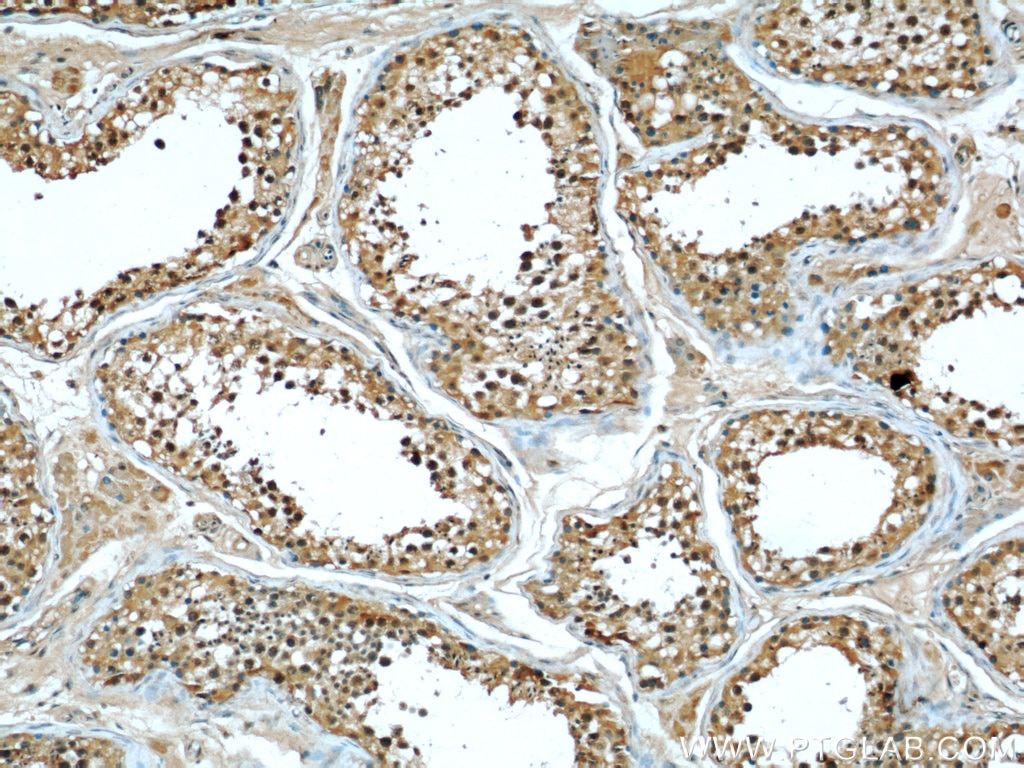
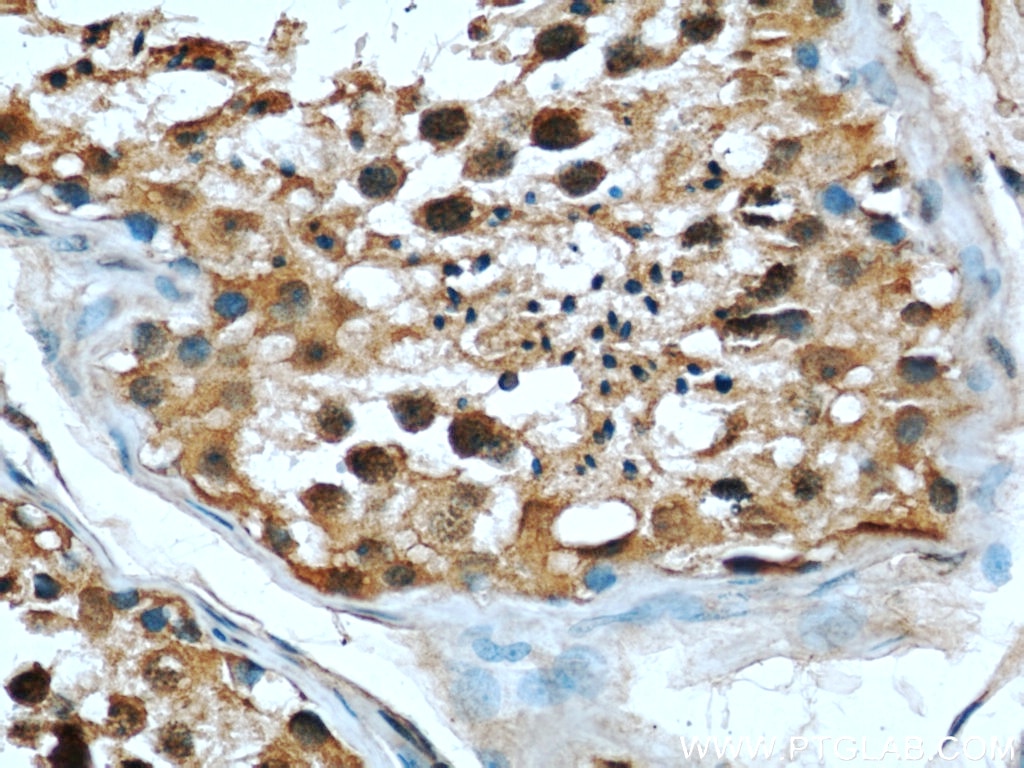
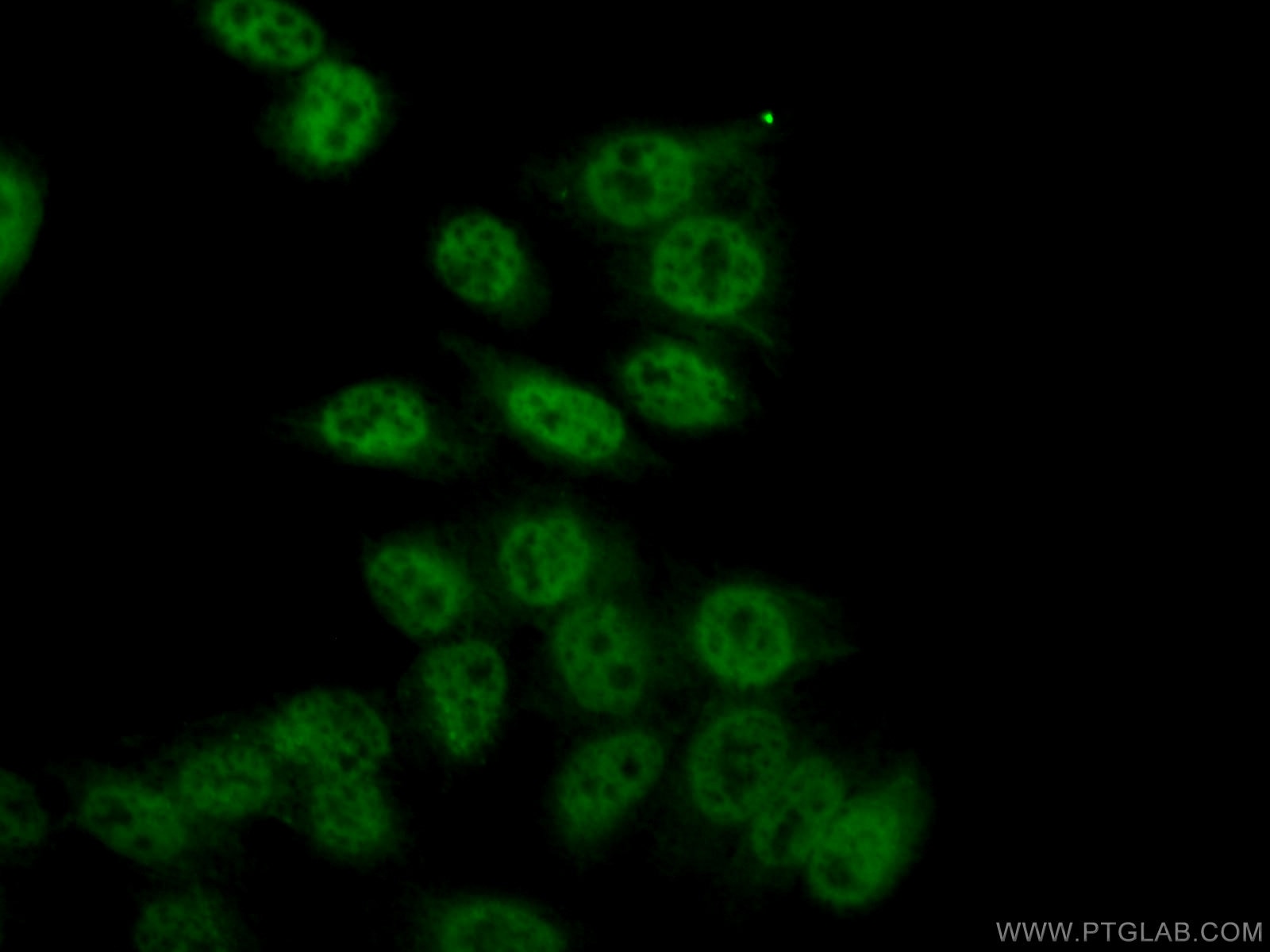
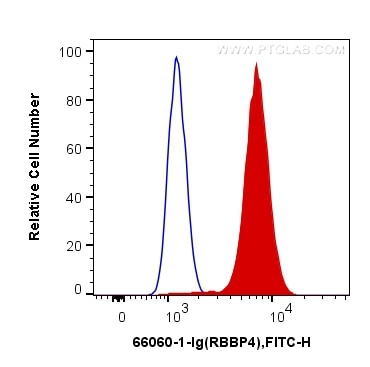
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
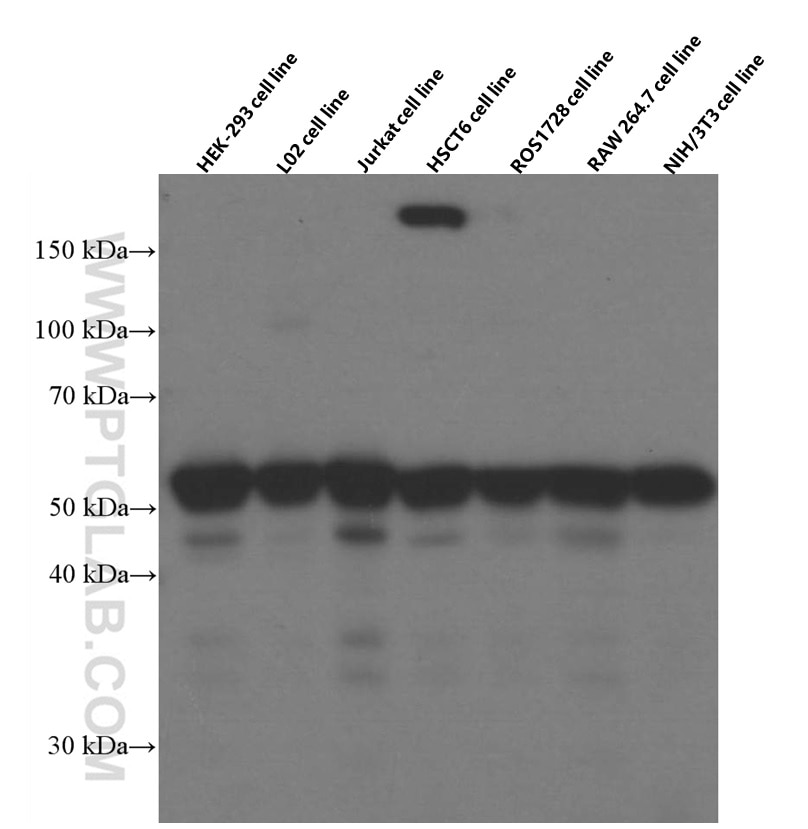
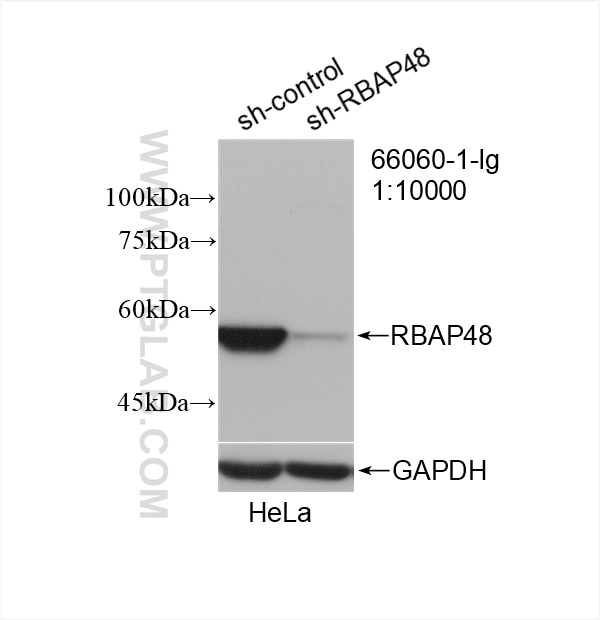
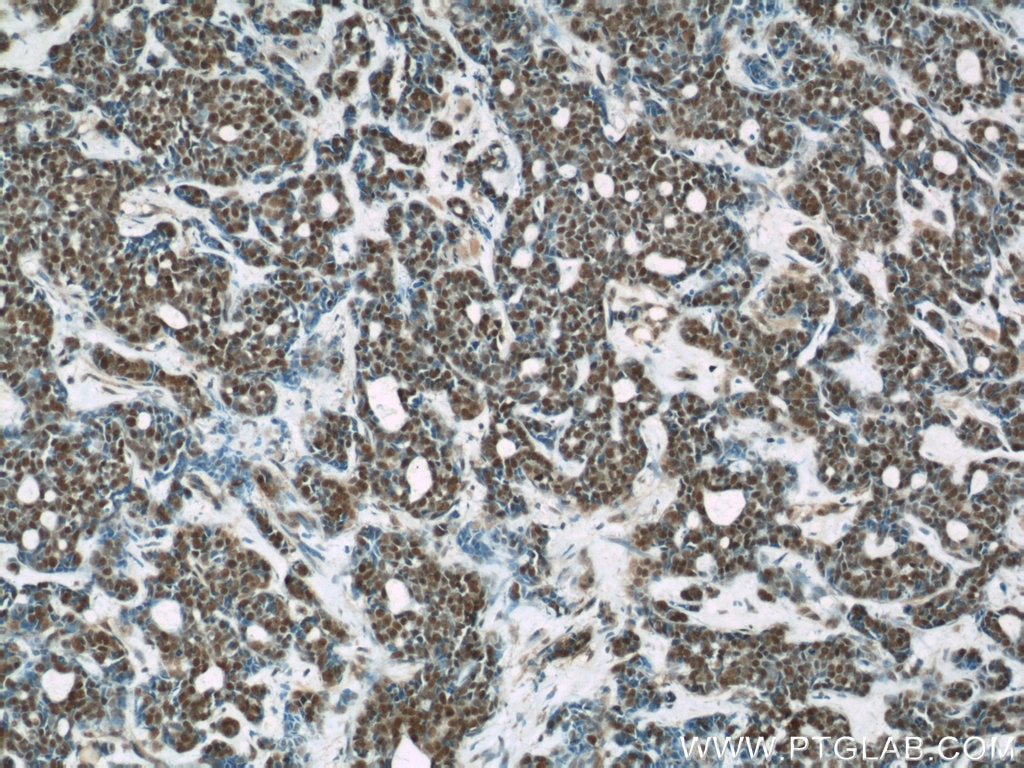
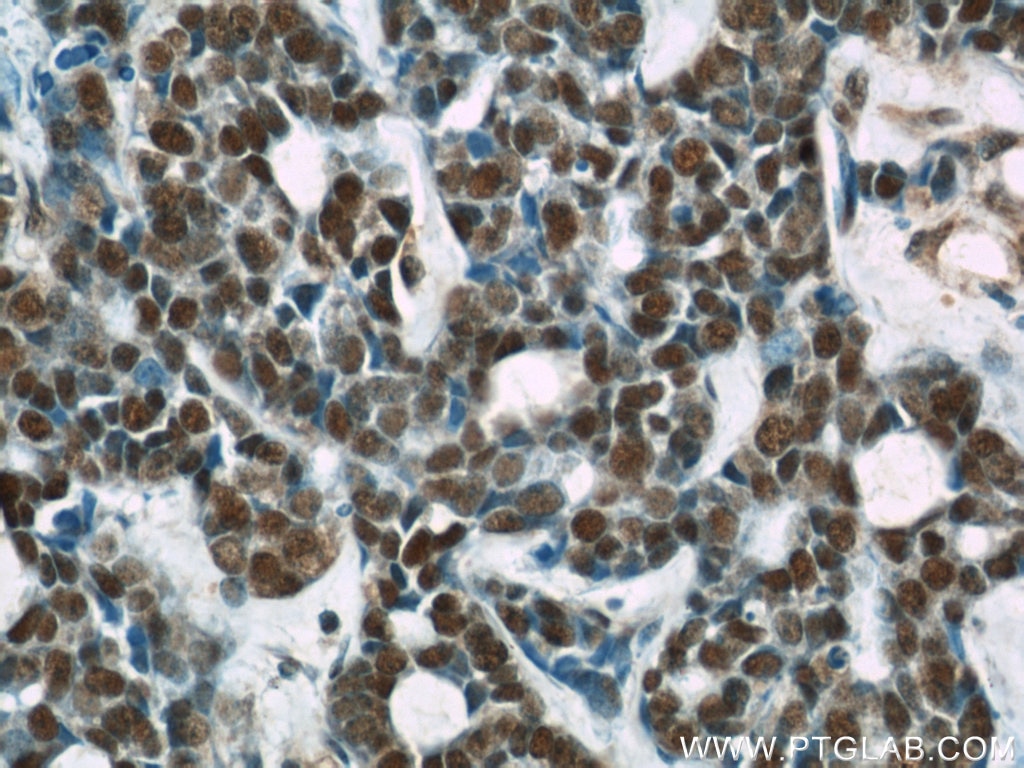
66060-1-PBS targets RBAP48 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with rat, mouse, human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | rat, mouse, human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG2b |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | RBAP48 fusion protein Ag6196 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | retinoblastoma binding protein 4 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 48 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 53 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC053904 |
| Gene Symbol | RBBP4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 5928 |
| RRID | AB_11064731 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q09028 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
Histone-binding protein RBBP4 (also known as RbAp48, or NURF55) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBBP4 gene. This gene encodes a ubiquitously expressed nuclear protein that belongs to a highly conserved subfamily of WD-repeat proteins. It is present in protein complexes involved in histone acetylation and chromatin assembly. It is part of the Mi-2/NuRD complex complex that has been implicated in chromatin remodeling and transcriptional repression associated with histone deacetylation. This encoded protein is also part of corepressor complexes, which is an integral component of transcriptional silencing. It is found among several cellular proteins that bind directly to retinoblastoma protein to regulate cell proliferation. A decrease of RbAp48 in the dentate gyrus (DG) of the hippocampus in the brain is suspected to be a main cause of memory loss in normal aging (PMID: 23986399).