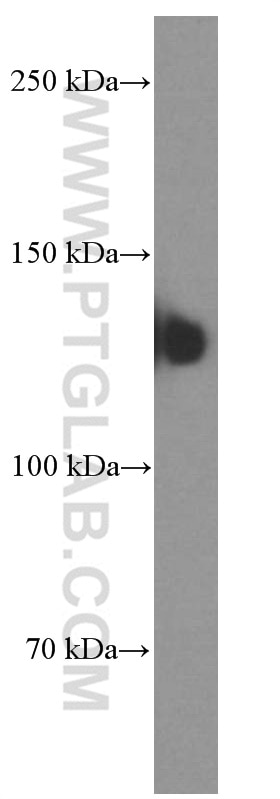
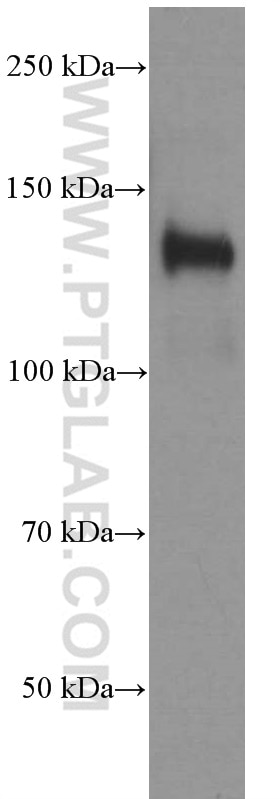
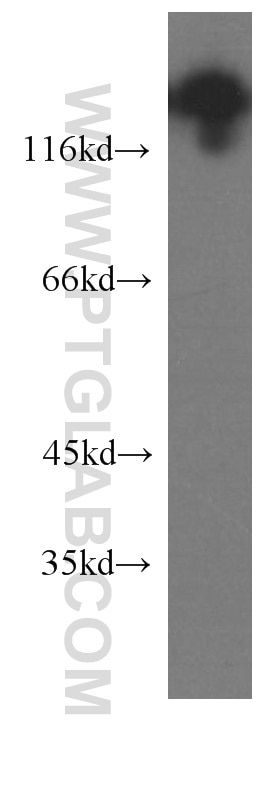
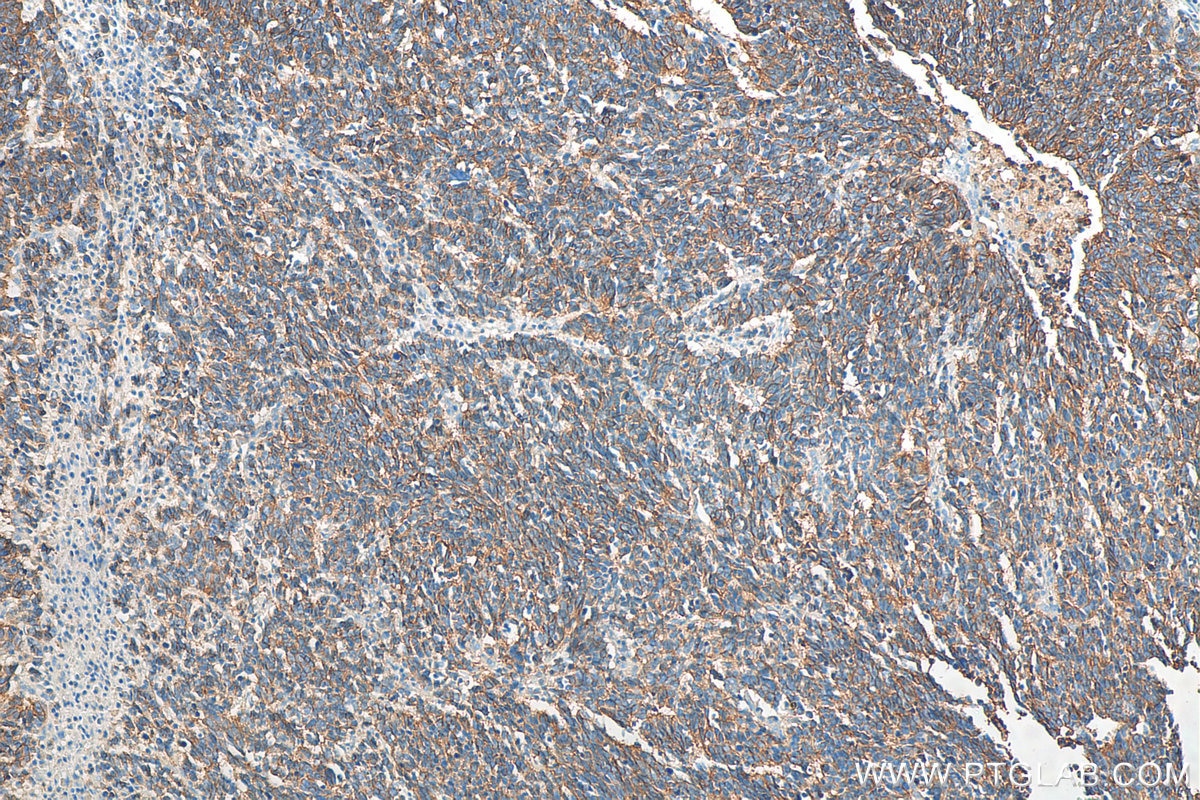
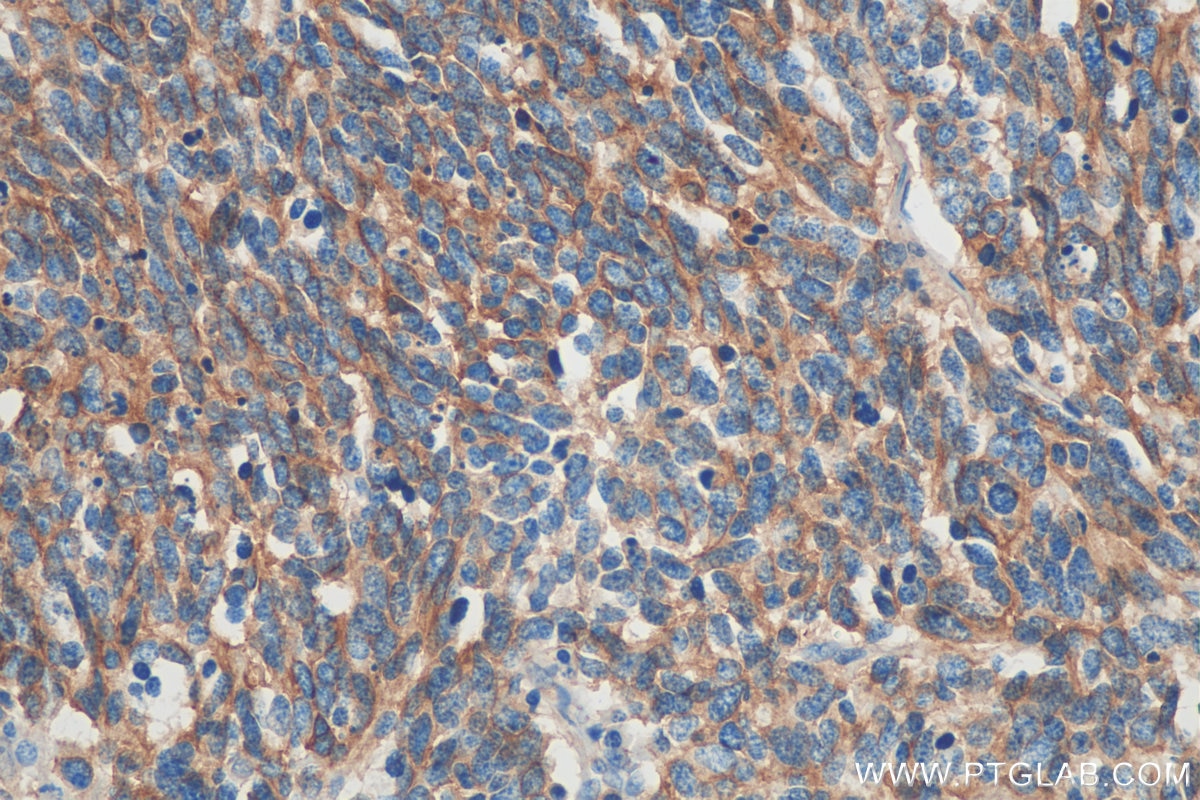
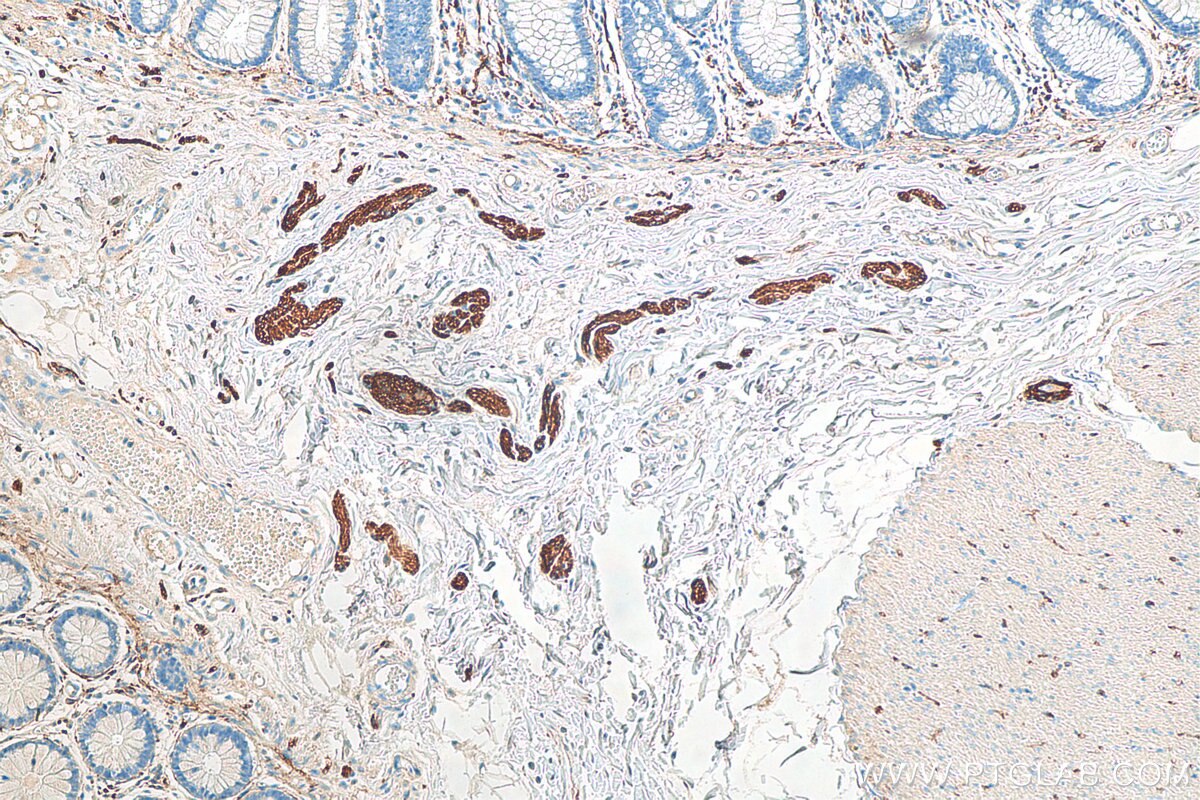
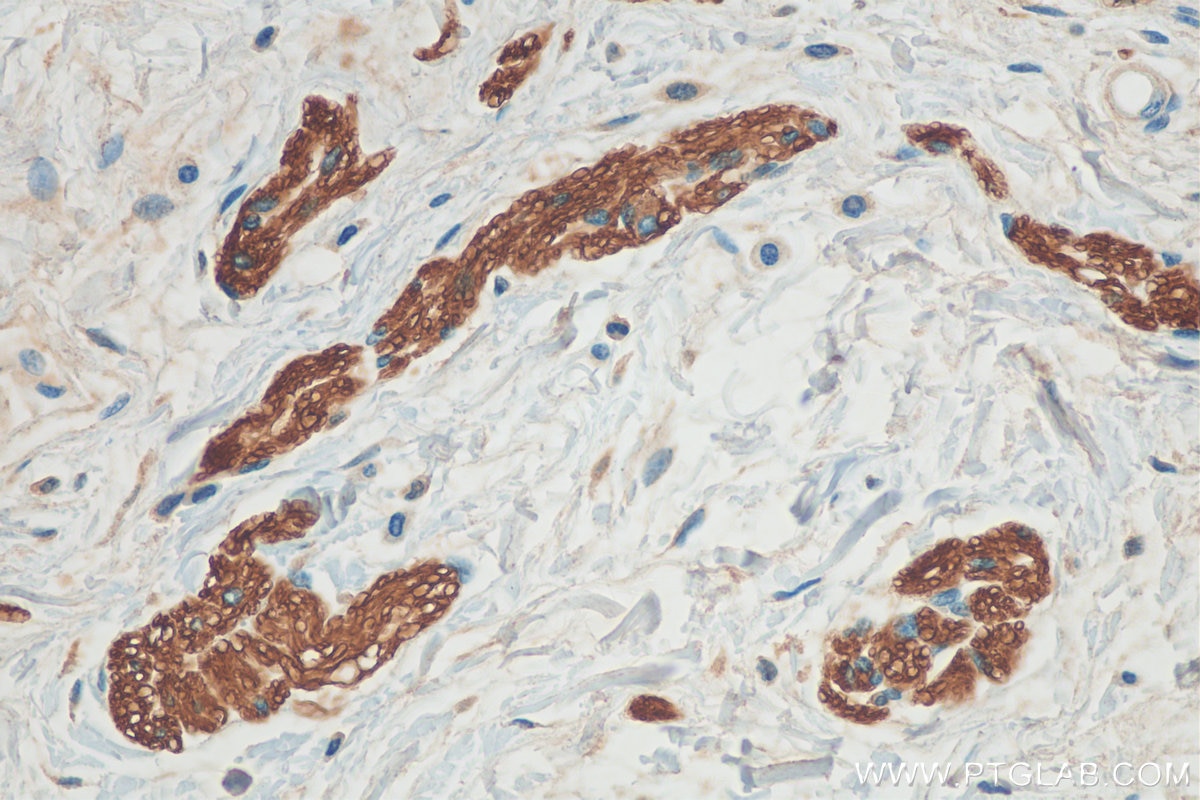
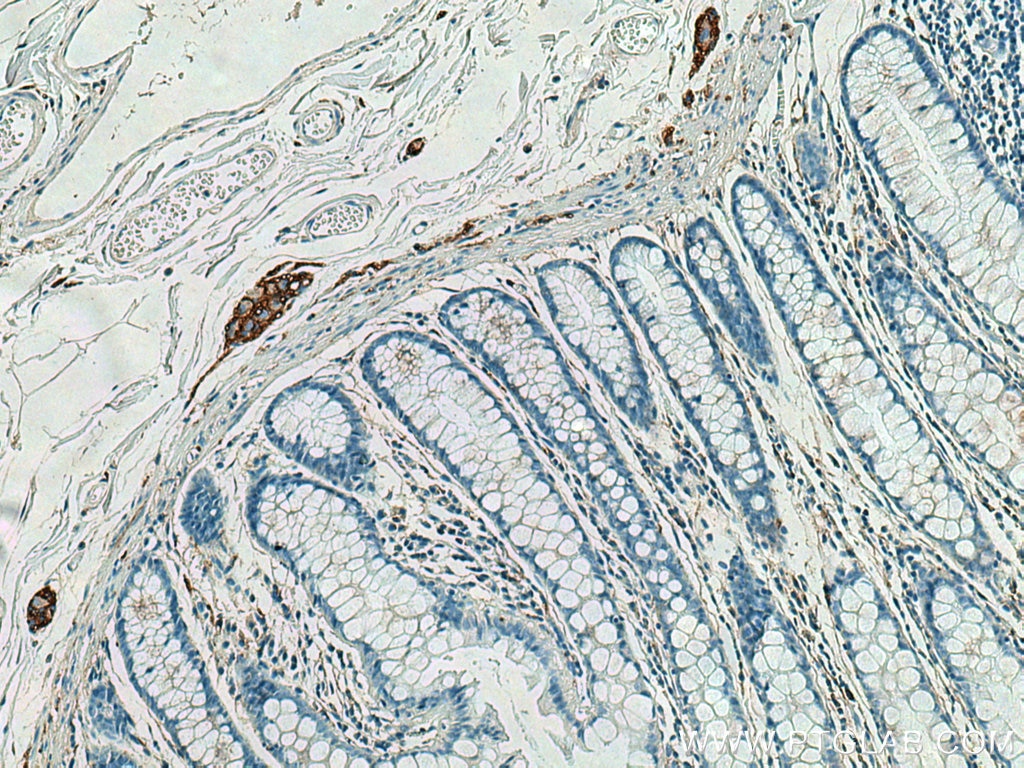
