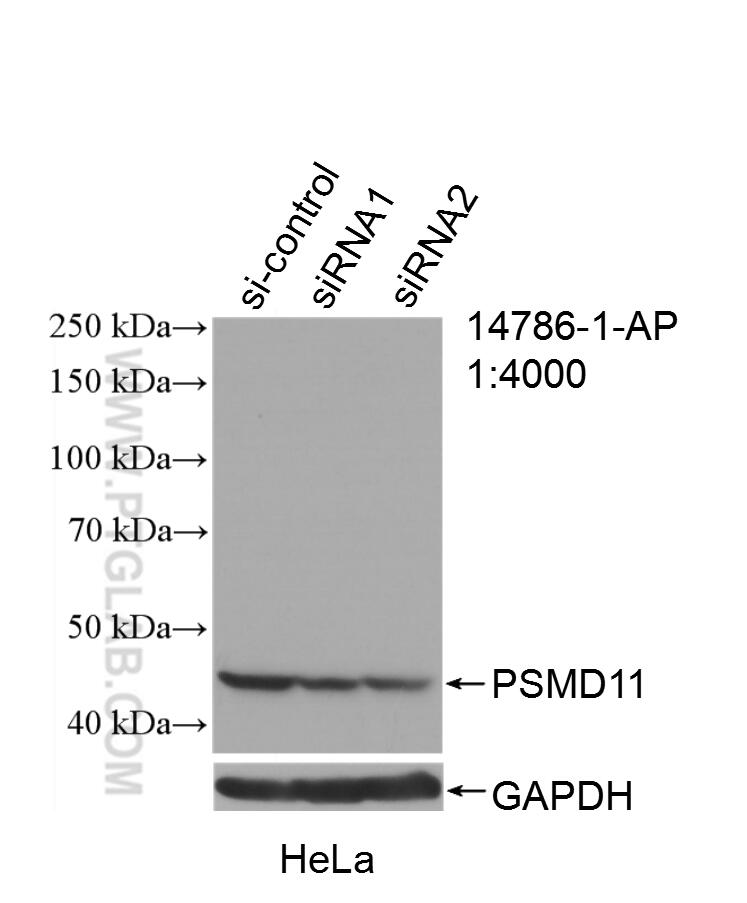
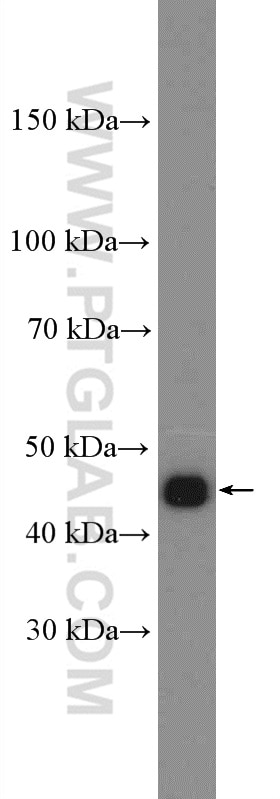
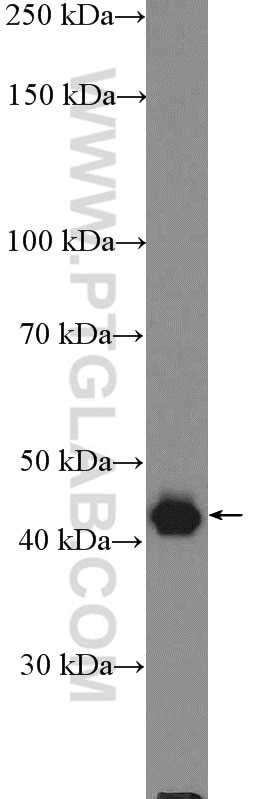
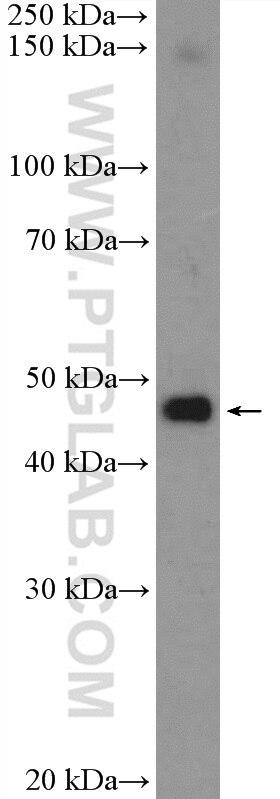
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
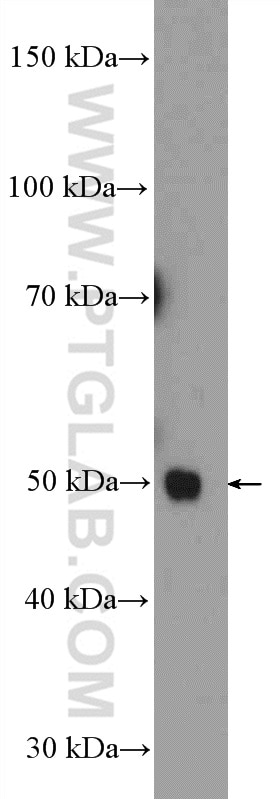
| Positive WB detected in | HeLa cells, MCF-7 cells, mouse testis tissue, rat brain tissue |
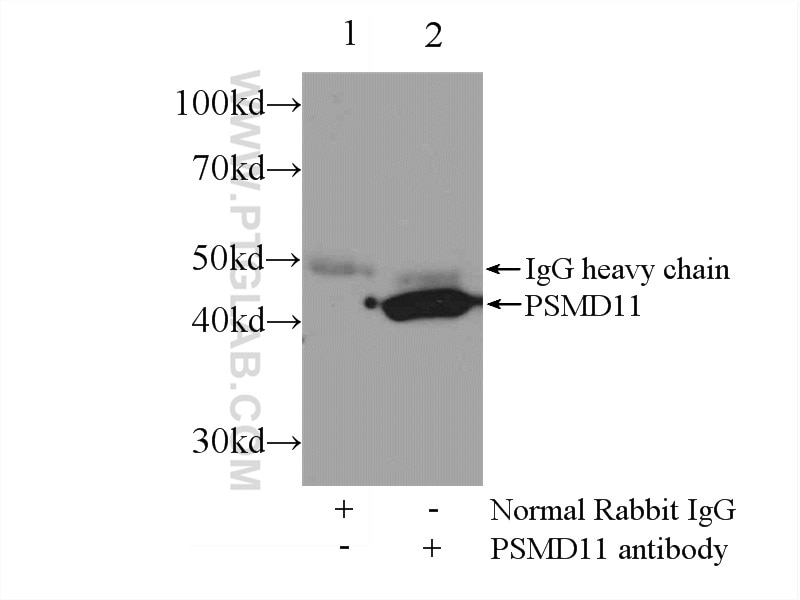
| Positive IP detected in | MCF-7 cells |
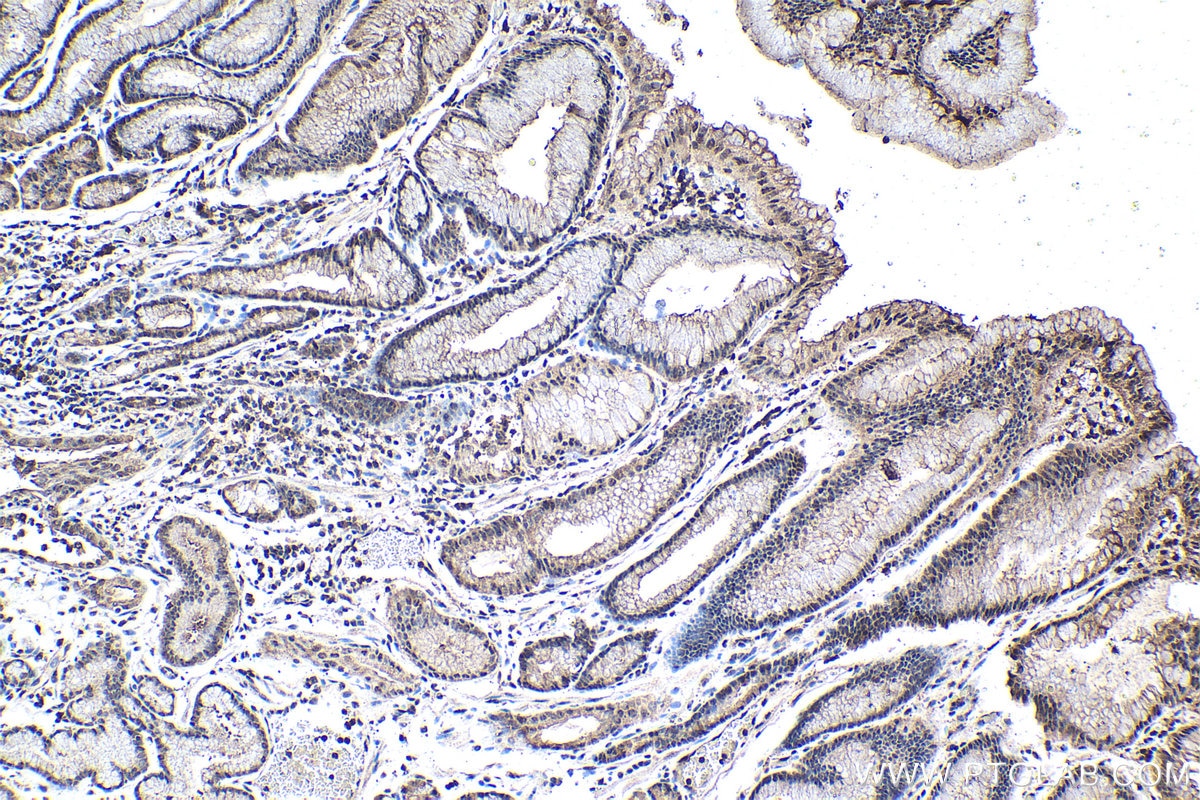
