Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
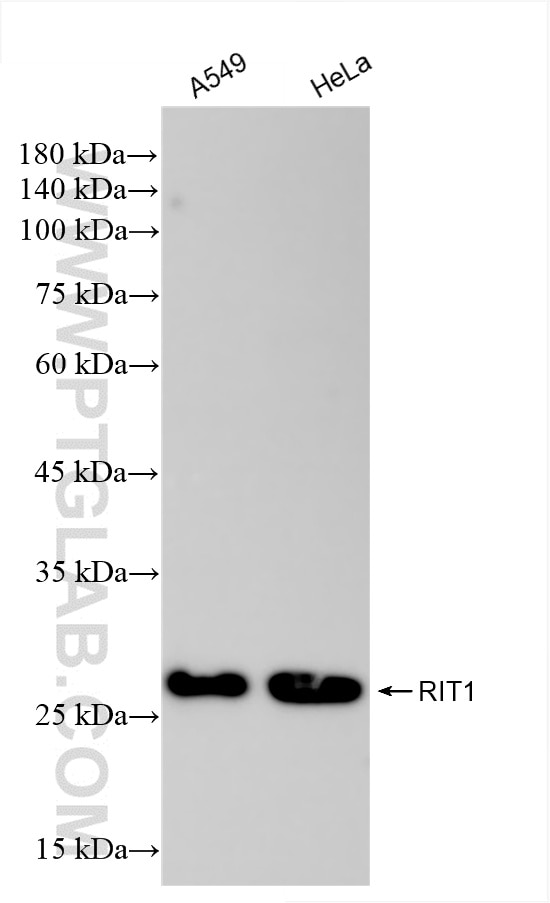
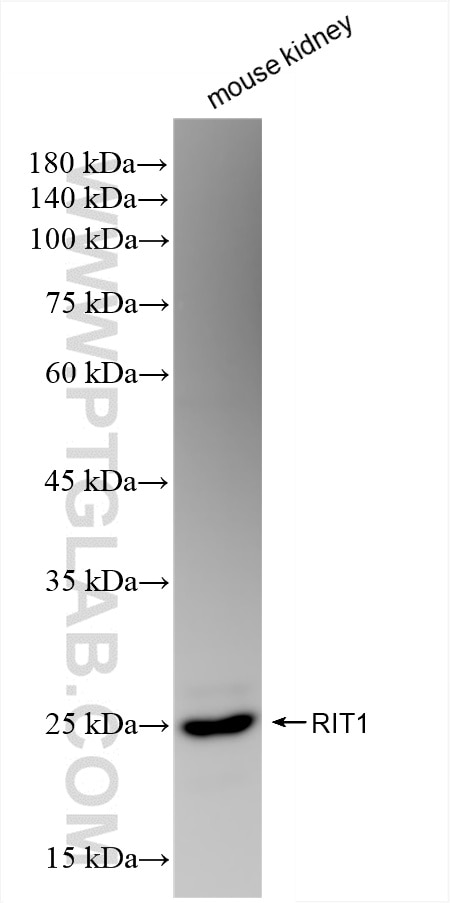
| Positive WB detected in | A549 cells, mouse kidney tissue, HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
85347-1-RR targets RIT1 in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Recombinant |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | RIT1 fusion protein Ag25636 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | Ras-like without CAAX 1 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 25 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 25-28 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC104186 |
| Gene Symbol | RIT1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6016 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein A purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q92963 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
RIT1 (Ras-like without CAAX protein 1) is also named as RIBB, ROC1 and GTP-binding protein Rit1. RIT1 serves as a regulatory factor for neuronal cell proliferation, survival, and differentiation (PMID: 28007959). Rit1 mediates oxidative stress resistance, contributing to cell survival via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway (PMID: 21737674). As a small G protein of Ras family, RIT1 plays a critical role in various tumors (such as hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC) (PMID: 38017479). It is worth noting that RIT1 is frequently amplified in various human cancers including HCC, lung adenocarcinoma, cholangiocarcinoma, uterine carcinosarcoma, breast cancer, and ovarian cancer (PMID: 38017479).
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for RIT1 antibody 85347-1-RR | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |