Neurochondrin Polyclonal antibody
Neurochondrin Polyclonal Antibody for WB, IHC, ELISA
Host / Isotype
Rabbit / IgG
Reactivity
human, mouse, rat
Applications
WB, IF, IHC, ELISA
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Cat no : 13187-1-AP
Synonyms
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
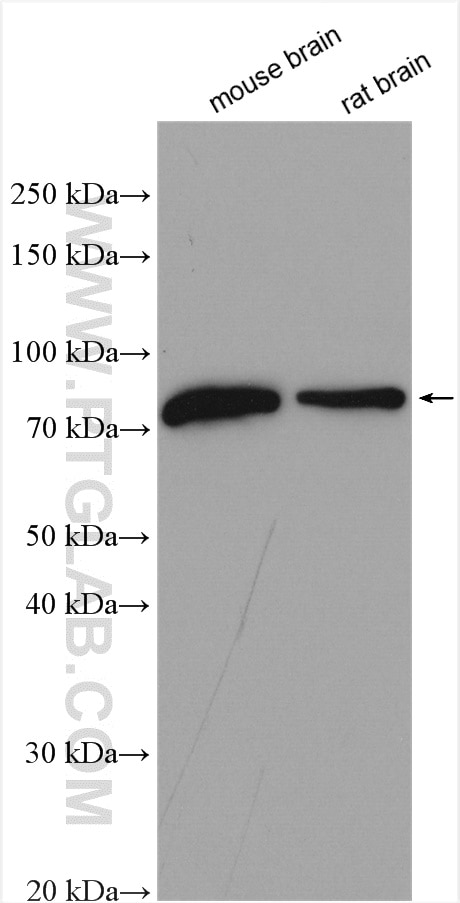
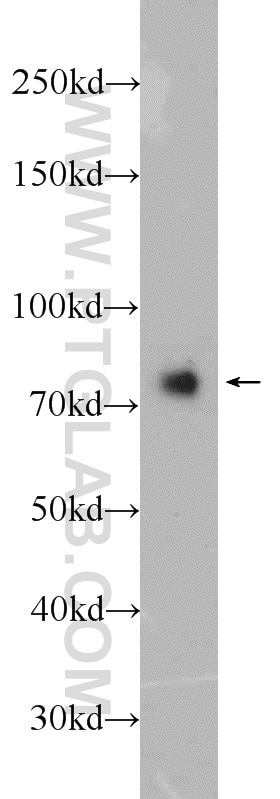
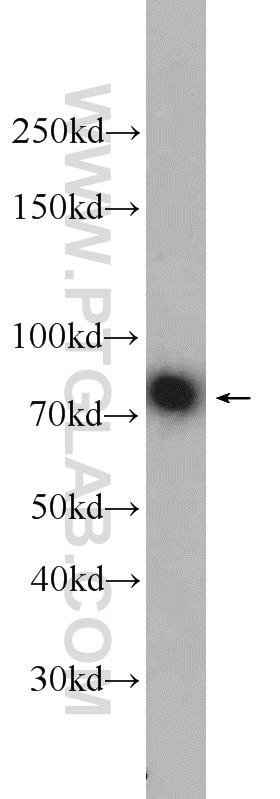
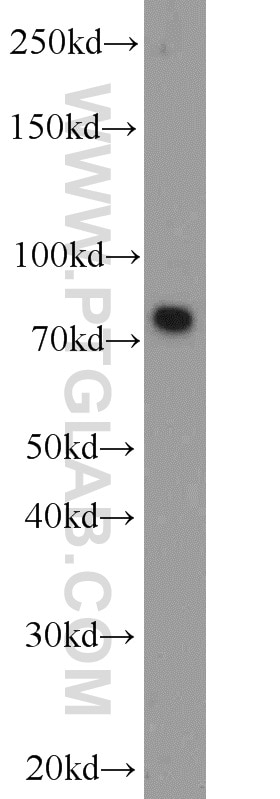
| Positive WB detected in | mouse brain tissue, human brain tissue, rat brain tissue |
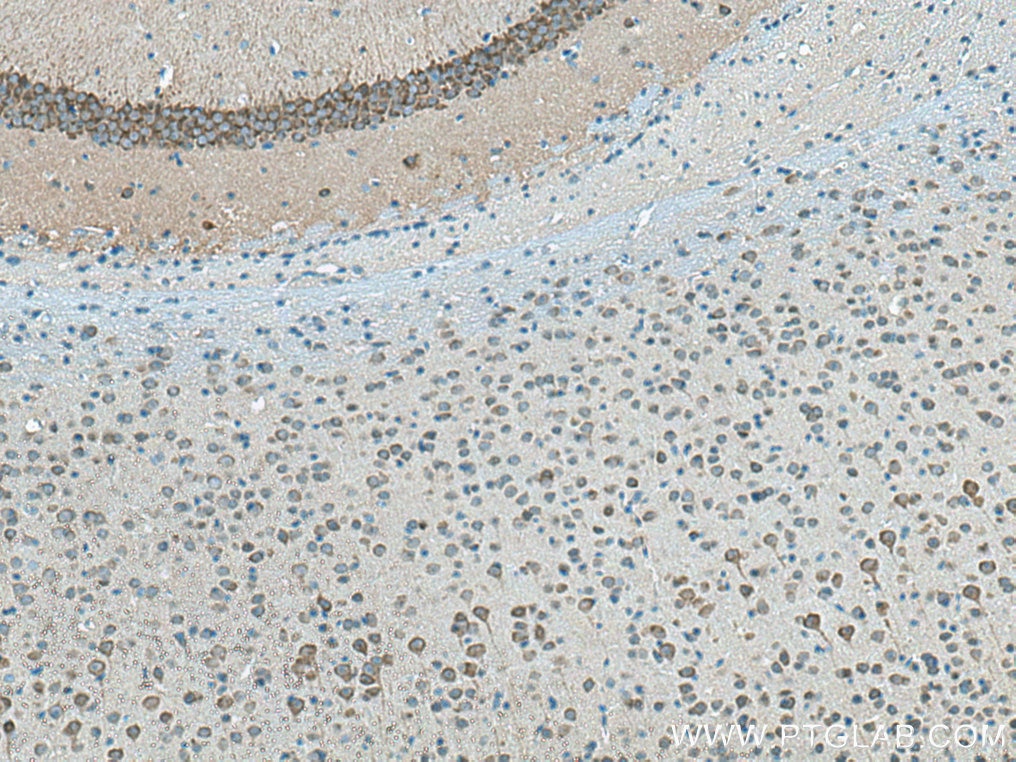
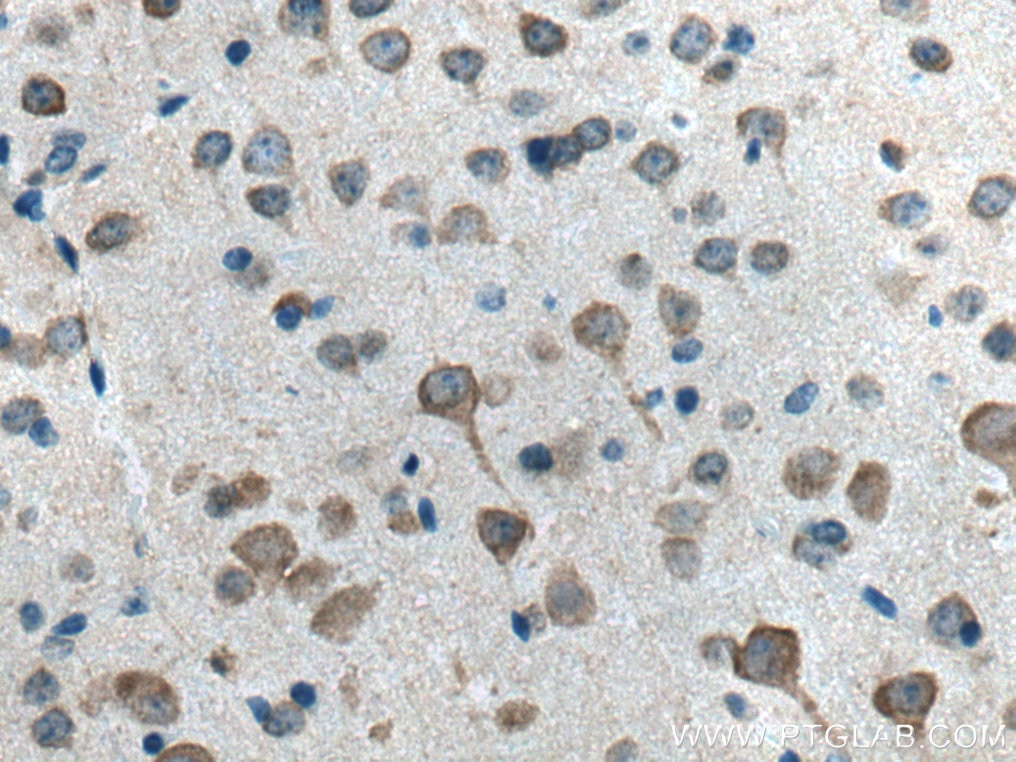
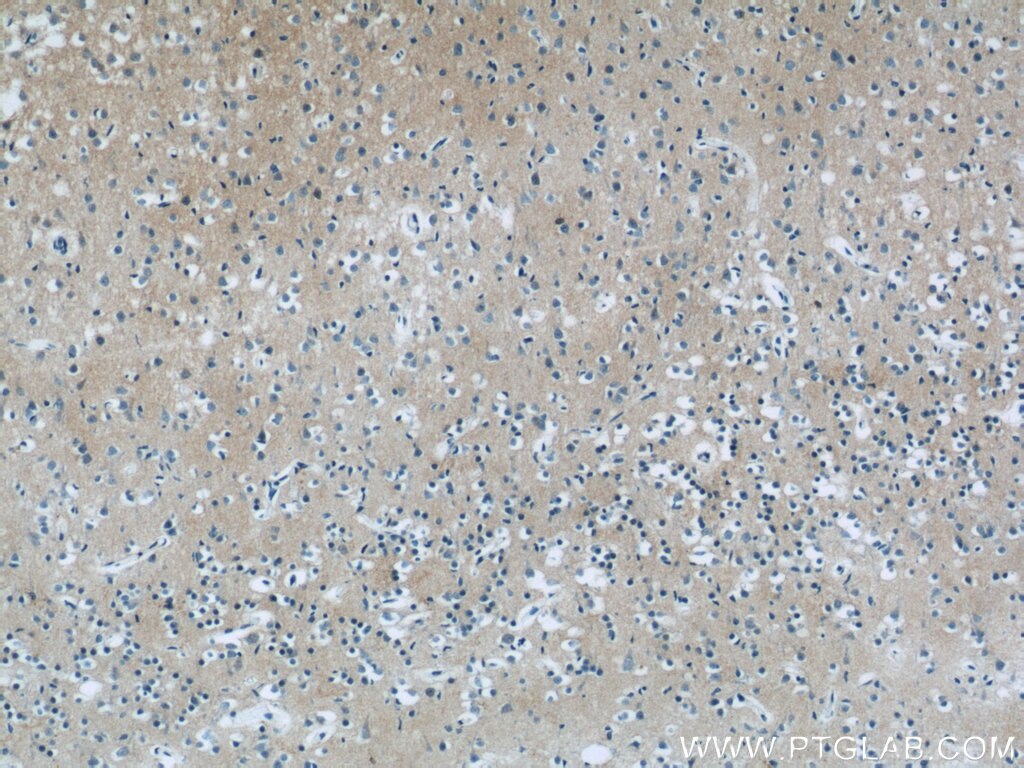
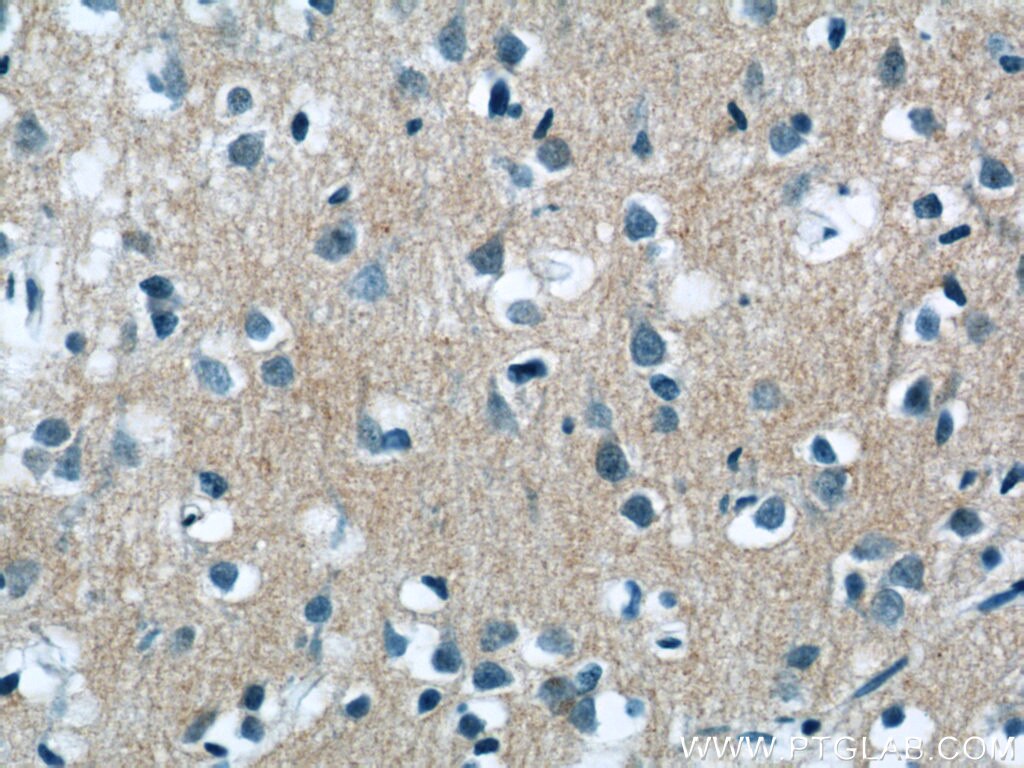
| Positive IHC detected in | mouse brain tissue, human brain tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
13187-1-AP targets Neurochondrin in WB, IF, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Neurochondrin fusion protein Ag3859 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | neurochondrin |
| Calculated molecular weight | 729 aa, 79 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 79 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC024592 |
| Gene symbol | Neurochondrin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 23154 |
| RRID | AB_2877919 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Neurochondrin antibody 13187-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for Neurochondrin antibody 13187-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
J Cell Sci Neurochondrin interacts with the SMN protein suggesting a novel mechanism for spinal muscular atrophy pathology. |