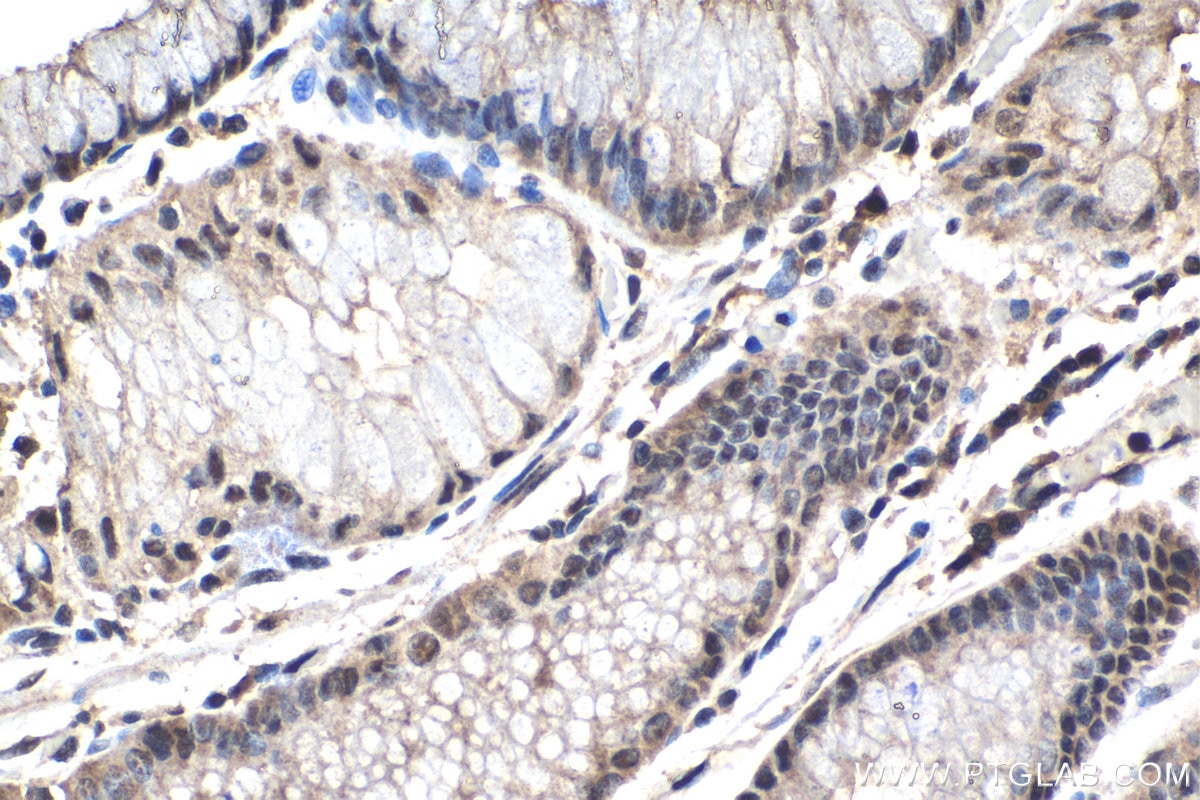
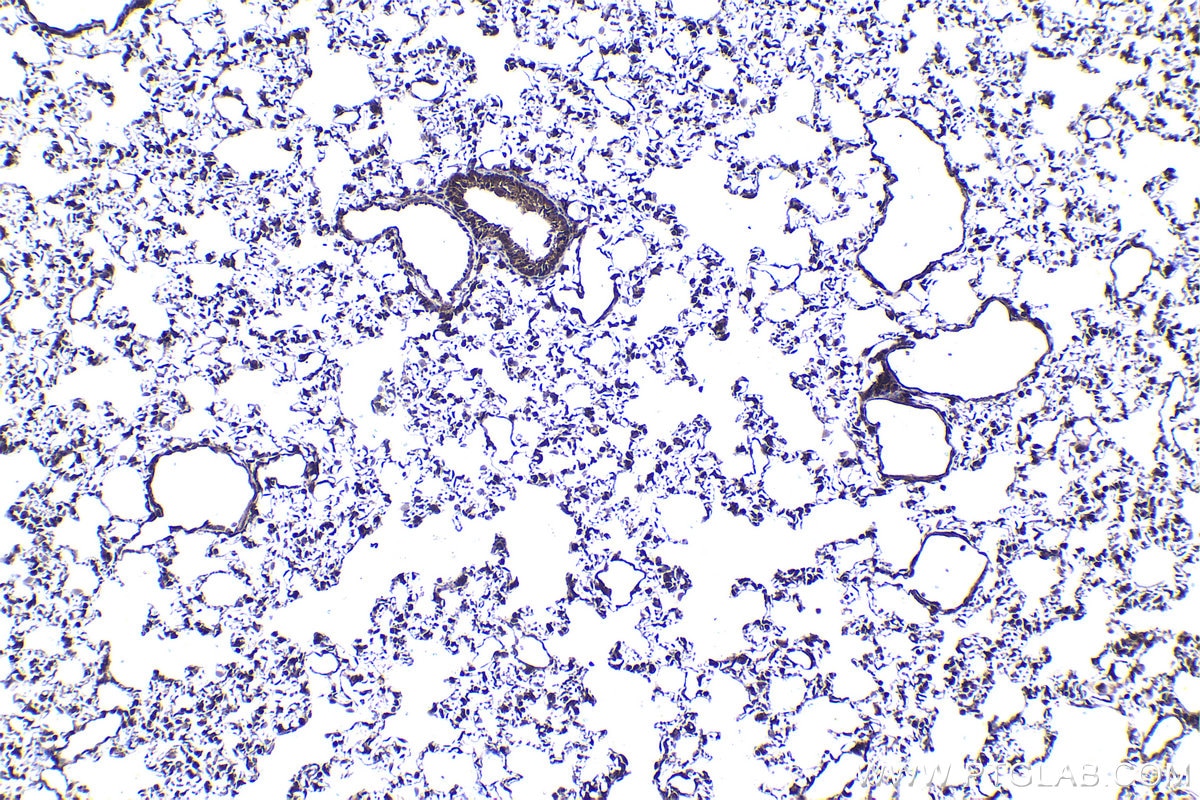
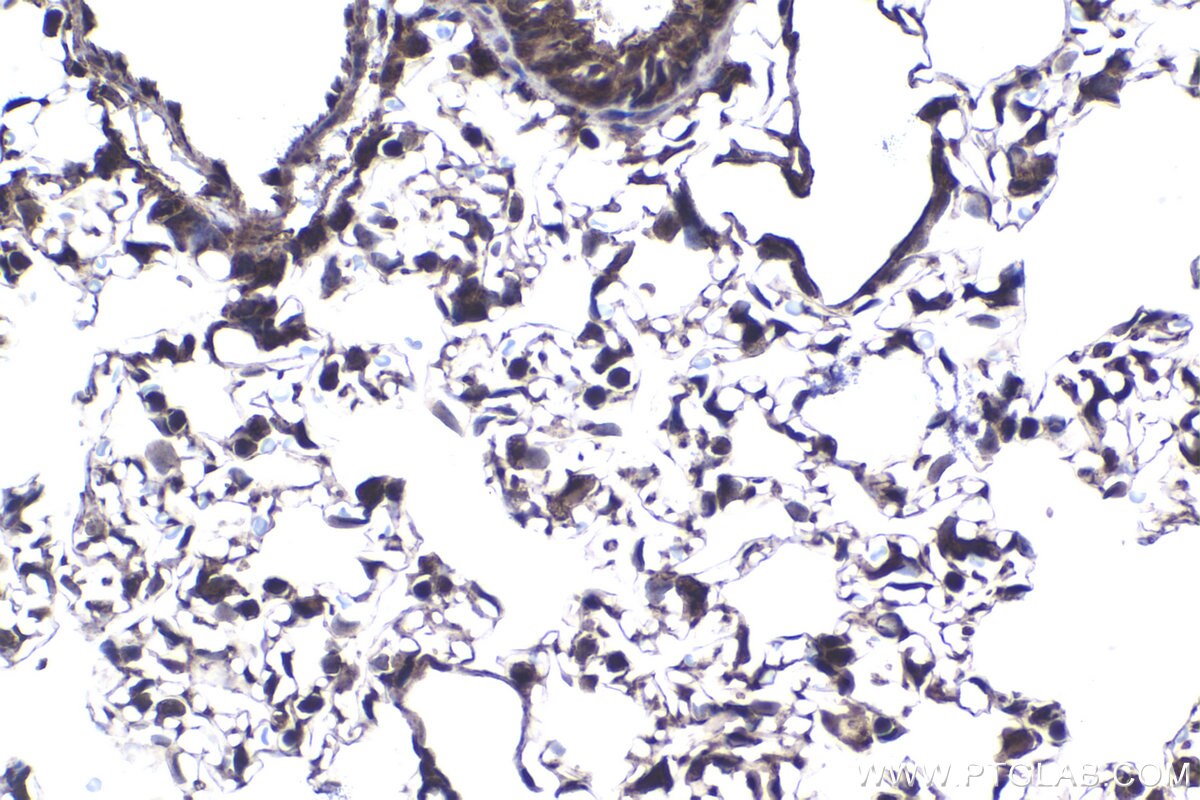
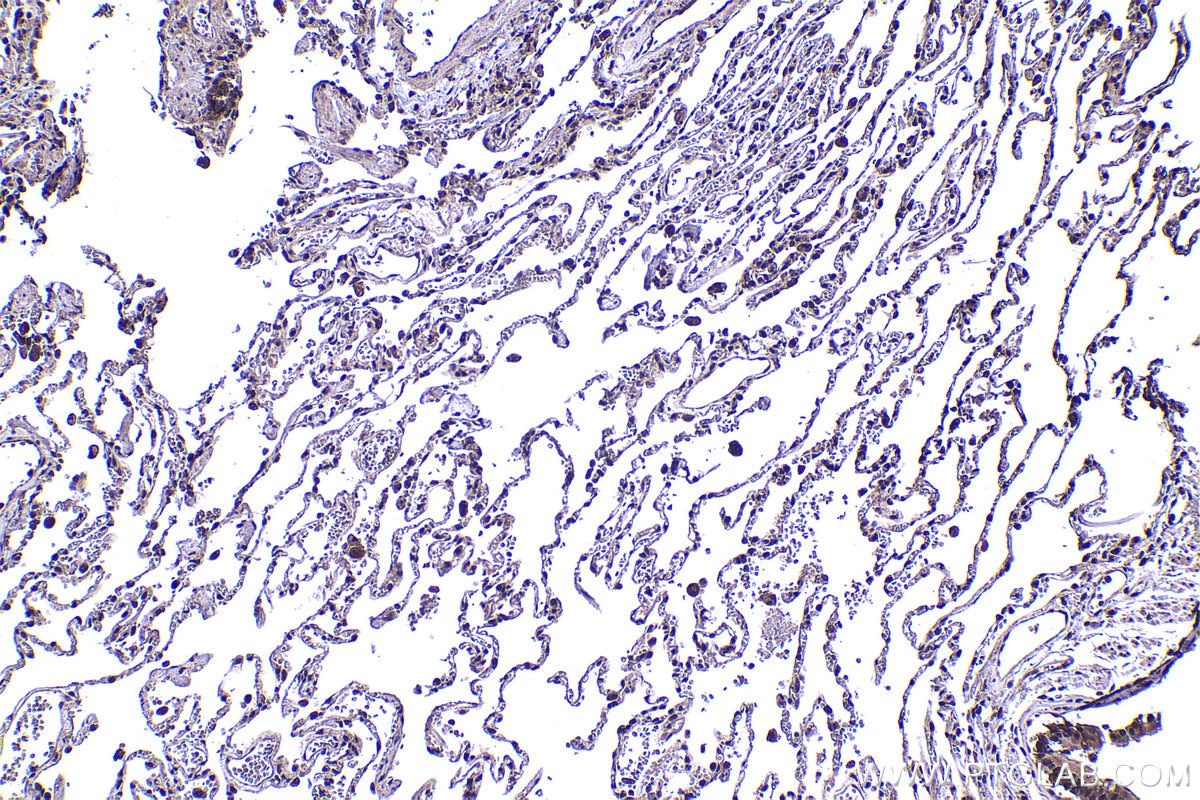
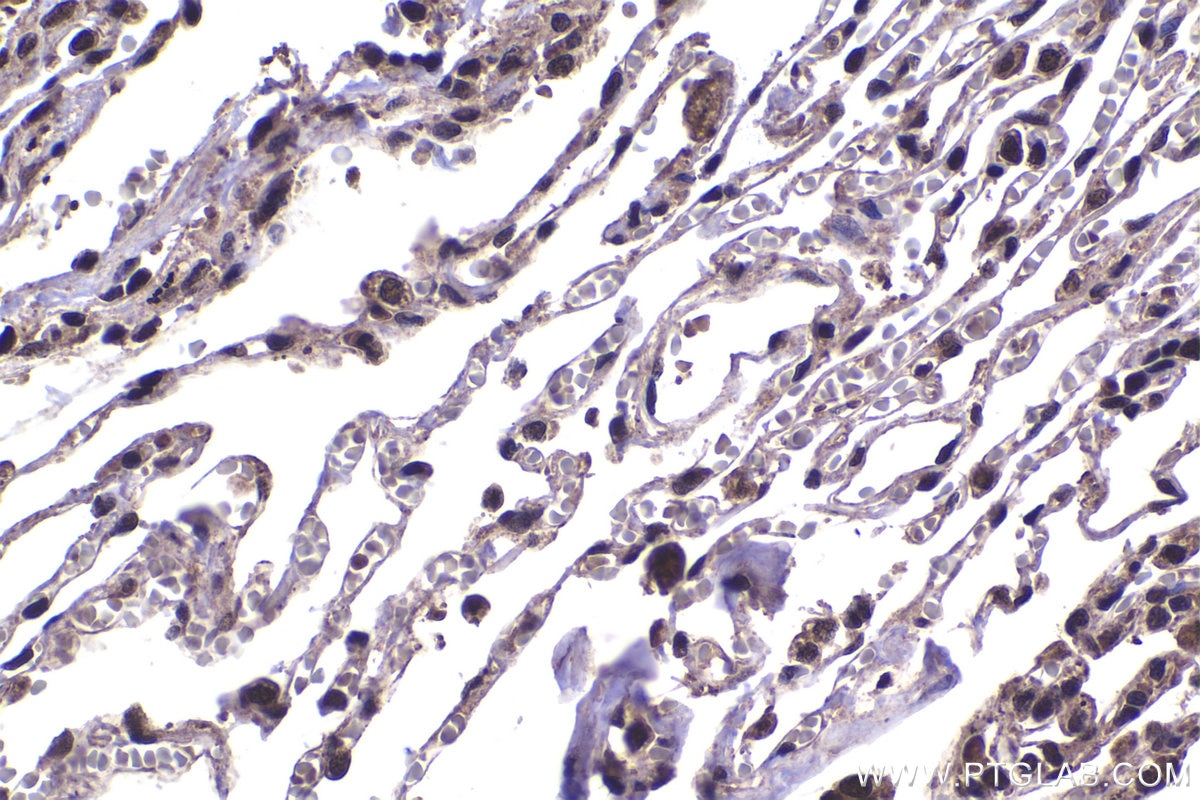
| Positive IHC detected in | human stomach cancer tissue, human lung tissue, rat lung tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
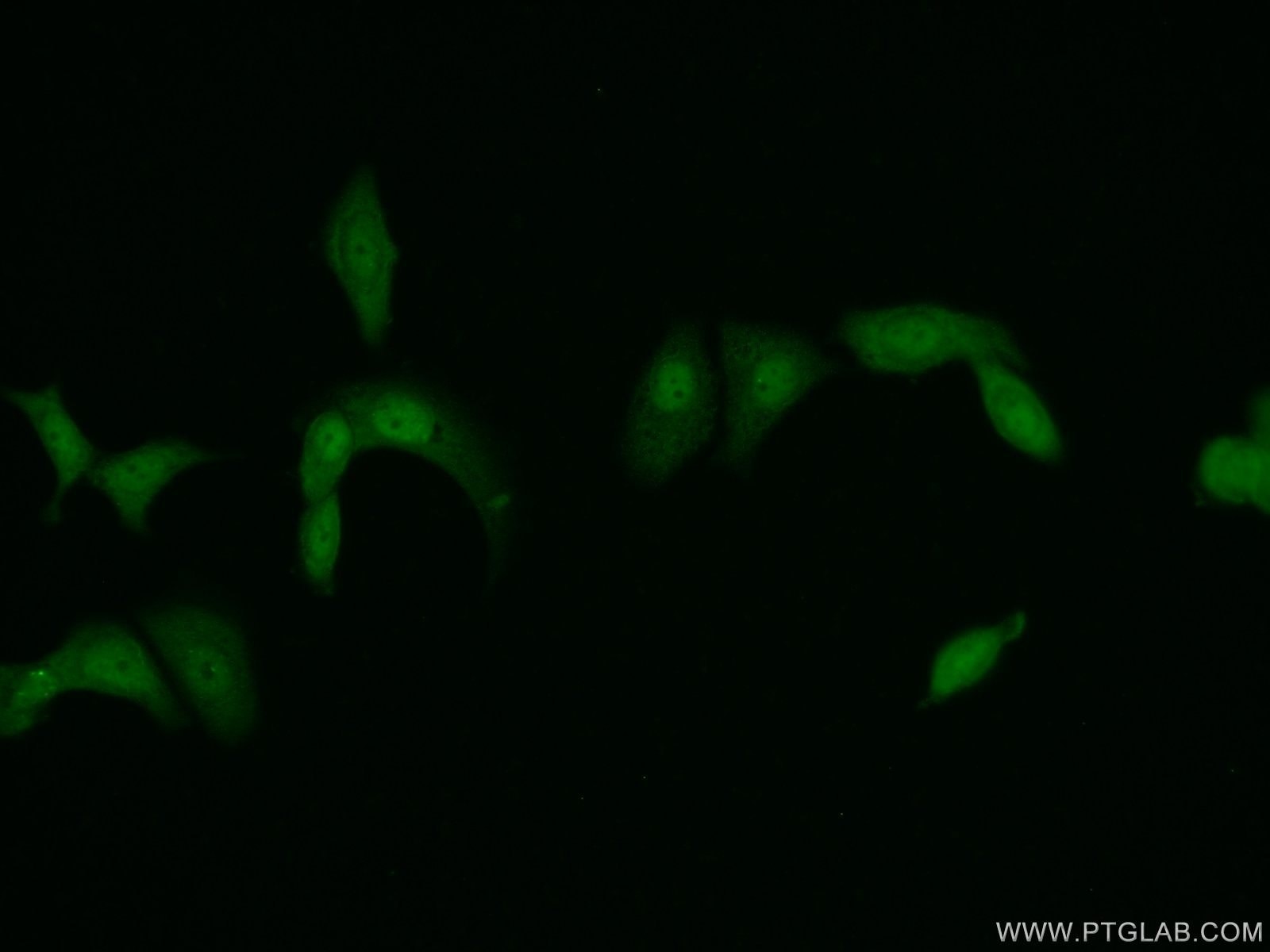
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | MCF-7 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:250-1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:10-1:100 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 9 publications below |
| IHC | See 1 publications below |
| IF | See 1 publications below |
| IP | See 1 publications below |
| CoIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
14786-1-AP targets PSMD11 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, CoIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | PSMD11 fusion protein Ag6435 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | proteasome (prosome, macropain) 26S subunit, non-ATPase, 11 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 47 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 47 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC000437 |
| Gene Symbol | PSMD11 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5717 |
| RRID | AB_2268979 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | O00231 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
The 26 S proteasome is a 2.5-MDa molecular machine that degrades ubiquitinated proteins in eukaryotic cells. It consists of a proteolytic core particle and two 19 S regulatory particles (RPs) composed of 6 ATPase (RPT) and 13 non-ATPase (RPN) subunits. PSMD11 gene encodes 19S proteasome subunit RPN6. Increased levels of PSMD11 and a corresponding increased assembly of the 26S/30S proteasome is correlated with high proteasome activity. In vitro ectopic expression of PSMD11 is sufficient to increase proteasome assembly and activity. Latest research has implicated PSMD11 in regulation of human embryonic stem cells function.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for PSMD11 antibody 14786-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for PSMD11 antibody 14786-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for PSMD11 antibody 14786-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for PSMD11 antibody 14786-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Oncogene The degradation of p53 and its major E3 ligase Mdm2 is differentially dependent on the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor S5a. | ||
Mol Cell Proteomics Proteomic Profiling Identified Multiple Short-lived Members of the Central Proteome as the Direct Targets of the Addicted oncogenes in Cancer Cells. | ||
J Med Chem Target Fishing Reveals a Novel Mechanism of 1,2,4-Oxadiazole Derivatives Targeting Rpn6, a Subunit of 26S Proteasome. | ||
FASEB J Susceptibility of microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3β (MAP1LC3B/ LC3B) knockout mice to lung injury and fibrosis. | ||
J Cell Biochem Homoharringtonine could induce quick protein synthesis of PSMD11 through activating MEK1/ERK1/2 signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. | ||
BMC Dev Biol Generation and identification of a conditional knockout allele for the PSMD11 gene in mice. |