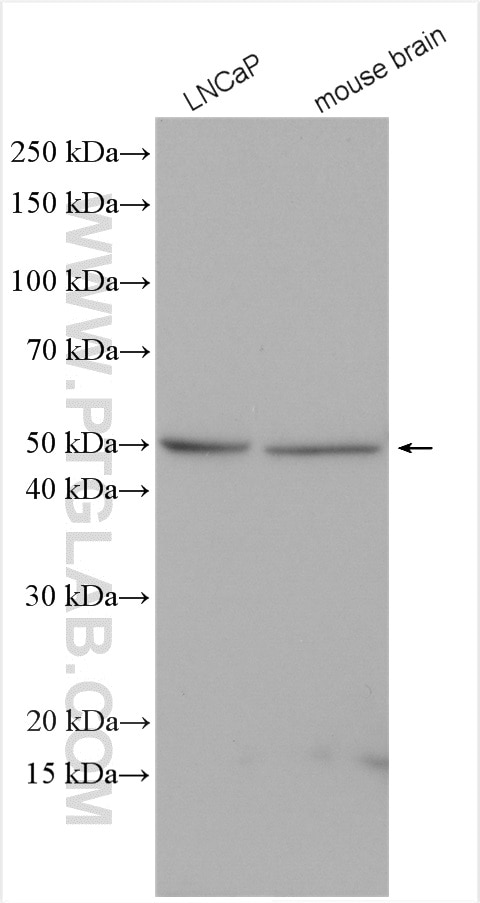
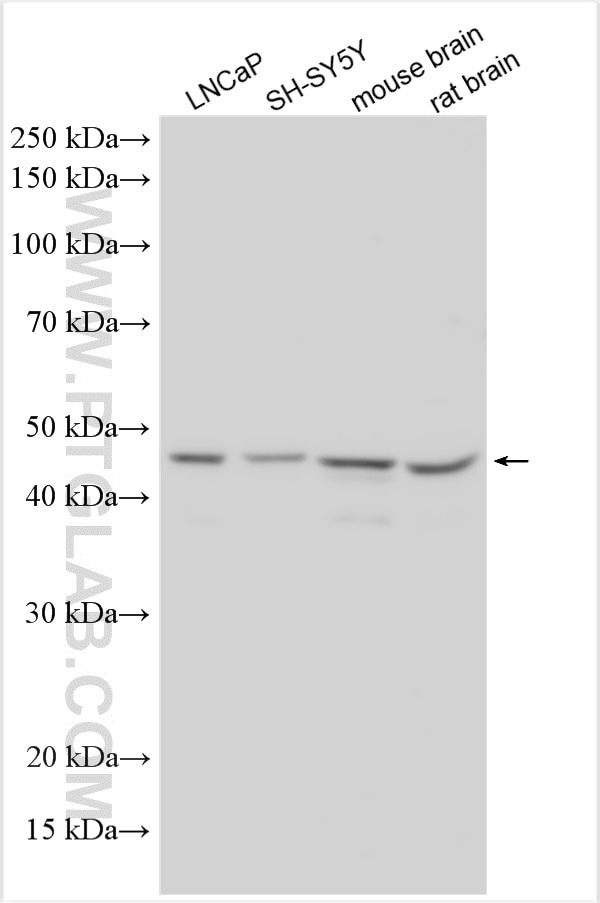
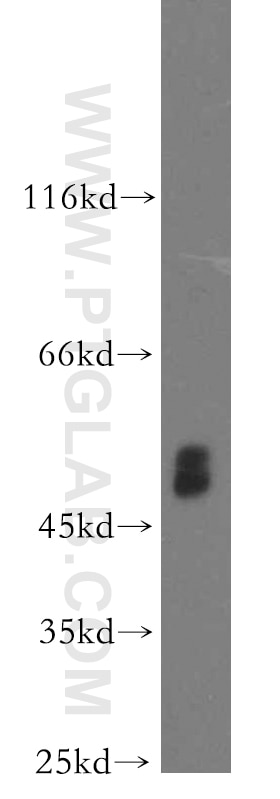
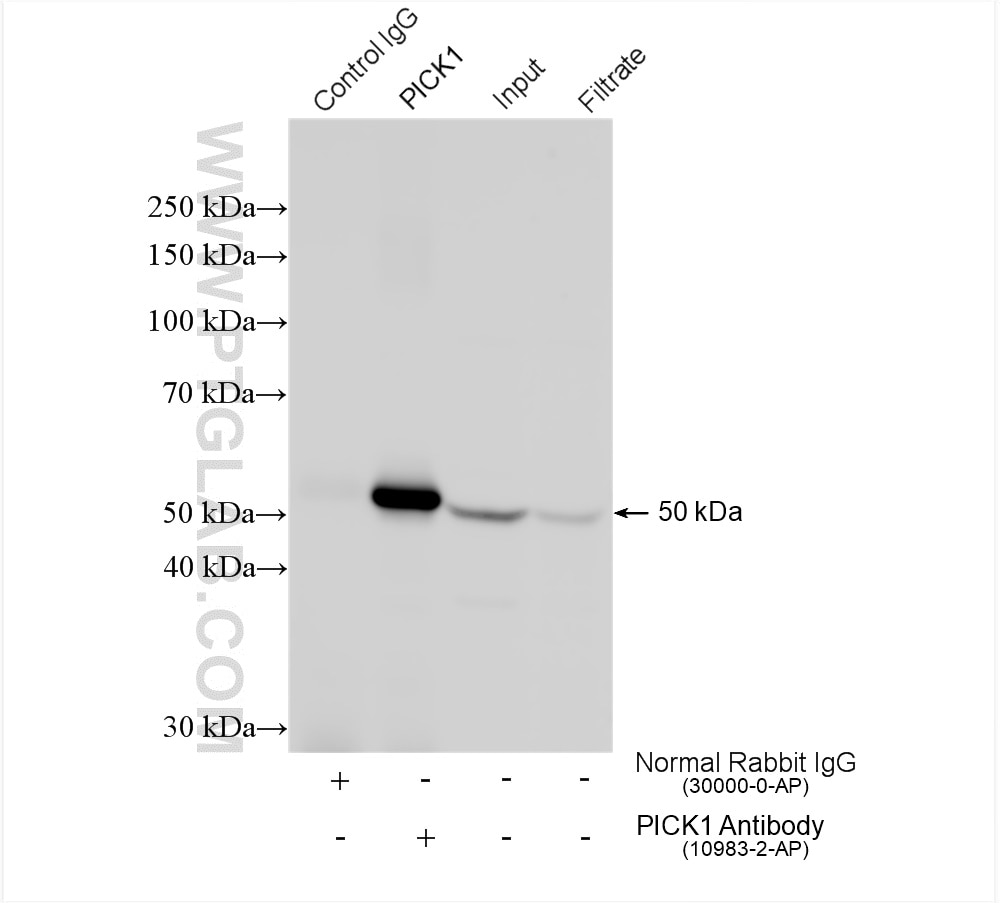
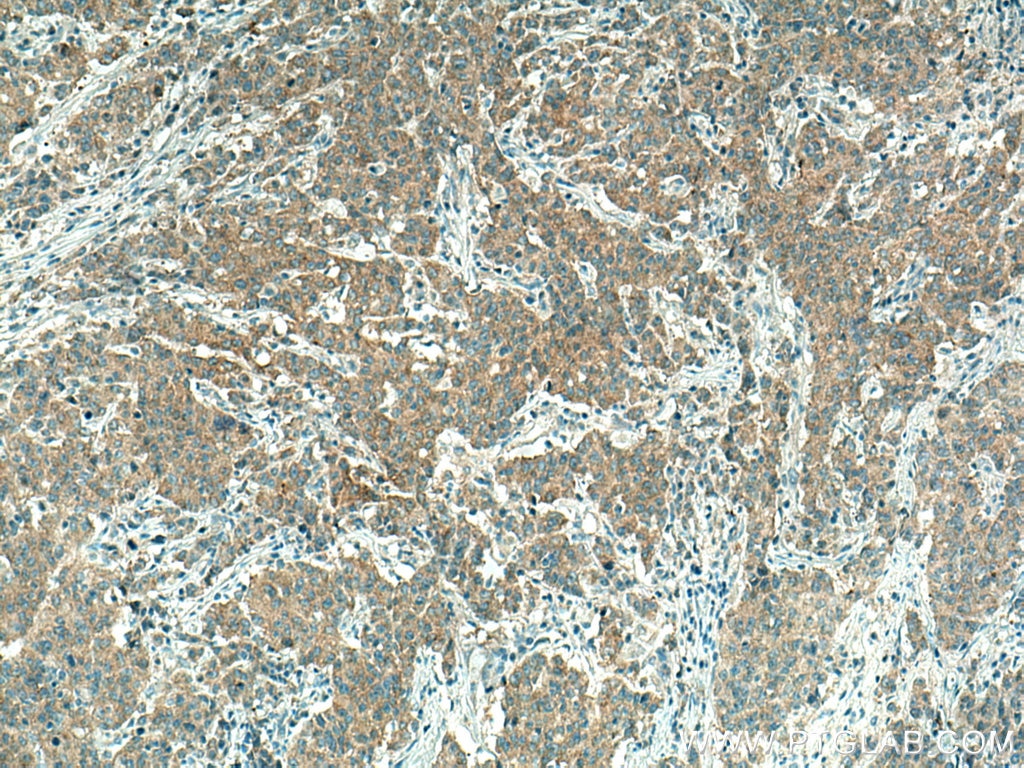
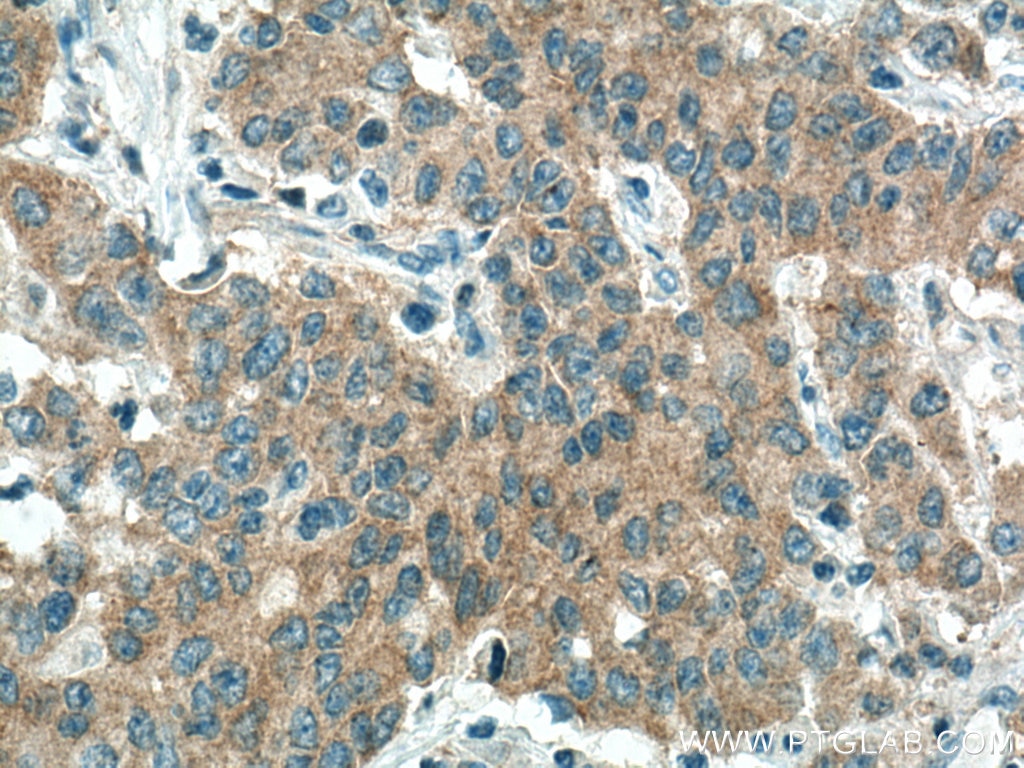
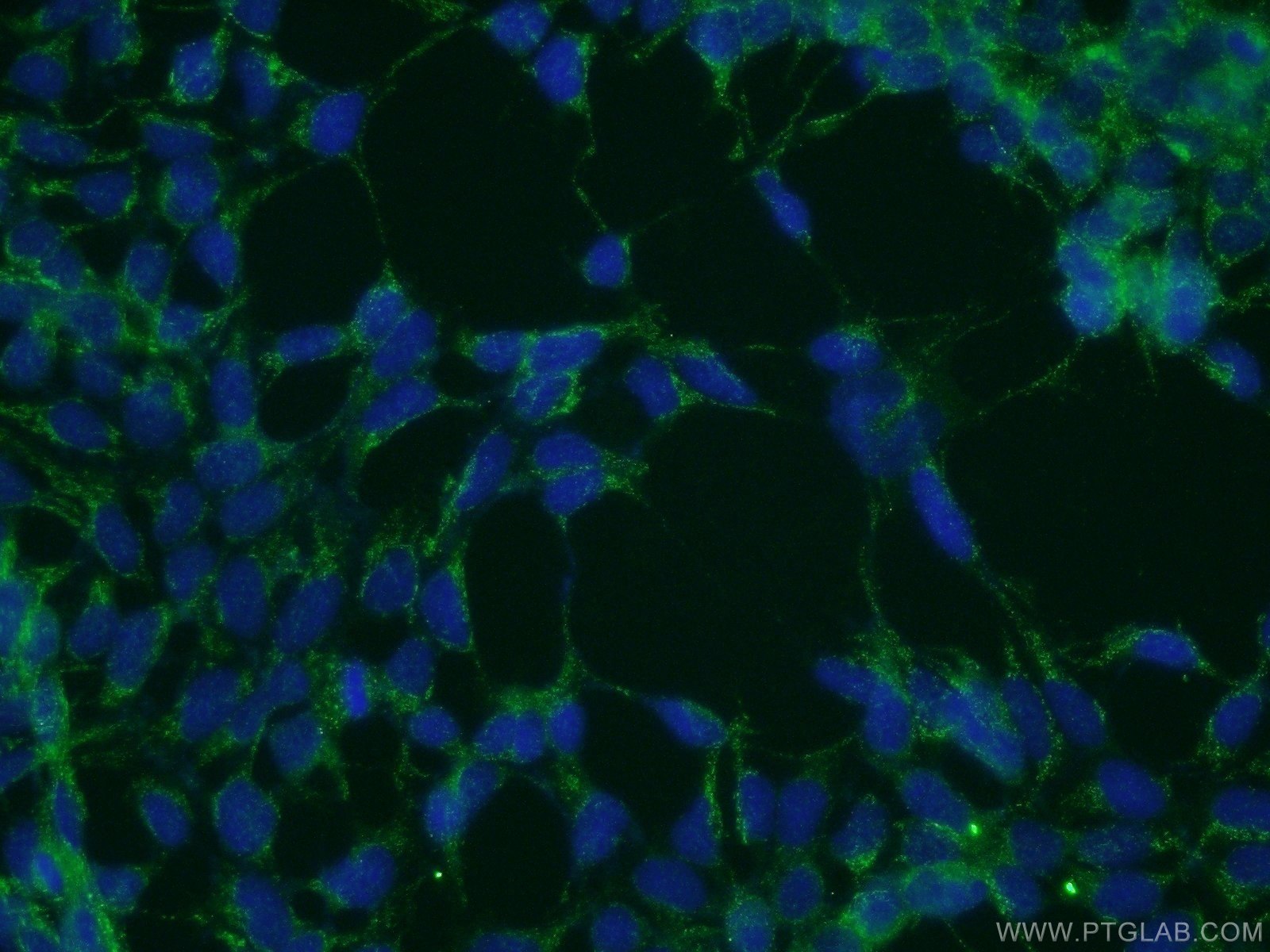
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
10983-2-PBS targets PICK1 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | PICK1 fusion protein Ag1443 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | protein interacting with PRKCA 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 47 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 50-55 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC017561 |
| Gene Symbol | PICK1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 9463 |
| RRID | AB_2164525 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9NRD5 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Protein interacting with C kinase 1 (PICK1) was first cloned as a PKC-binding partner through yeast two hybrid system. PICK1 acts as a critical regulator of membrane receptors' subcellular trafficking to modulate neural processes such as learning and memory, and is widely expressed in brain, testis, heart, lung, liver, kidney and muscle. It probably binds to and organize the subcellular localization of a variety of membrane proteins containing some PDZ recognition sequence, for instance, PICK1 is a critical mediator of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor (AMPAR) trafficking in neural synapses. PICK1 expression on D-serine release and glutamate transport in astrocytes suggests a potential implication of PICK1 in the progression of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). PICK1 may also participate in breast cancer development through inhibition of TGF-β signaling.