Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
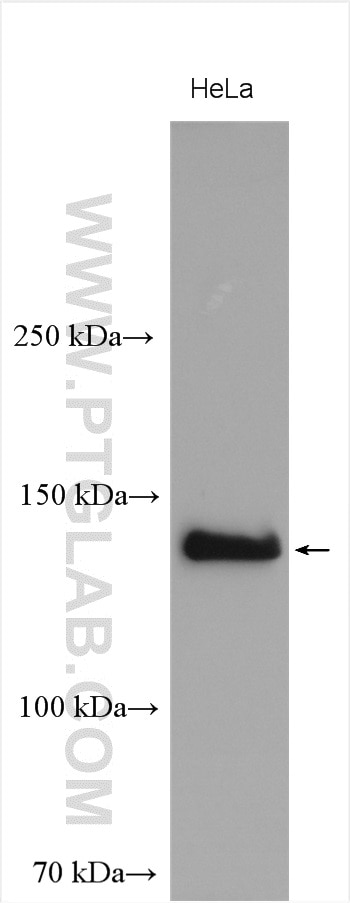
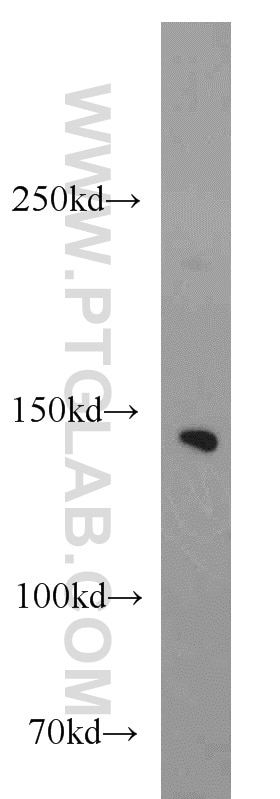
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, COS-7 cells |
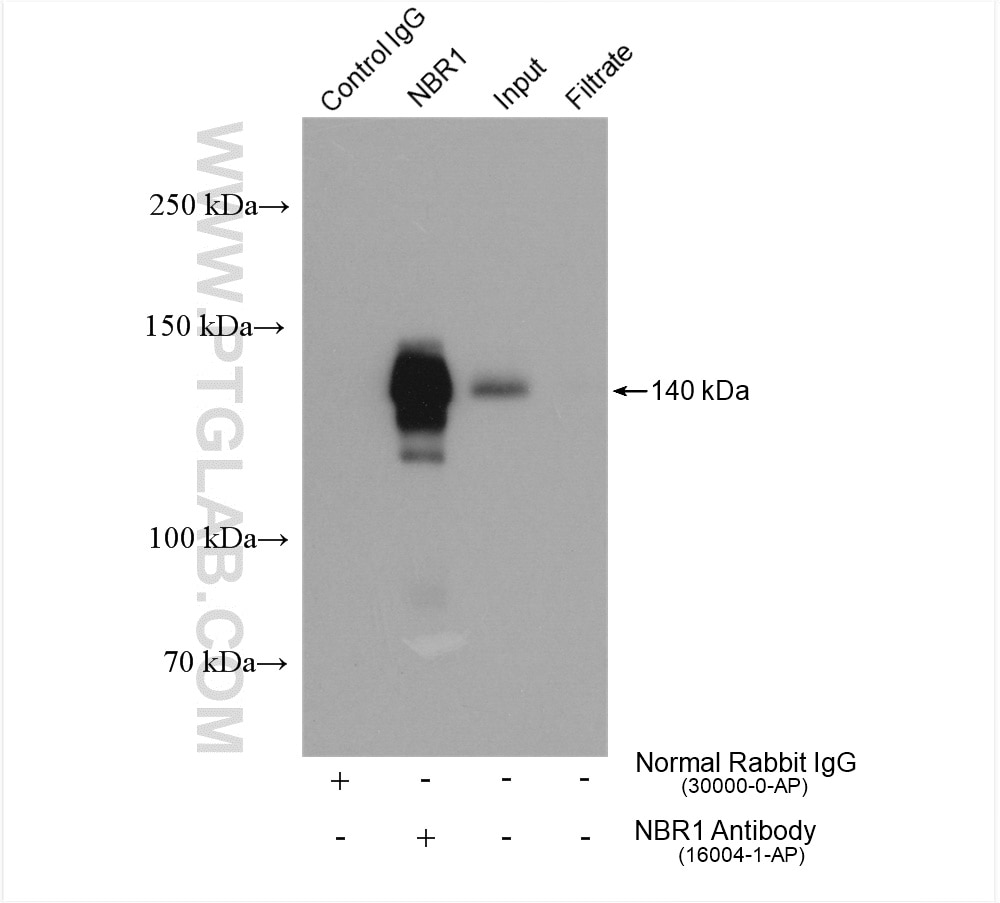
| Positive IP detected in | HeLa cells |
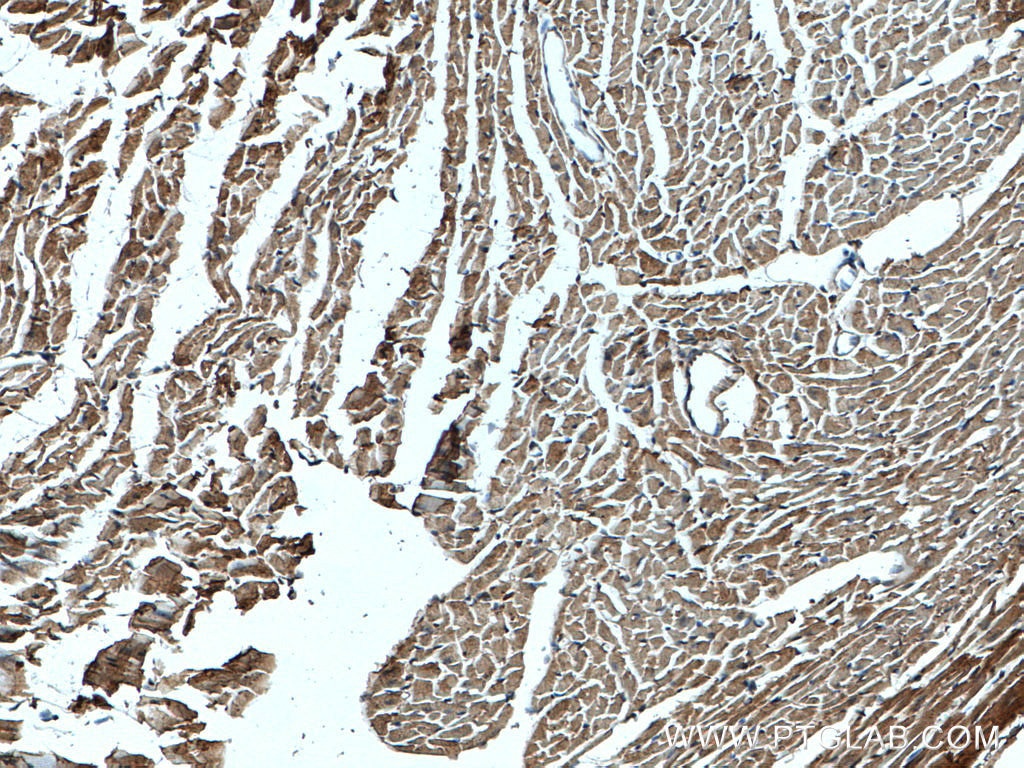
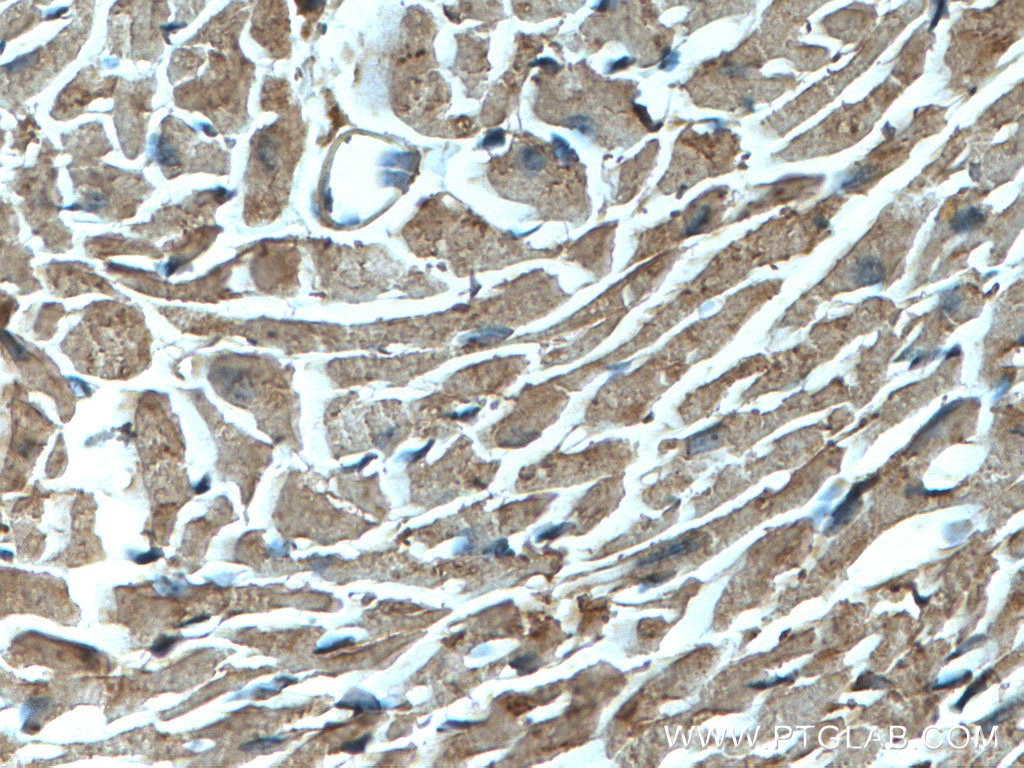
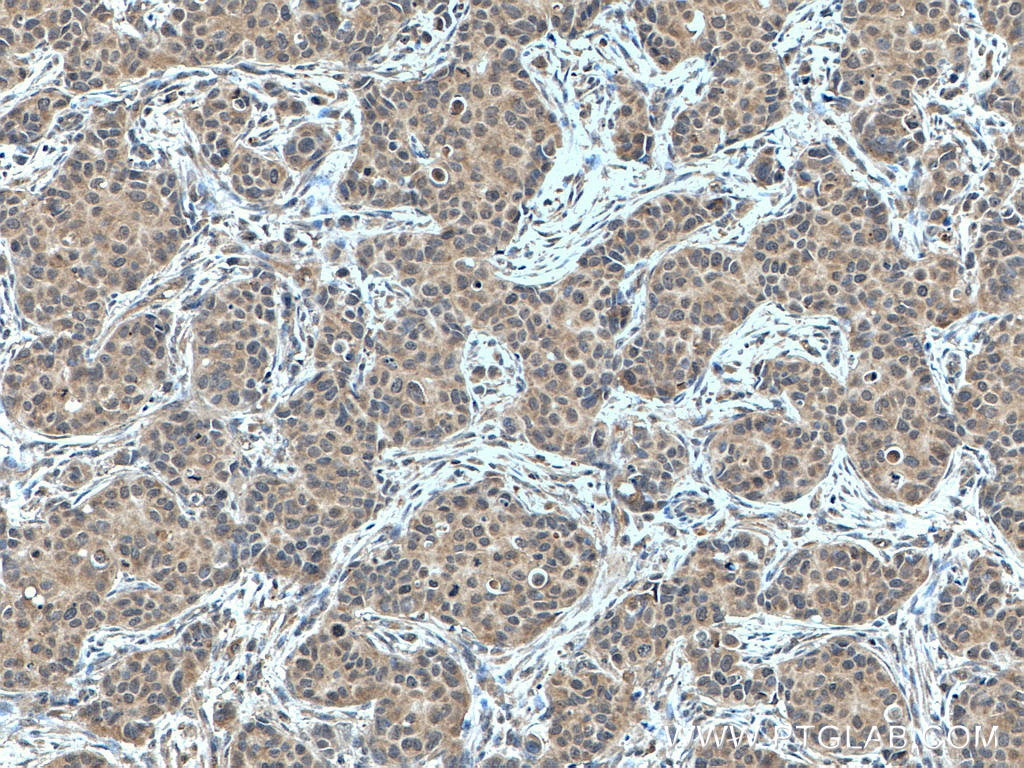
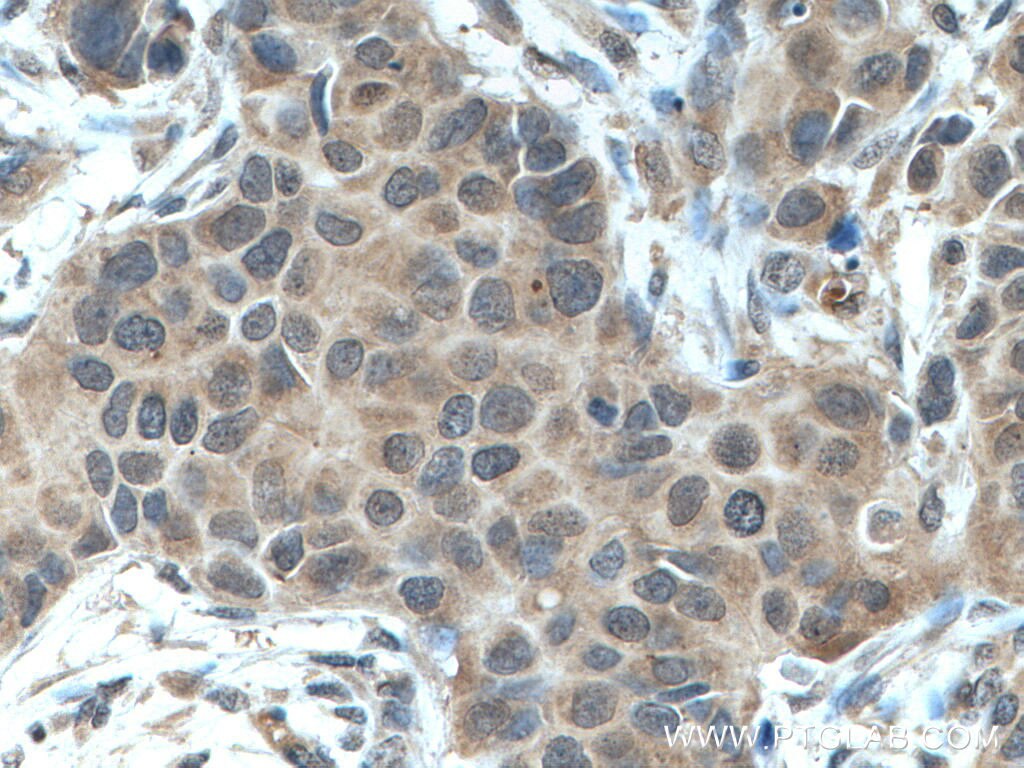
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse heart tissue, human breast cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
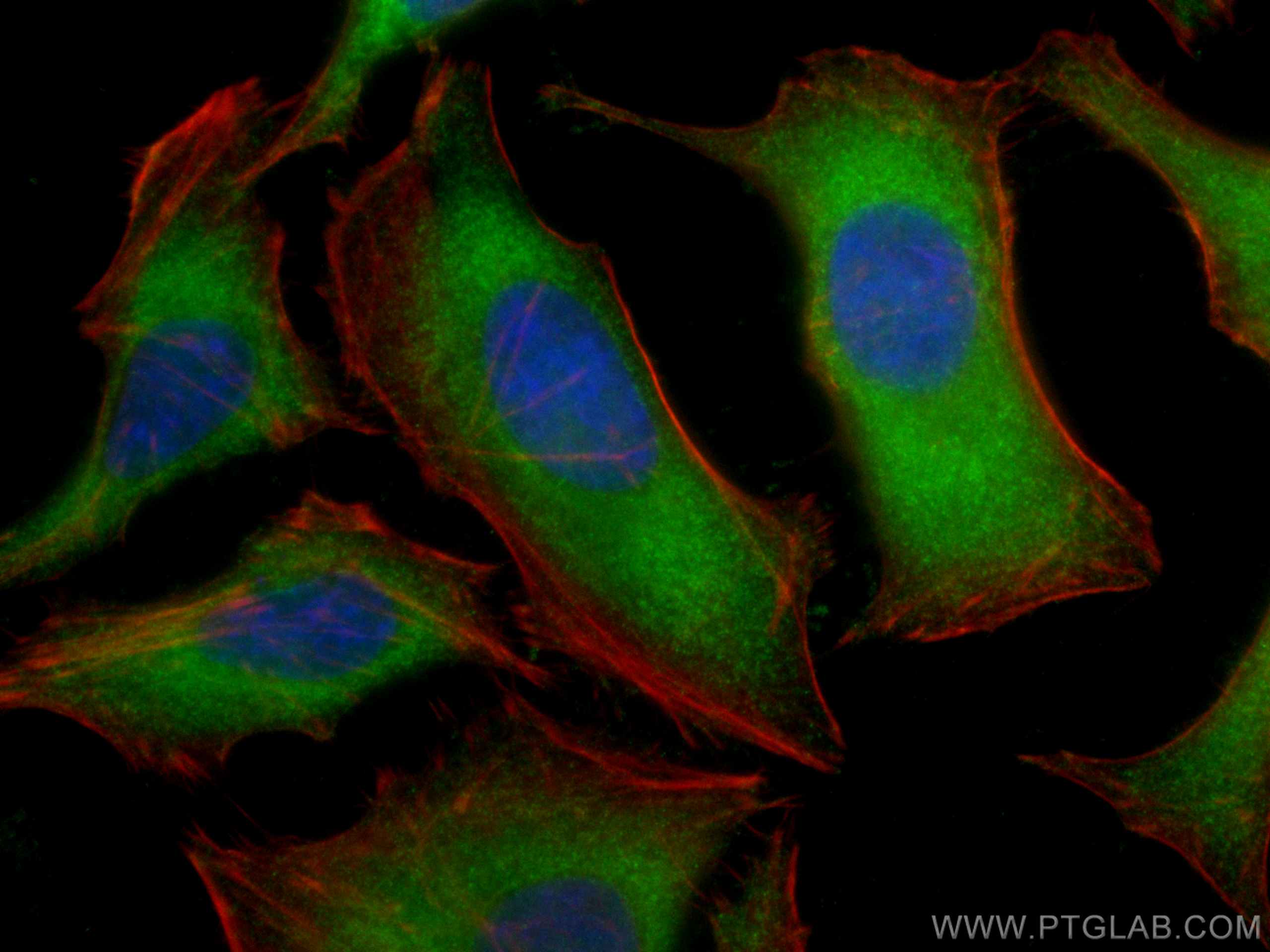
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 6 publications below |
