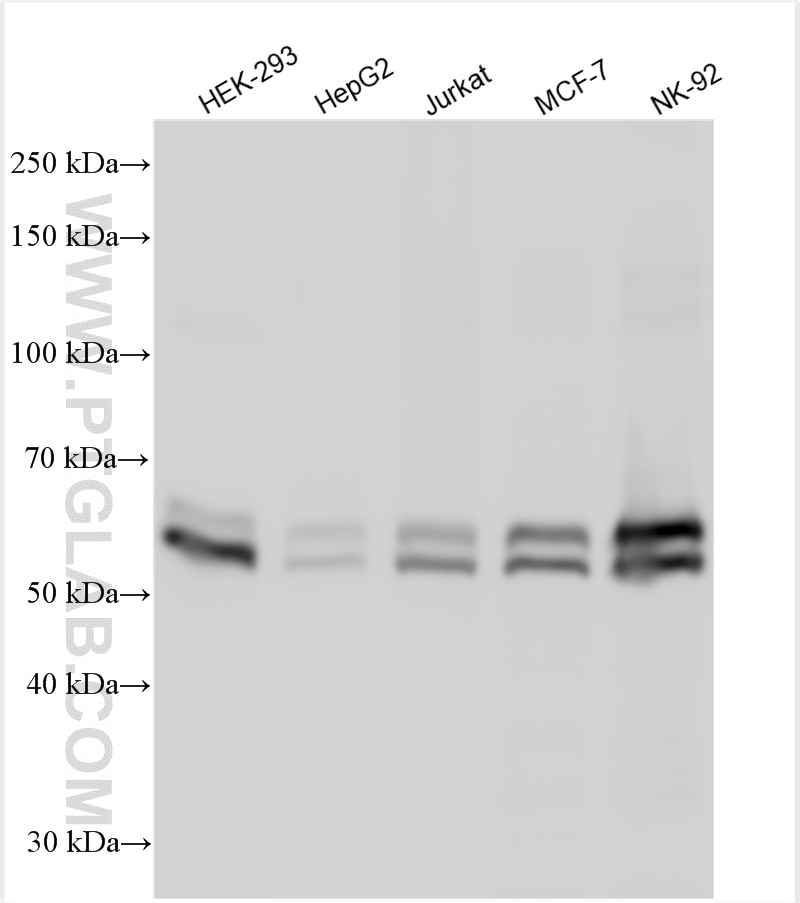
30041-1-PBS targets KEAP1 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen |
CatNo: Ag32512 Product name: Recombinant human KEAP1 protein Source: e coli.-derived, PGEX-4T Tag: GST Domain: 480-624 aa of BC002930 Sequence: GTNRLNSAECYYPERNEWRMITAMNTIRSGAGVCVLHNCIYAAGGYDGQDQLNSVERYDVETETWTFVAPMKHRRSALGITVHQGRIYVLGGYDGHTFLDSVECYDPDTDTWSEVTRMTSGRSGVGVAVTMEPCRKQIDQQNCTC 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 624 aa, 70 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 55-70 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC002930 |
| Gene Symbol | KEAP1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9817 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q14145 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
KEAP1, also named as INRF2, KIAA0132 and KLHL19, is part of a multiprotein complex that contains the CUL3-ROC1 ubiquitin ligase, which can ubiquitinate the N-terminal domain of NRF2[PMID: 20173742]. Two molecules of KEAP1 bind to two distinct sites in the N-terminal region of NRF2, the ETGE and DLG sites, which affect the KEAP1-NRF2 interaction and/or its physiological consequences[PMID: 22215675]. KEAP1 retains NFE2L2/NRF2 in the cytosol. It functions as substrate adapter protein for the E3 ubiquitin ligase complex formed by CUL3 and RBX1[PMID: 20427290]. It also retains BPTF in the cytosol. This antibody is a rabbit polyclonal antibody raised against residues near the C terminus of human KEAP1.