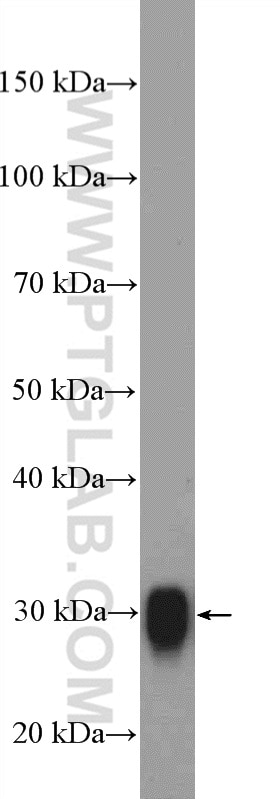
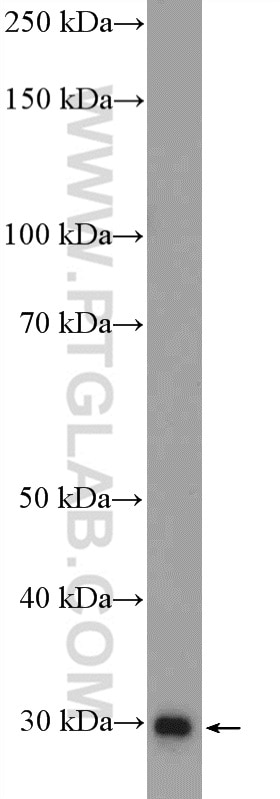
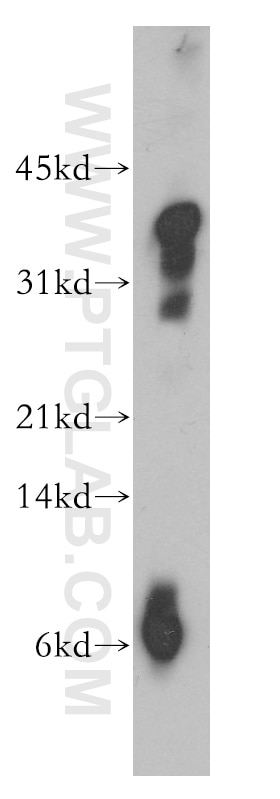
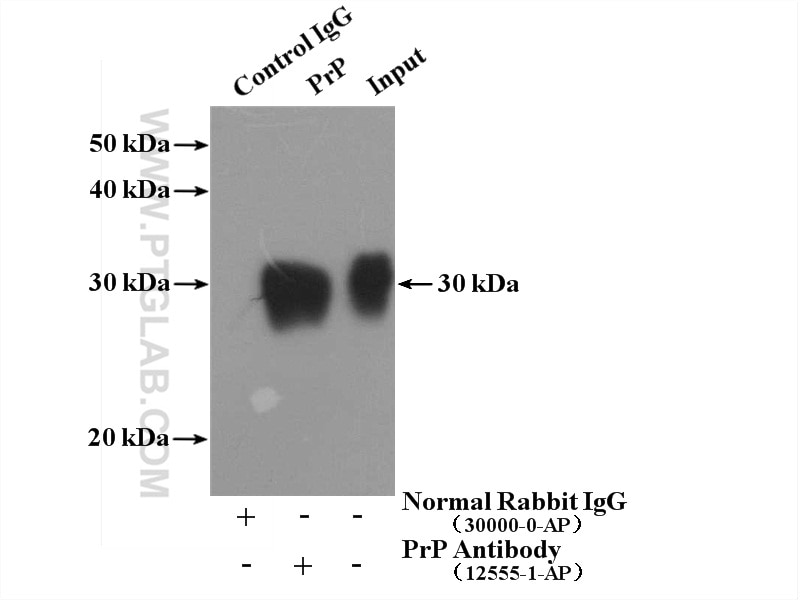
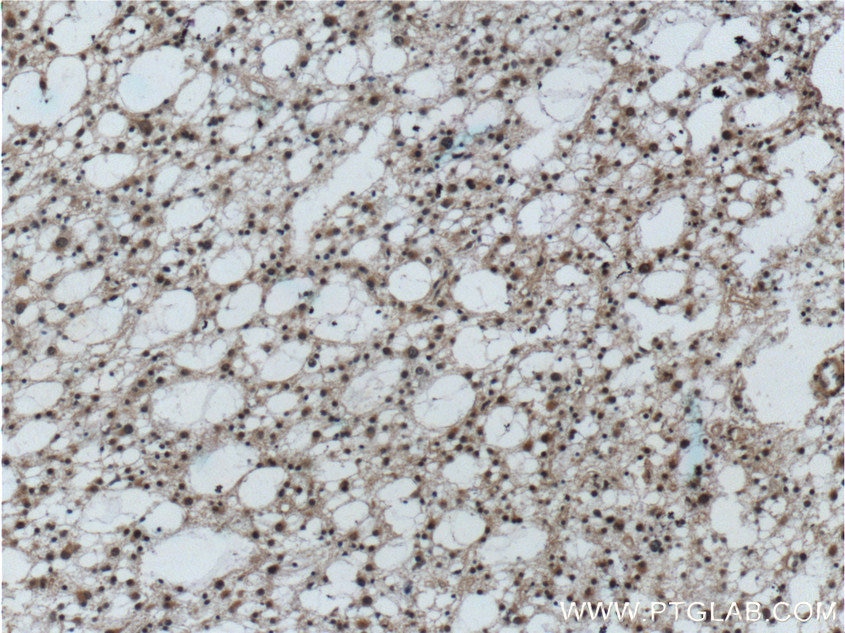
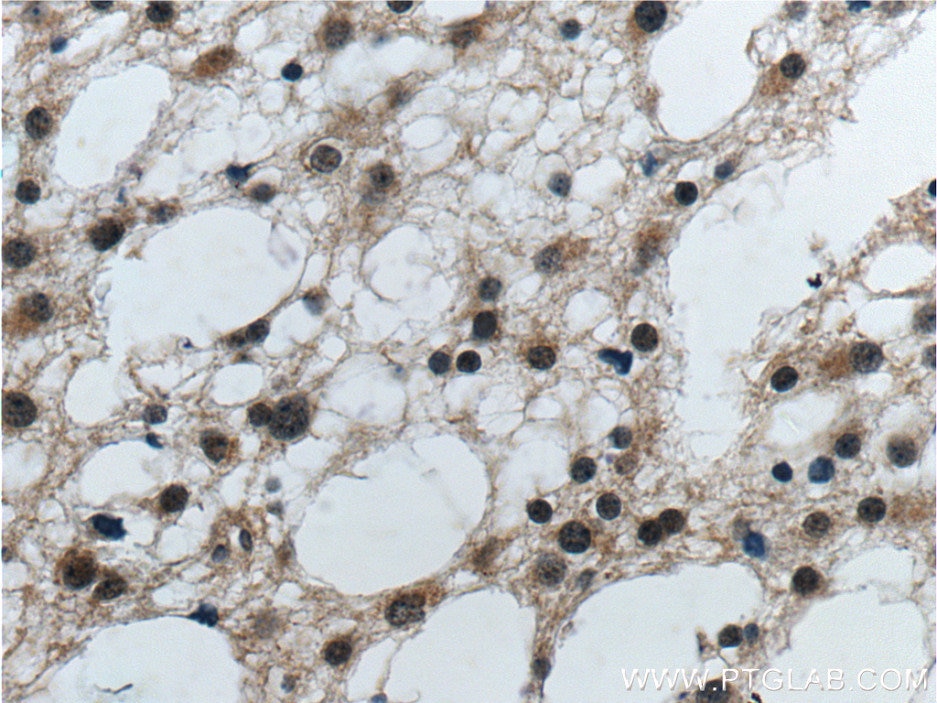
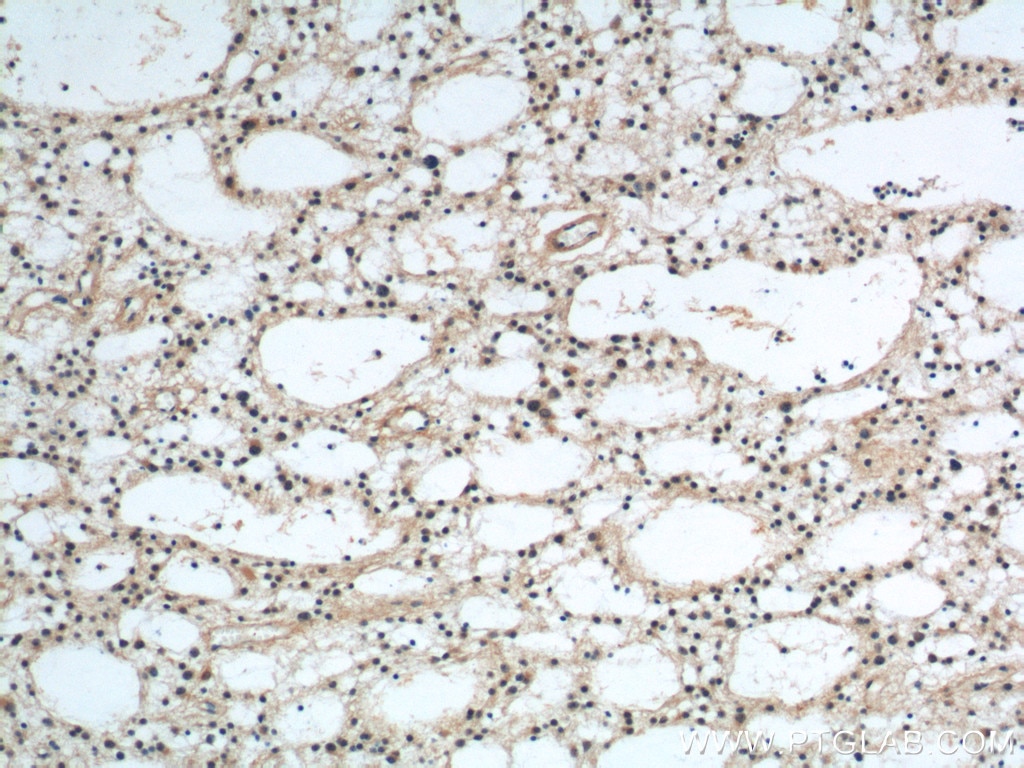
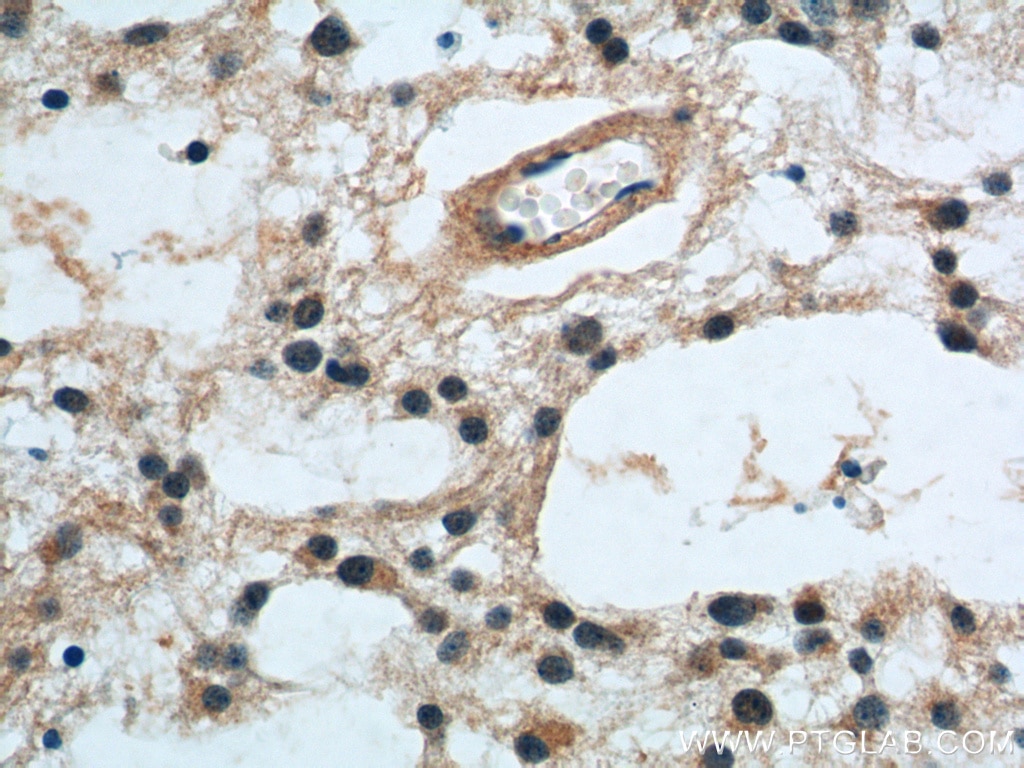
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
12555-1-PBS targets Prion protein PrP/CD230 in WB, IHC, IP, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Prion protein PrP/CD230 fusion protein Ag3257 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | prion protein |
| Calculated molecular weight | 34 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 30 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC022532 |
| Gene Symbol | PrP |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5621 |
| RRID | AB_2237745 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P04156 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Prion protein (PRNP) is a ubiquitous membrane glycoprotein whose abnormal self-replicating, misfolded form is widely believed to cause several central nervous system disorders, collectively known as Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies (TSE). Prion diseases are TSEs, attributed to conformational conversion of the cellular prion protein (PrPC) into an abnormal conformer that accumulates in the brain. The two isoforms, PrPC and PrPS, have the same primary amino acid sequence and only differ in conformation. While PrPC is composed of 42% α-helix and only 3% β-sheet, PrPSc is composed of 30% α-helix and 43% β-sheet. PrPC converts to its pathogenic isoform when the region corresponding to the residues 108-144 fold into β-sheets. PrPC is very soluble in detergents and easily digested by proteases while the PrPSc is insoluble in detergents and resistant to protease digestion. Prion diseases exist in infectious, sporadic, and genetic forms.