| WB | See 38 publications below |
| IHC | See 10 publications below |
| IF | See 16 publications below |
| IP | See 5 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
16004-1-AP targets NBR1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat, monkey samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, monkey |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, canine |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | NBR1 fusion protein Ag8652 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | neighbor of BRCA1 gene 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 966 aa, 107 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 140 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC009808 |
| Gene Symbol | NBR1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4077 |
| RRID | AB_2251178 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q14596 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
NBR1, also named as 1A13B, KIAA0049 and M17S2, acts probably as a receptor for selective autophagosomal degradation of ubiquitinated targets. NBR1 and P62 can bind to autophagic effector proteins (Atg8 in yeast, MAP1LC3 protein family in mammals) anchored in the membrane of autophagosomes. It is a highly conserved multidomain scaffold protein with proposed roles in endocytic trafficking and selective autophagy. NBR1 is a novel PB1 adapter in Th2 differentiation and asthma. It functions as an autophagy receptor involved in targeting ubiquitinated proteins for degradation. It also has a dual role as a scaffold protein to regulate growth-factor receptor and downstream signaling pathways. Observed MW of NBR1 is 140 kDa (PMID: 22654911, PMID: 22484440).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for NBR1 antibody 16004-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for NBR1 antibody 16004-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for NBR1 antibody 16004-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for NBR1 antibody 16004-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Lack of Neuronal IFN-β-IFNAR Causes Lewy Body- and Parkinson's Disease-like Dementia. | ||
Autophagy TOLLIP-mediated autophagic degradation pathway links the VCP-TMEM63A-DERL1 signaling axis to triple-negative breast cancer progression | ||
Autophagy Stress granule homeostasis is modulated by TRIM21-mediated ubiquitination of G3BP1 and autophagy-dependent elimination of stress granules
| ||
Autophagy Identification of a lung cancer cell line deficient in atg7-dependent autophagy. | ||
Autophagy Export-deficient monoubiquitinated PEX5 triggers peroxisome removal in SV40 large T antigen-transformed mouse embryonic fibroblasts. |