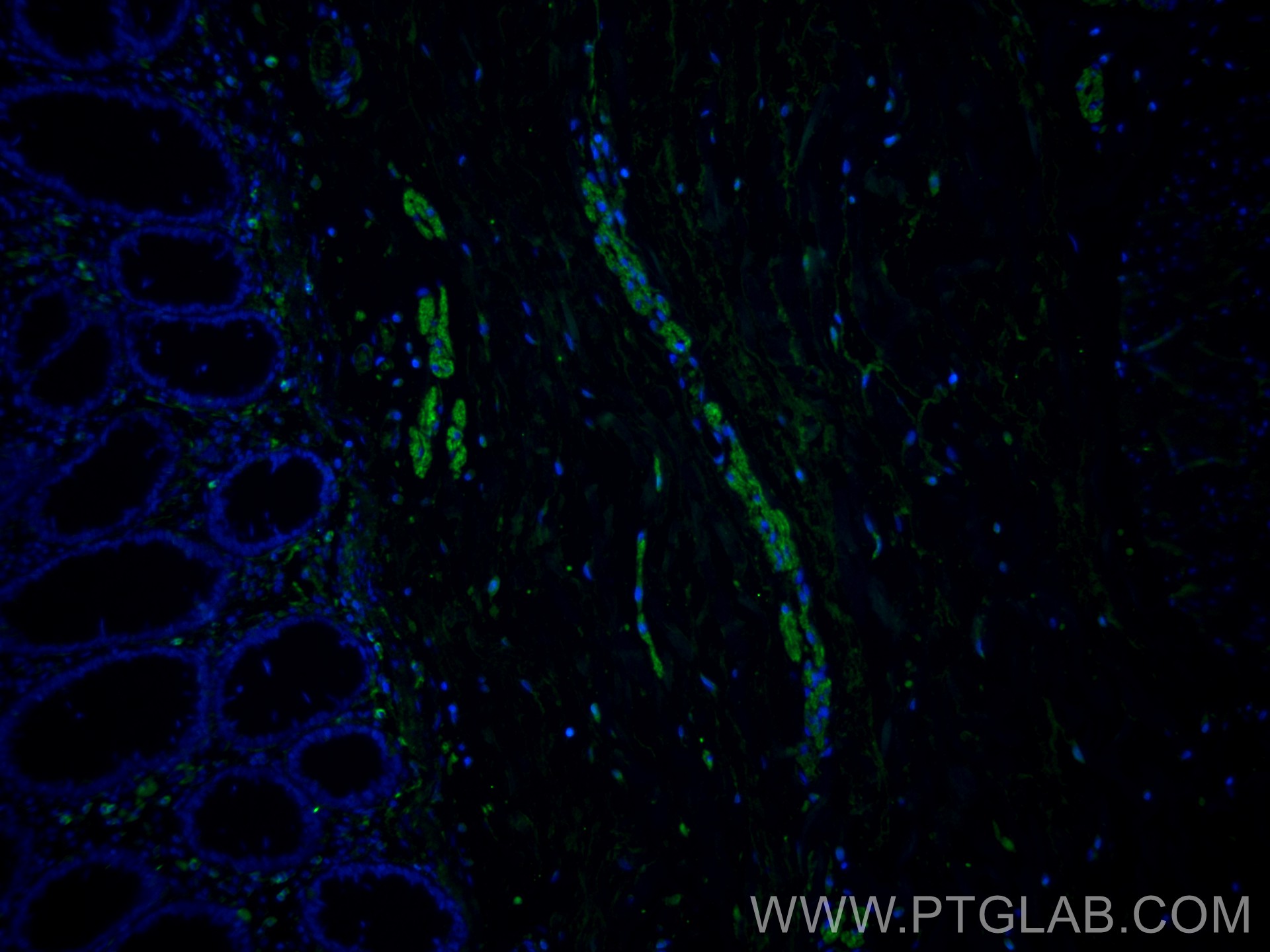
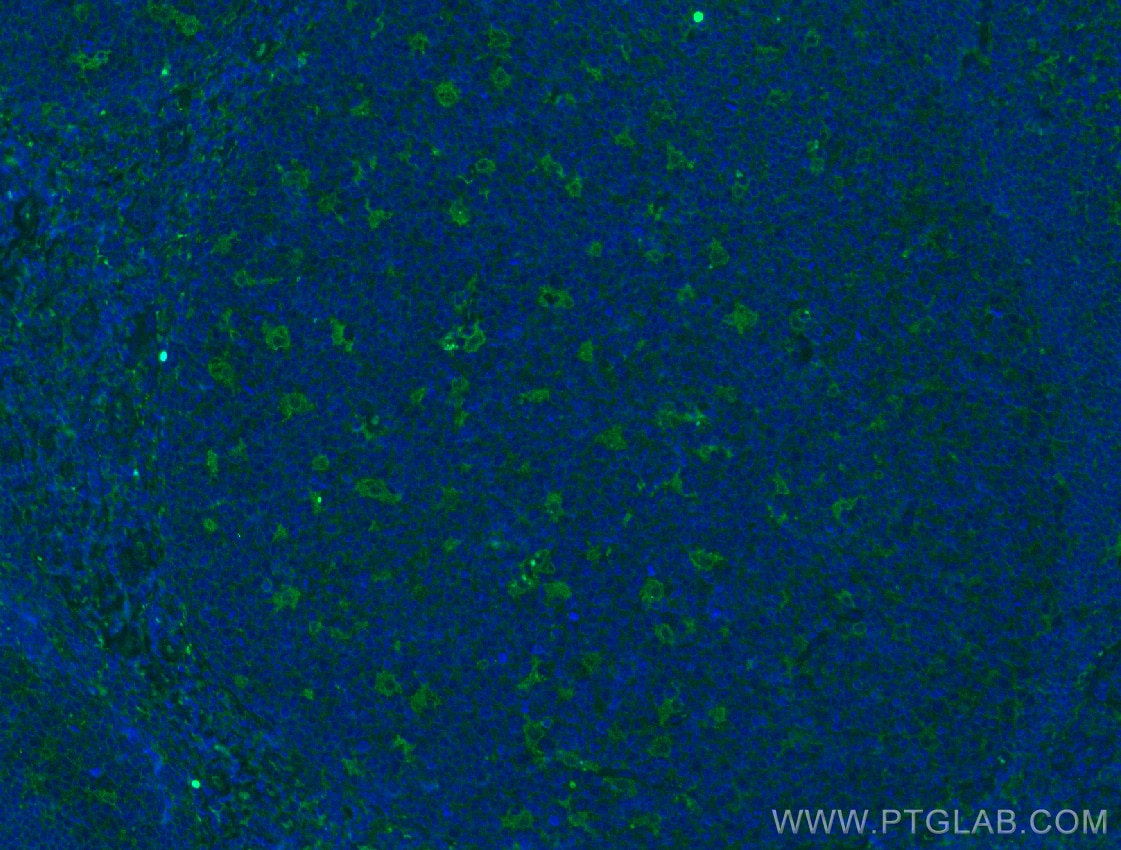
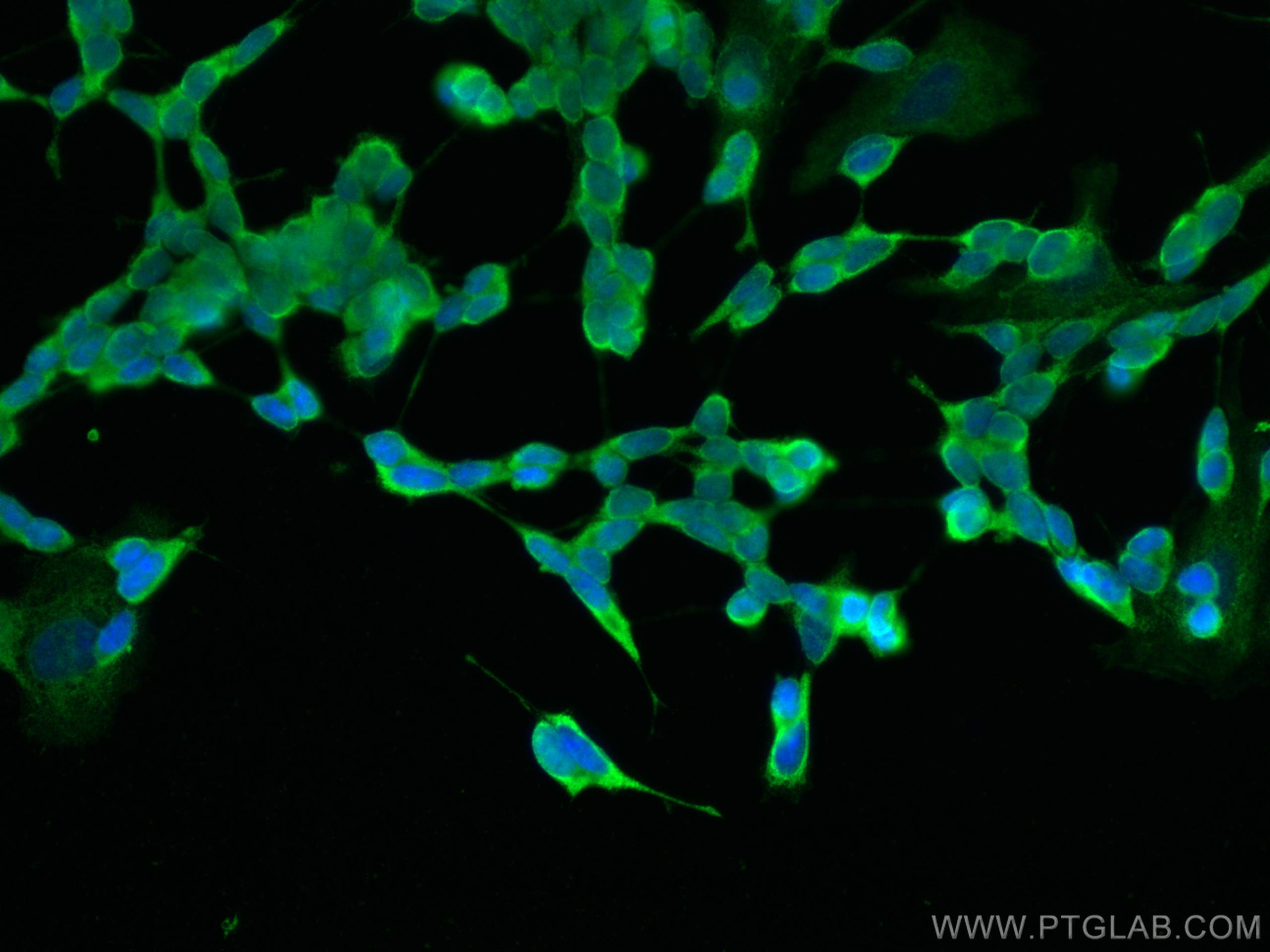
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
60238-1-PBS targets NCAM1/CD56 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IF-P, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, rat, pig samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, rat, pig |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | NCAM1/CD56 fusion protein Ag5732 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | neural cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 95 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 140 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC047244 |
| Gene Symbol | NCAM1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4684 |
| ENSEMBL Gene ID | ENSG00000149294 |
| RRID | AB_2881361 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P13591 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Neural cell adhesion molecule 1 (NCAM1, also known as CD56) is a cell adhesion glycoprotein of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily. It is a multifunction protein involved in synaptic plasticity, neurodevelopment, and neurogenesis. NCAM1 is expressed on human neurons, glial cells, skeletal muscle cells, NK cells and a subset of T cells, and the expression is observed in a wide variety of human tumors, including myeloma, myeloid leukemia, neuroendocrine tumors, Wilms' tumor, neuroblastoma, and NK/T cell lymphomas. Three major isoforms of NCAM1, with molecular masses of 120, 140, and 180 kDa, are generated by alternative splicing of mRNA (PMID: 9696812). The glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI)-anchored NCAM120 and the transmembrane NCAM140 and NCAM180 consist of five Ig-like domains and two fibronection-type III repeats (FNIII). All three forms can be posttranslationally modified by addition of polysialic acid (PSA) (PMID: 14976519). Several other isofroms have also been described (PMID: 1856291).