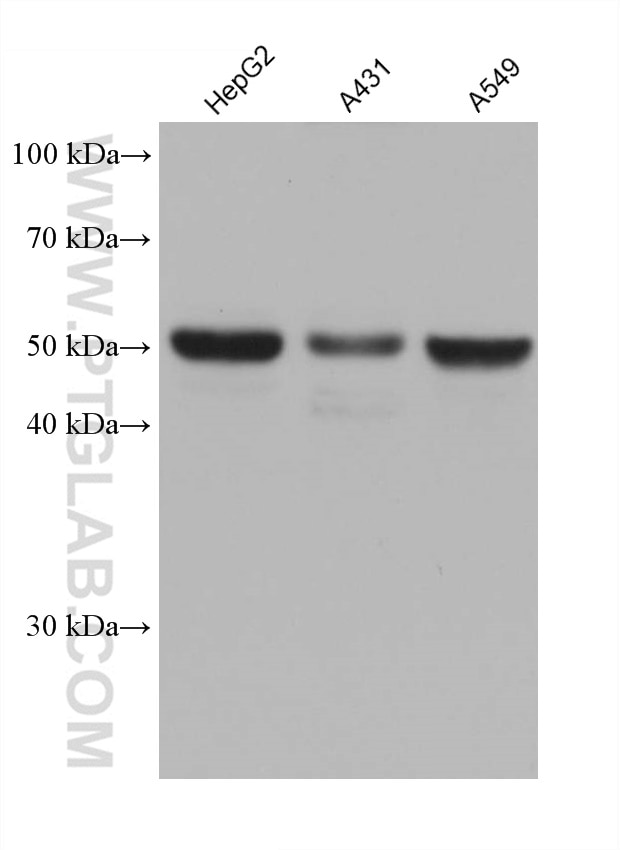
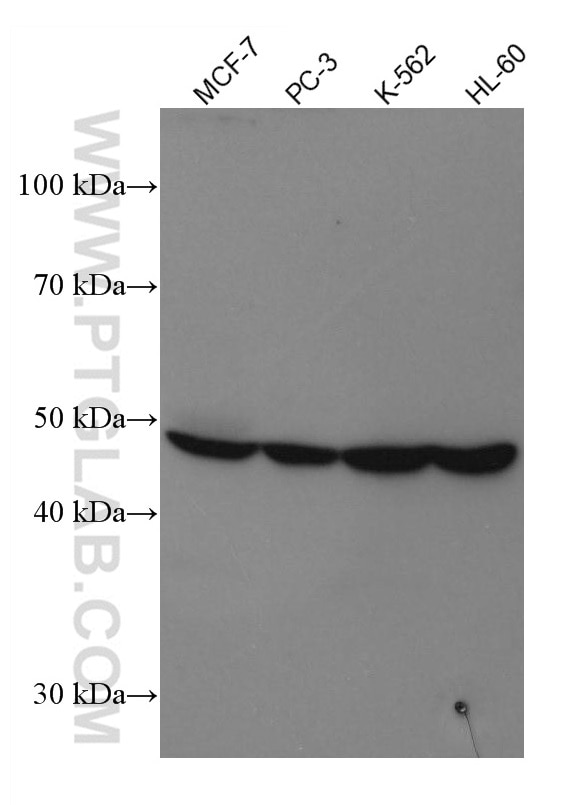
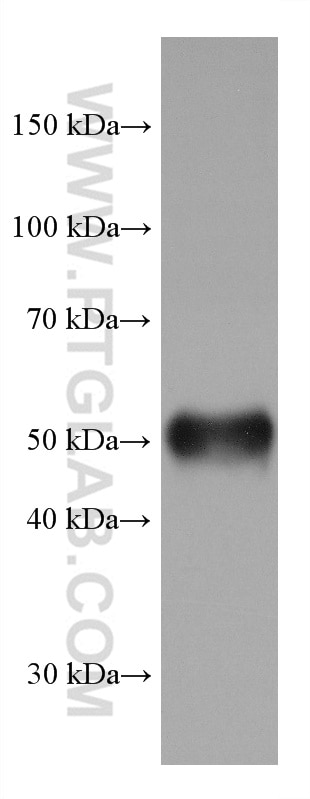
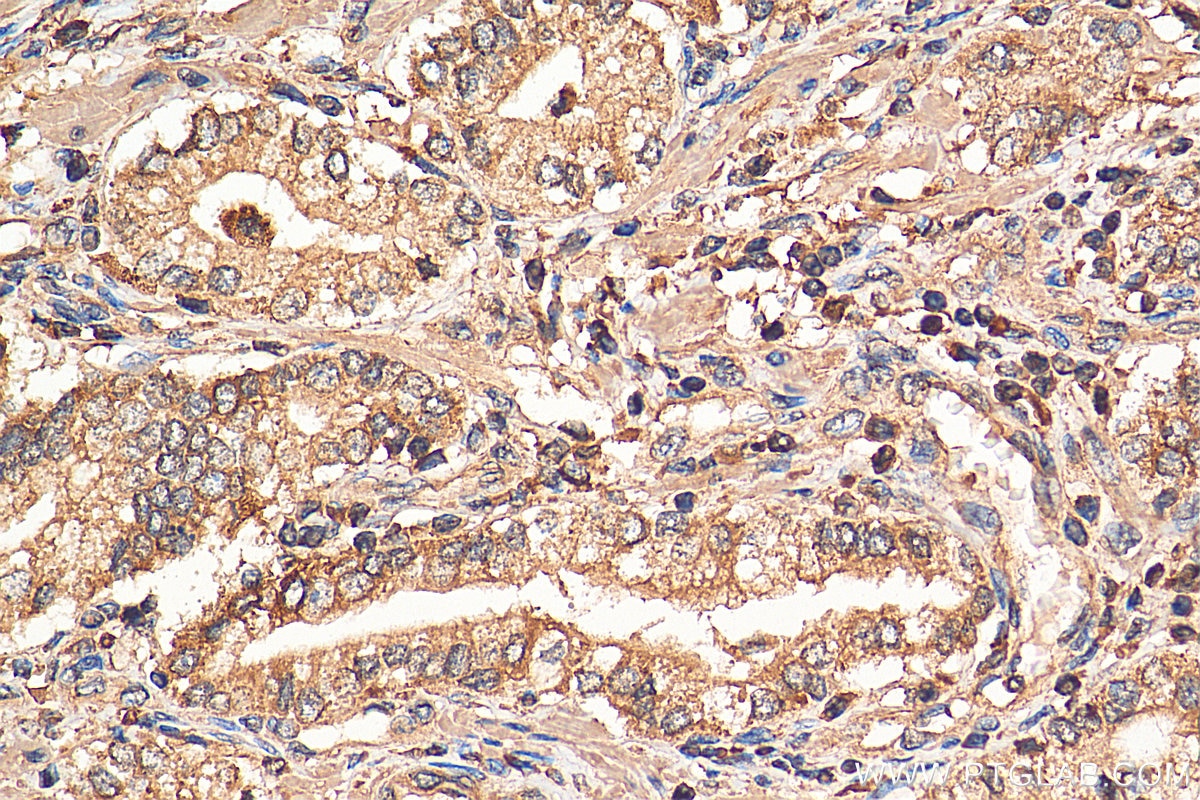
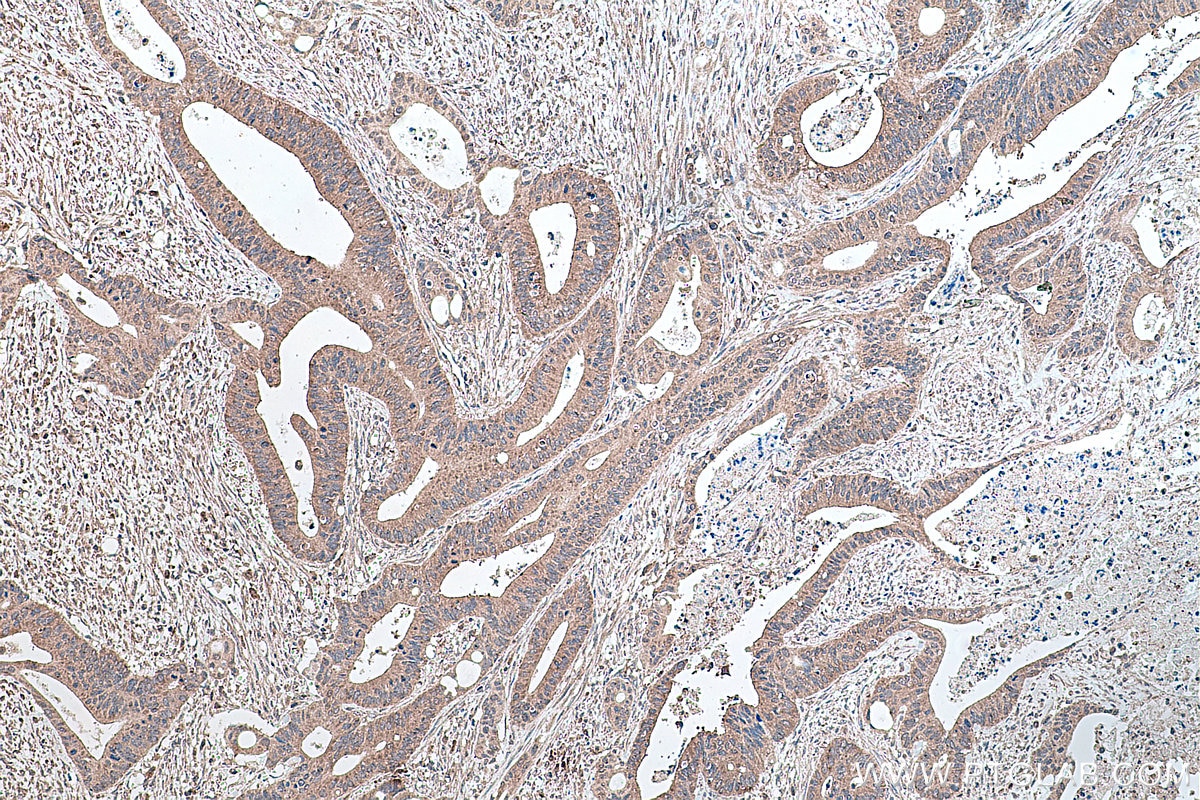
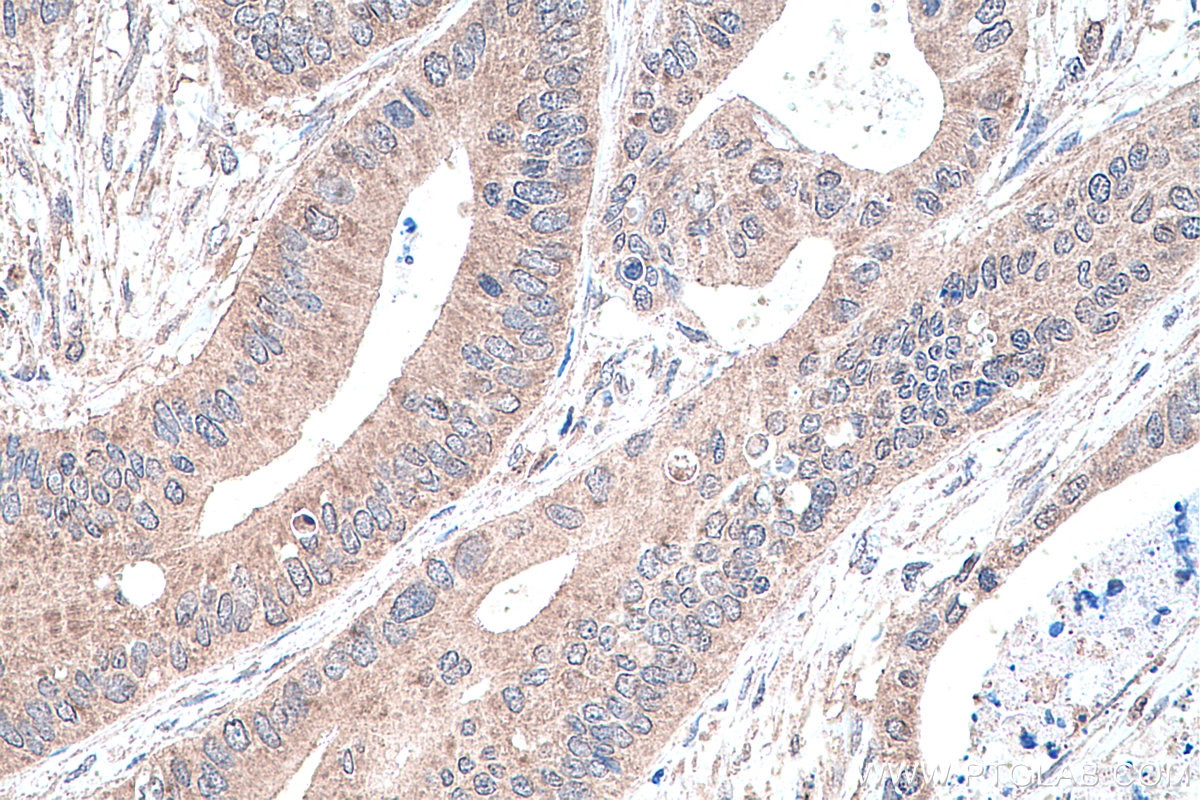
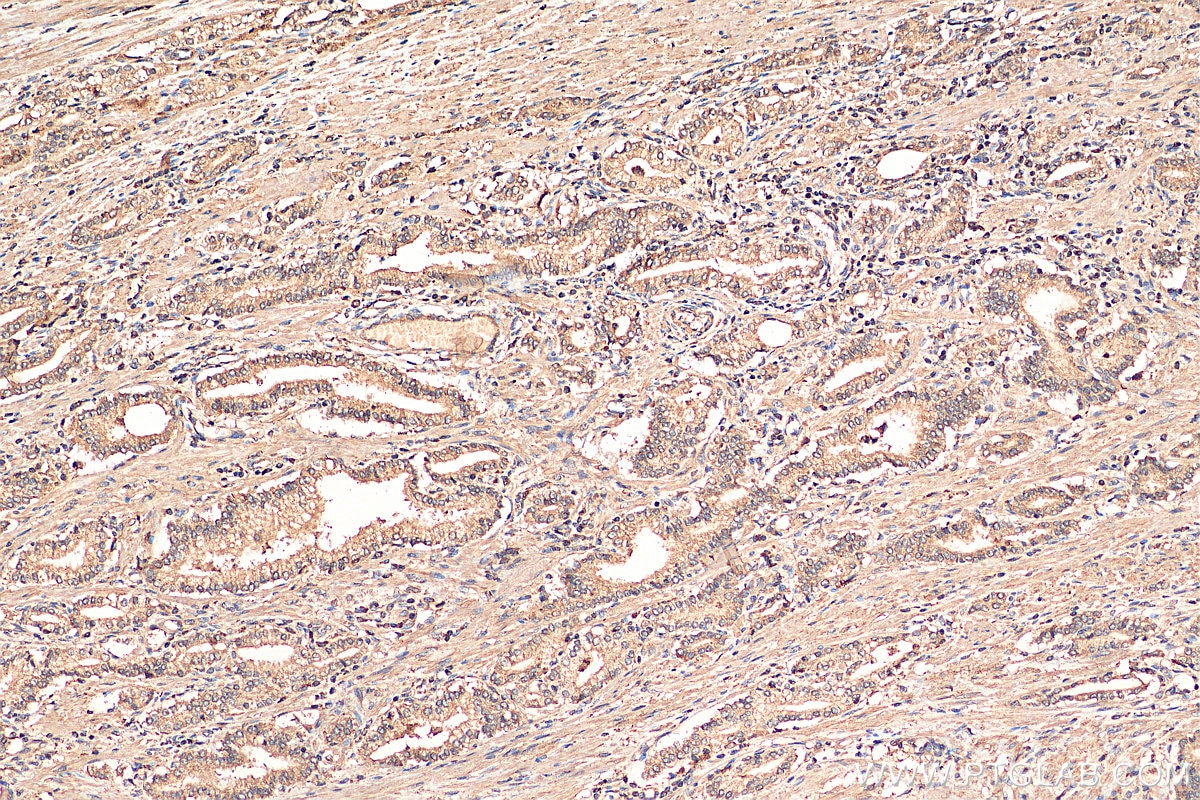
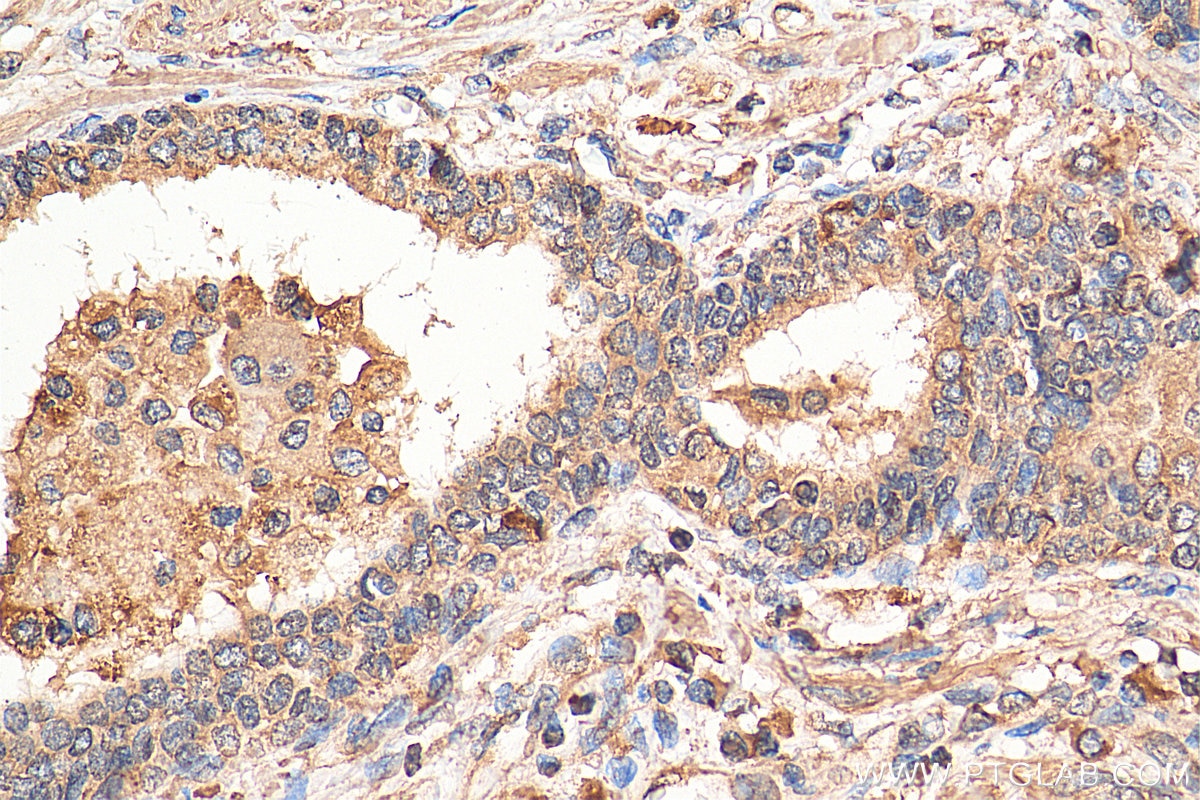
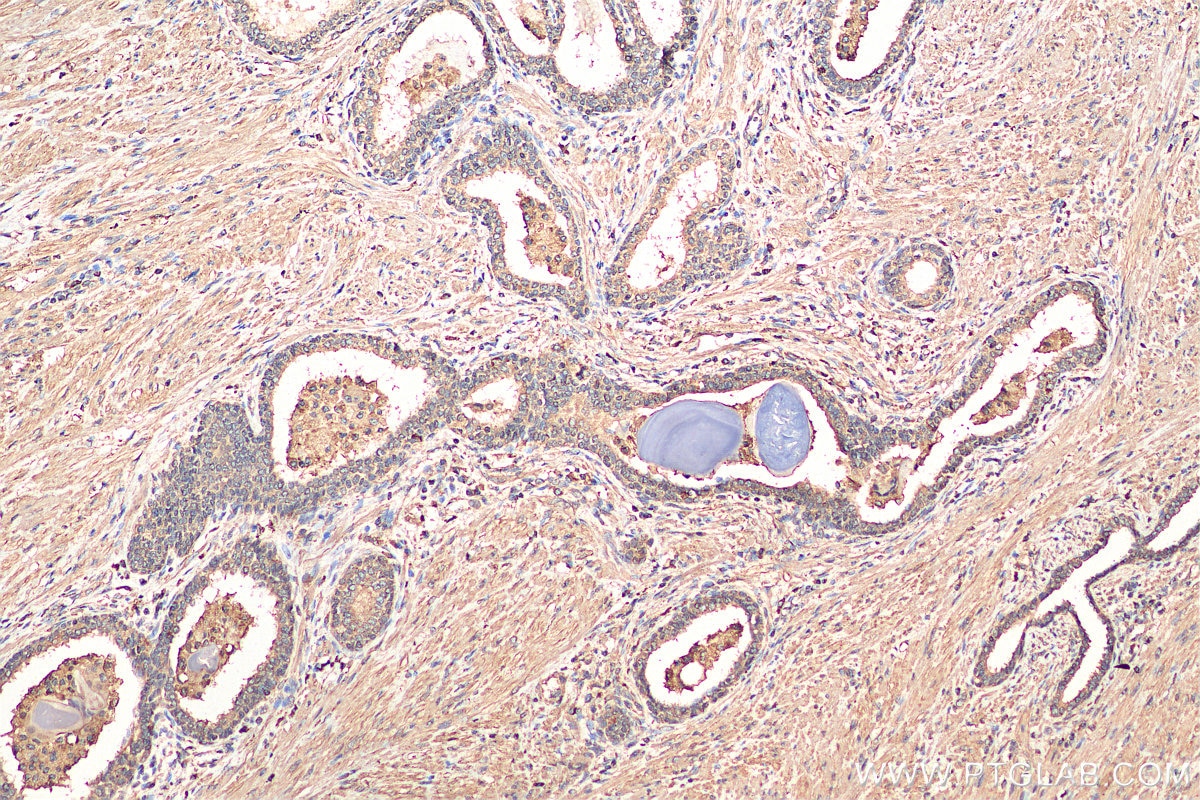
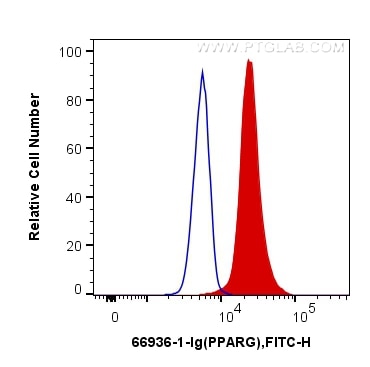
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
