Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
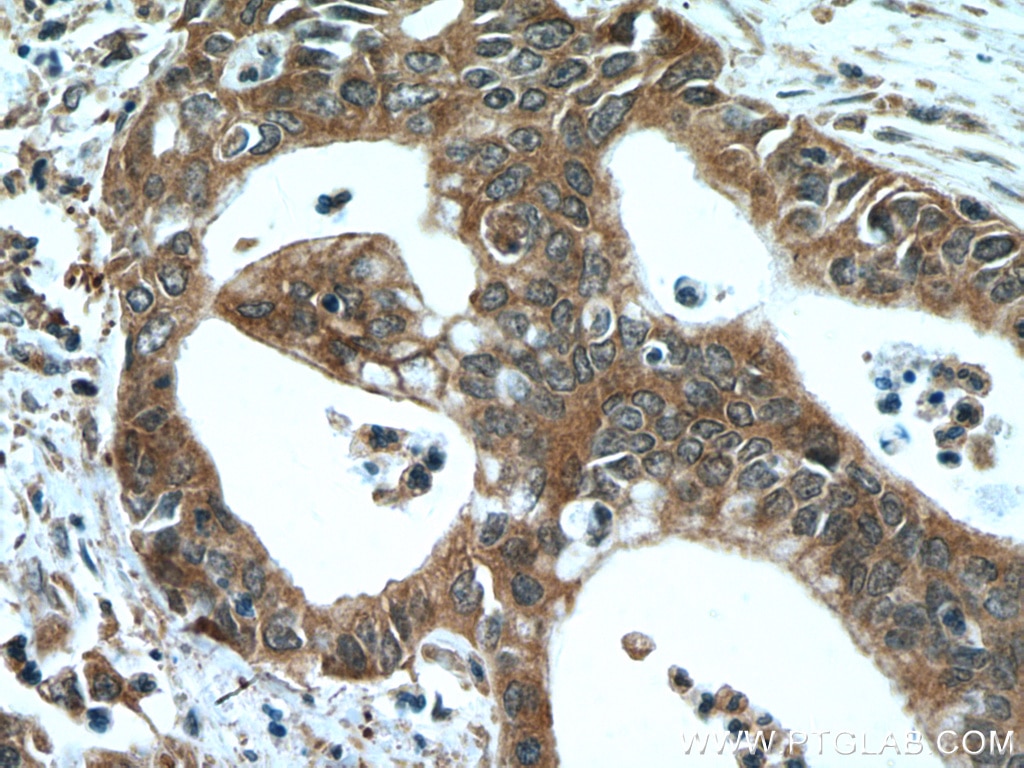
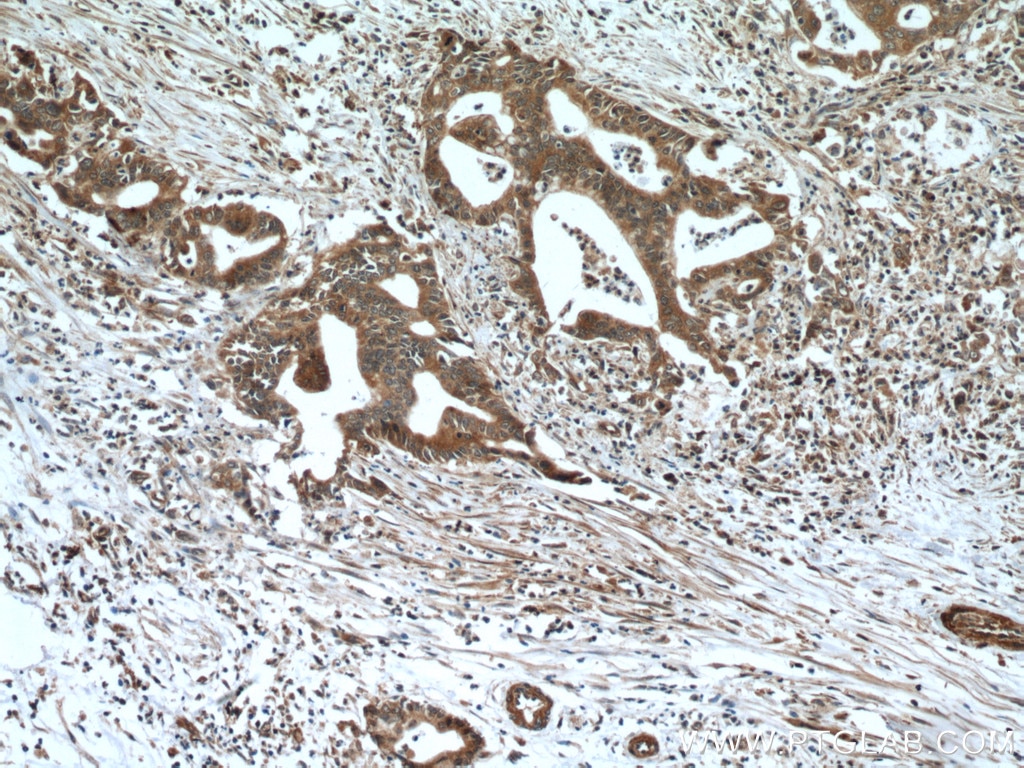
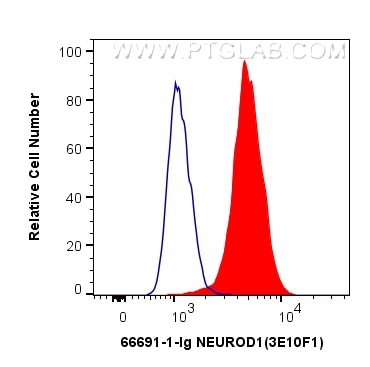
66691-1-PBS targets NEUROD1 in WB, IHC, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | NEUROD1 fusion protein Ag27606 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | neurogenic differentiation 1 |
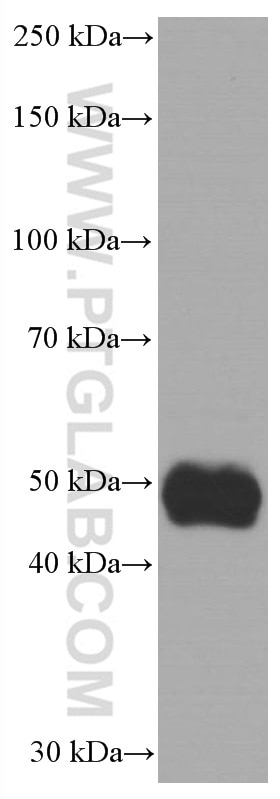
| Calculated molecular weight | 356 aa, 40 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 40-50 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC009046 |
| Gene Symbol | NEUROD1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 4760 |
| RRID | AB_2882045 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q13562 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
NeuroD is a member of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family of transcription factors. The basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) proteins are transcription factors that are required for several aspects of development, including cell type determination, terminal differentiation and sex determination. Members of the myogenic determination family, MyoD, myf5, myogenin and MRF4, all have bHLH domains.These proteins function by forming heterodimers with E-proteins and binding to the canonical E-box sequence CANNTG. Neuro D is expressed transiently in a subset of neurons in the central and peripheral nervous systems at the time of their terminal differentiation into mature neurons. Moreover, ectopic expression of Neuro D in Xenopus embryos induces premature differentiation of neuronal precursors and Neuro D can convert presumptive epidermal cells into neurons.The lack of NeuroD in the brain results in severe defects in development. Human mutations have been linked to a number of types of diabetes including type I diabetes mellitus and maturity-onset diabetes of the young. The calculated molecular weight of NEUROD1 is 39 kDa, but the modified NEUROD1 protein is about 45-50 kDa.