Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
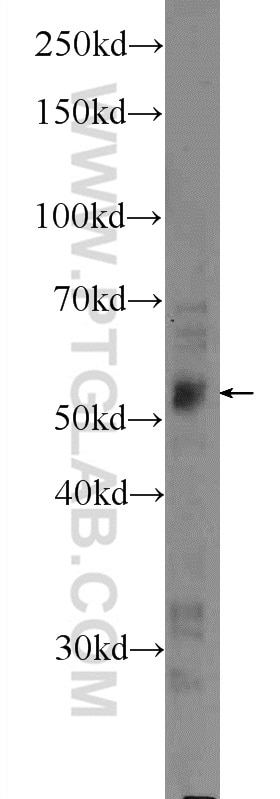
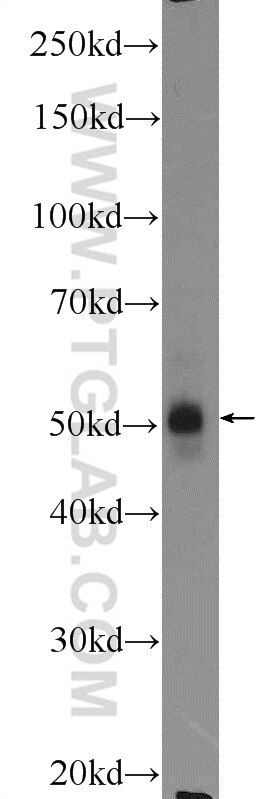
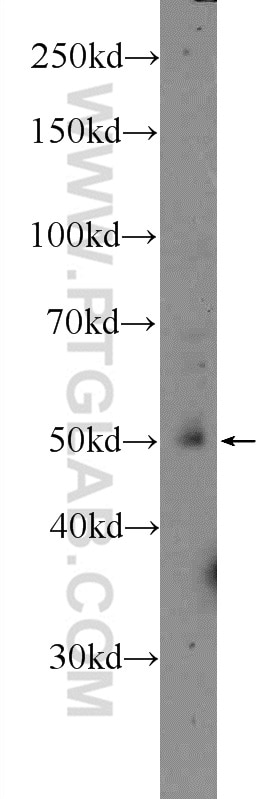
| Positive WB detected in | MCF-7 cells, HeLa cells, mouse skeletal muscle tissue |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:200-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 2 publications below |
Product Information
16899-1-AP targets LPL in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | LPL fusion protein Ag10431 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | lipoprotein lipase |
| Calculated molecular weight | 475 aa, 53 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 53 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC011353 |
| Gene Symbol | LPL |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4023 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P06858 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
LPL(lipoprotein lipase) is also named as LIPD and belongs to the AB hydrolase superfamily. LPL catalyses the hydrolysis of the triacylglycerol component of circulating chylomicrons and very low density lipoproteins. It plays a role in the binding of lipoprotein particles to cell-surface molecules, including sulfated glycosaminoglycans (GAGs)(PMID:21177248). The gene encodes a protein of 475 amino acids that becomes a mature protein of 448 residues after cleavage of a signal peptide. This protein is highly glycosylated and functions as a head-to-tail dimer under well-defined conditions(PMID:11154699).
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Diabetes Rab8a Deficiency in Skeletal Muscle Causes Hyperlipidemia and Hepatosteatosis Via Impairment of Muscle Lipid Uptake and Storage. | ||
Diabetes Tissue-specific splicing and dietary interaction of a mutant As160 allele determine muscle metabolic fitness in rodents. | ||
Biology (Basel) Curcumin-Rich Diet Mitigates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) by Attenuating Fat Accumulation and Improving Insulin Sensitivity in Aged Female Mice under Nutritional Stress |