66936-1-PBS targets PPAR Gamma in WB, IHC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | PPAR Gamma fusion protein Ag16657 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| Calculated molecular weight | 58 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 50 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC006811 |
| Gene Symbol | PPARG |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5468 |
| RRID | AB_2882260 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P37231 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors (PPARs) are ligand-activated intracellular transcription factors, members of the nuclear hormone receptor superfamily (NR), that includes estrogen, thyroid hormone receptors, retinoic acid, Vitamin D3 as well as retinoid X receptors (RXRs). The PPAR subfamily consists of three subtypes encoded by distinct genes denoted PPARα (NR1C1), PPARβ/δ (NR1C2) and PPARγ (NR1C3), which are activated by selective ligands. PPARγ, also named as PPARG, contains one nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain and is a receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. It plays an important role in the regulation of lipid homeostasis, adipogenesis, INS resistance, and development of various organs. Defects in PPARG are the cause of familial partial lipodystrophy type 3 (FPLD3) and may be associated with susceptibility to obesity. Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 INS-resistant diabetes and hypertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. Genetic variations in PPARG are associated with susceptibility to glioma type 1 (GLM1). PPARG has two isoforms with molecular weight 57 kDa and 54 kDa (PMID: 9831621), but modified PPARG is about 67 KDa (PMID: 16809887). PPARG2 is a splice variant and has an additional 30 amino acids at the N-terminus (PMID: 15689403). Experimental data indicate that a 45 kDa protein displaying three different sequences immunologically related to the nuclear receptor PPARG2 is located in mitochondria (mt-PPAR). However, the molecular weight of this protein is clearly less when compared to that of PPARG2 (57 kDa) (PMID: 10922459). PPARG has been reported to be localized mainly (but not always) in the nucleus. PPARG can also be detected in the cytoplasm and was reported to possess extra-nuclear/non-genomic actions (PMID: 17611413; 19432669; 14681322).