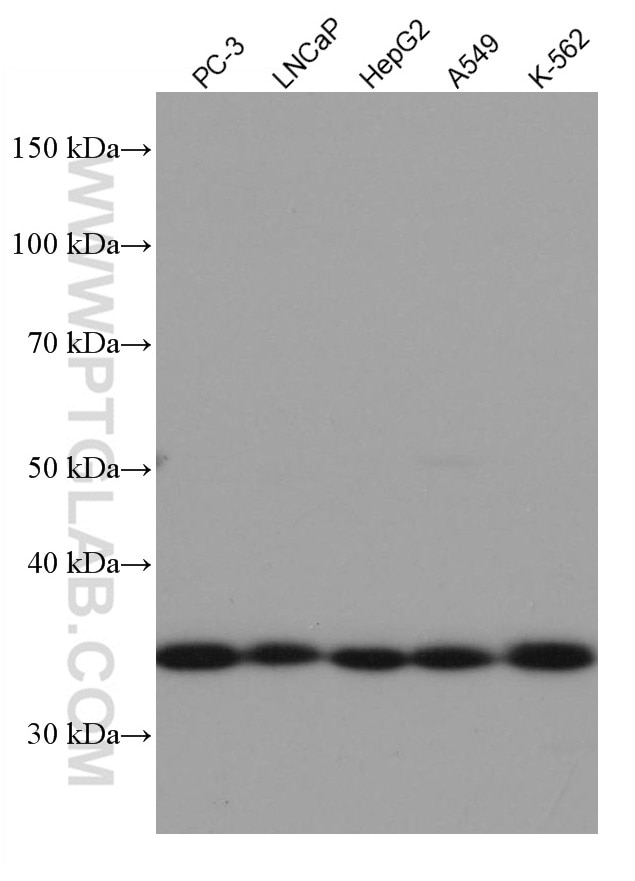
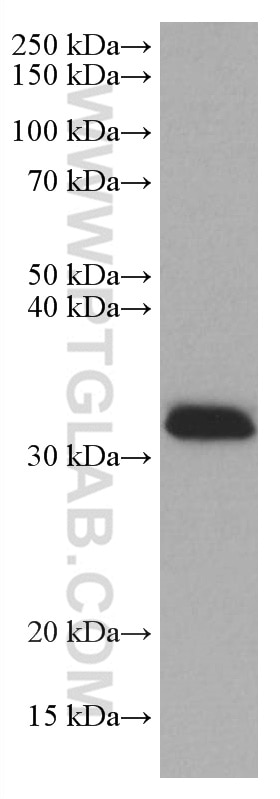
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
Product Information
67059-1-PBS targets REDD1 in WB, Indirect ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | REDD1 fusion protein Ag0965 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | DNA-damage-inducible transcript 4 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 25 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 32-35 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC007714 |
| Gene Symbol | REDD1/DDIT4 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 54541 |
| RRID | AB_2882369 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9NX09 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS only , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -80°C. |
Background Information
REDD1, also named as RTP801 and DDIT4, belongs to the DDIT4 family. REDD1 promotes neuronal cell death. It is a novel transcriptional target of p53 implicated ROS in the p53-dependent DNA damage response. REDD1 controlled cell growth under energy stress, as an essential regulator of TOR activity through the TSC1/2 complex. REDD-1 expression has also been linked to apoptosis, Aβ toxicity and the pathogenesis of ischemic diseases. As an HIF-1-responsive gene, REDD-1 exhibits strong hypoxia-dependent upregulation in ischemic cells of neuronal origin[PMID: 19996311]. In response to stress due to DNA damage and glucocorticoid treatment, REDD-1 is upregulated at the transcriptional level[PMID: 21733849]. REDD-1 negatively regulates the mammalian target of Rapamycin, a serine/threonine kinase often referred to as mTOR[PMID: 22951983]. It is crucial in the coupling of extra- and intracellular cues to mTOR regulation. The absence of REDD-1 is associated with the development of retinopathy, a major cause of blindness[PMID: 22304497]. REDD1 is a new host defense factor, and chemical activation of REDD1 expression represents a potent antiviral intervention strategy[PMID: 21909097]. The calculated molecular weight of REDD1 is 25 kDa. Because of multiple lysines in the proteins, REDD1 offen migrates around 35 kDa on Western blot[PMID: 19221489].