Paxillin Polyclonal antibody
Paxillin Polyclonal Antibody for WB, ELISA
Host / Isotype
Rabbit / IgG
Reactivity
human
Applications
WB, ELISA
Conjugate
Unconjugated
Cat no : 32083-1-AP
Synonyms
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
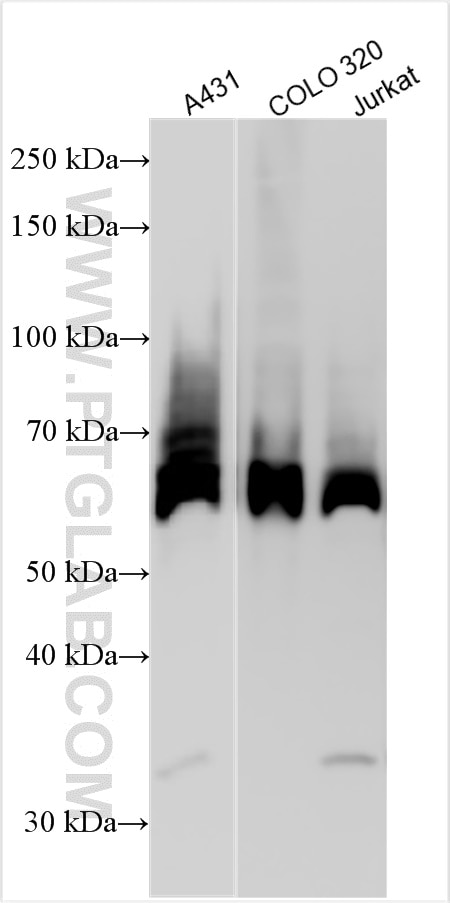
| Positive WB detected in | A431 cells, COLO 320 cells, Jurkat cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:5000-1:50000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
32083-1-AP targets Paxillin in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Paxillin fusion protein Ag33616 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | paxillin |
| Calculated molecular weight | 68kd |
| Observed molecular weight | 68 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_001080855 |
| Gene symbol | Paxillin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5829 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol pH 7.3. |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
PXN (paxillin) is a 68 kDa scaffold protein that interacts with multiple structural and signaling proteins and regulates cell adhesion, migration, proliferation, and apoptosis. PXN is thought to play an important role in tumor migration, invasion, and metastasis (21045234). PXN has been identified as a direct substrate of protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor-type T (PTPRT), a potent tumor suppressor gene. Increased phospho-PXN at tyrosine residue 88 (Y88) has been found as a common feature of human colon cancers (20133777).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for Paxillin antibody 32083-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |