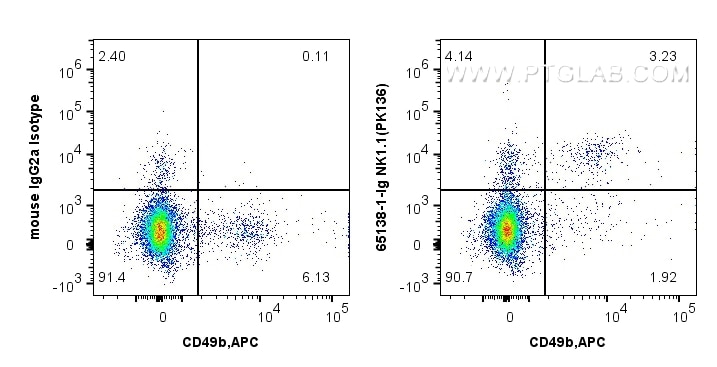
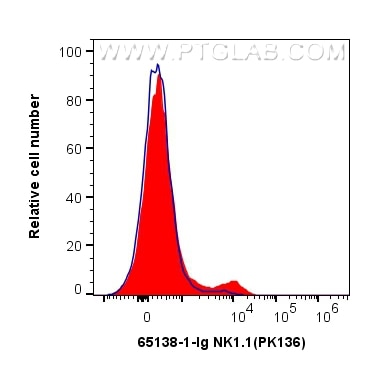
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
| Positive FC detected in | C57BL/6 mouse splenocytes |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| This reagent has been tested for flow cytometric analysis. It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
65138-1-Ig targets NK1.1 (CD161) in FC applications and shows reactivity with Mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2a, kappa |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | NK-1+ cells from mouse spleen and bone marrow 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | killer cell lectin-like receptor subfamily B member 1A |
| GenBank accession number | BC120707 |
| Gene Symbol | NK1.1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 17057 |
| RRID | AB_2918425 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P27811 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.09% sodium azide , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at 2-8°C. Stable for one year after shipment. |
Background Information
NK1.1 (CD161), also known as KLRB1 or NKR-P1A, is a type II transmembrane C-type lectin-like receptor and is expressed on the cell membrane as disulfide-linked homodimer (PMID: 8077657). It is expressed by the majority of NK cells and subsets of peripheral T cells, including both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, and is expressed preferentially on adult T cells with a "memory" antigenic phenotype (PMID: 8077657; 22566826). Expression of CD161 correlates with the cytotoxic function of CD16+ NK cells, and ligation of CD161 with its ligand LLT1 inhibits NK cell cytotoxicity and cytokine secretion (PMID: 29686665).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| FC protocol for NK1.1 (CD161) antibody 65138-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |