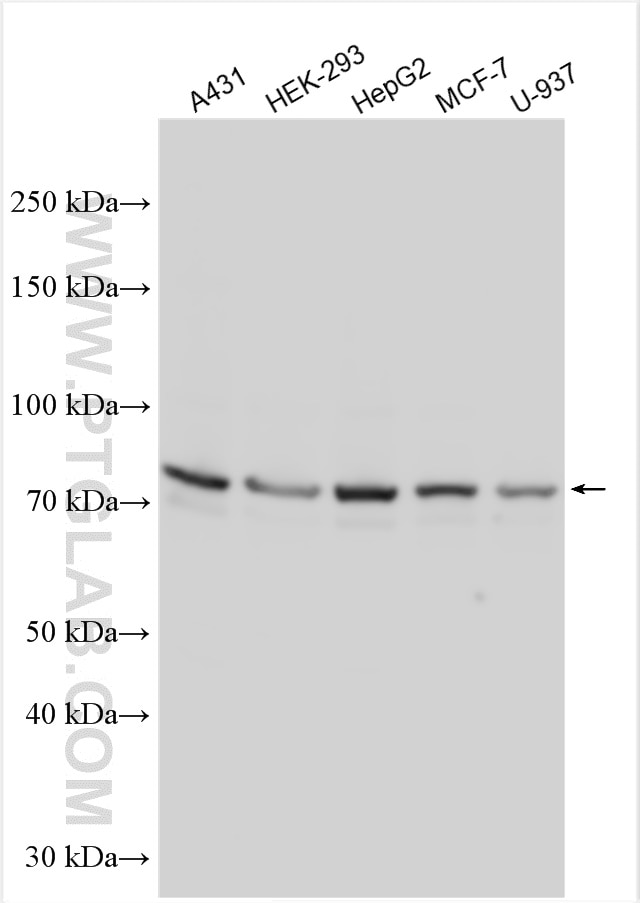
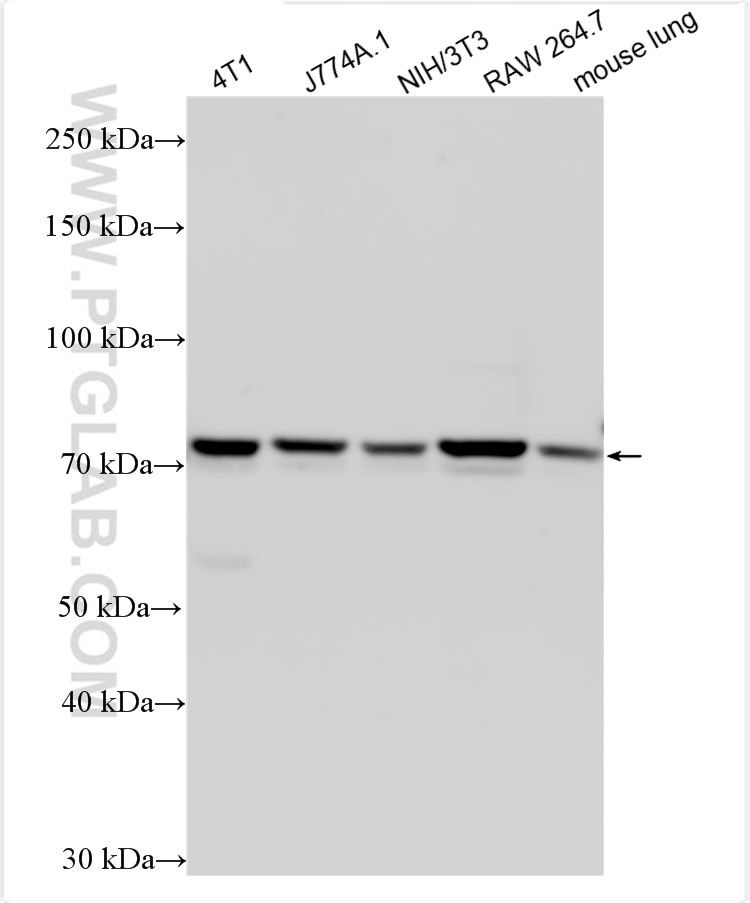
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
29491-1-PBS targets Progranulin/PGRN in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | Progranulin/PGRN fusion protein Ag30723 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | granulin |
| Calculated molecular weight | 64 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 70-75 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC000324 |
| Gene Symbol | Granulin |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 2896 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P28799 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
GRN, also known as PGRN or PCDGF, is a cysteine-rich protein of 68.5 kDa that is typically secreted into a highly glycosylated 88 kDa form. PGRN is a unique growth factor that plays an important role in cutaneous wound healing. It has an anti-inflammatory effect and promotes cell proliferation. When PCDGF is degraded to several 6-25 kDa fragments, called granulins (GRNs) by neutrophil proteases, a pro-inflammatory reaction occurs. PGRN is widely expressed, particularly in epithelial cells, immune cells, neurons, and chondrocytes. High levels of PGRN expression have been reported in human cancers, and its expression is closely correlated with the development and metastasis of several cancers. The recent discovery that mutations in the gene encoding for pro-granulin (GRN) cause frontotemporal lobar degeneration (FTLD), and other neurodegenerative diseases leading to dementia, has brought renewed interest in progranulin and its functions in the central nervous system.