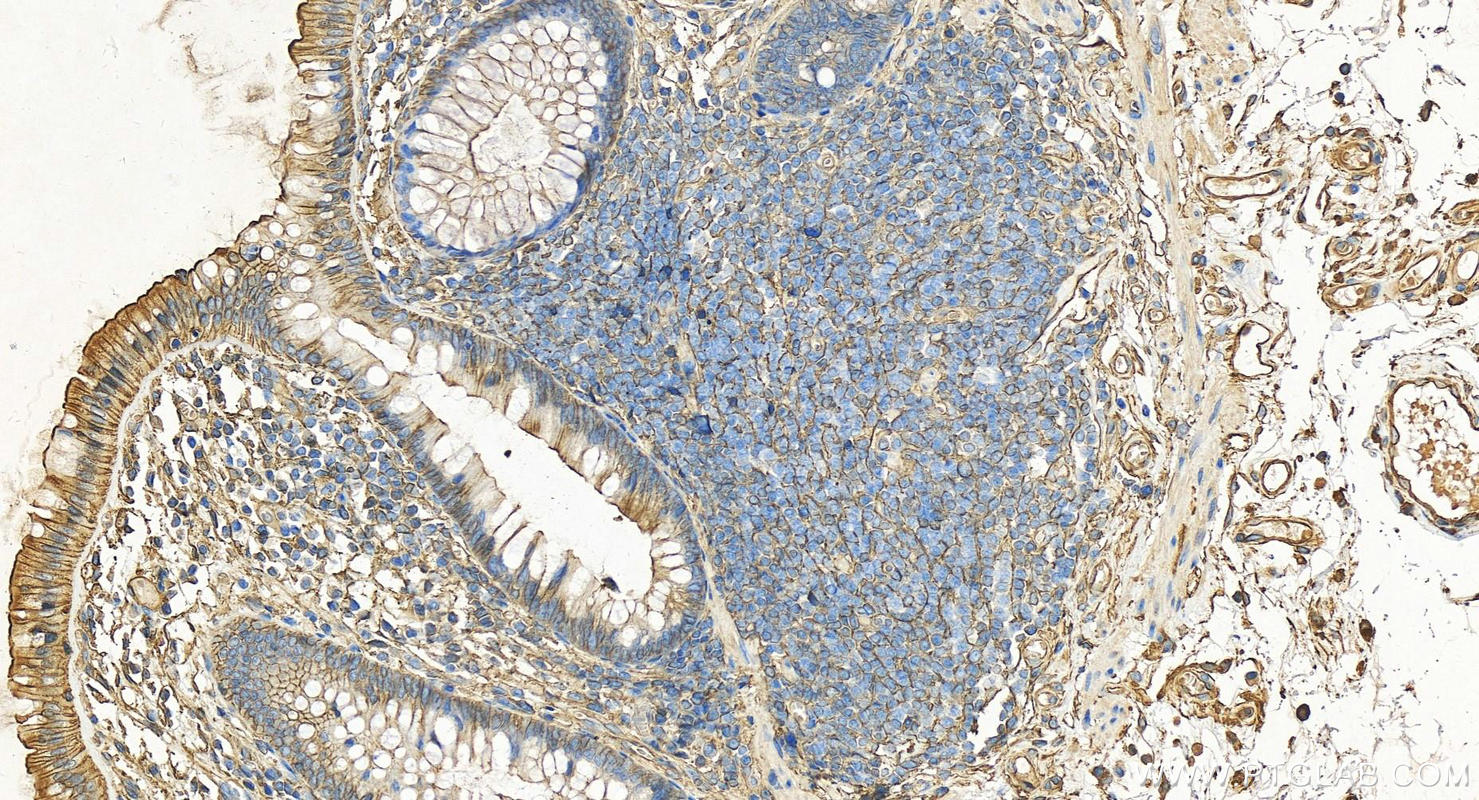
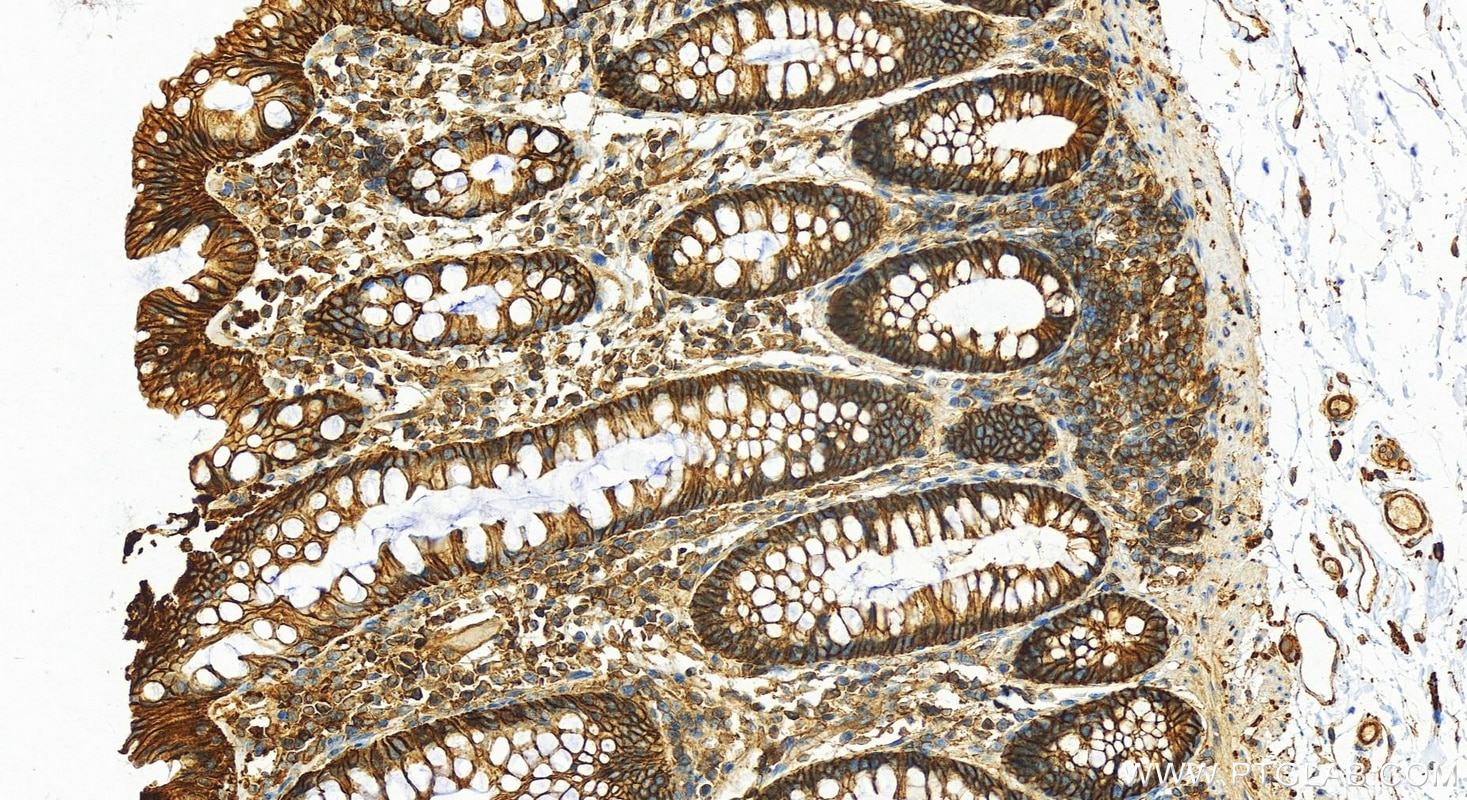
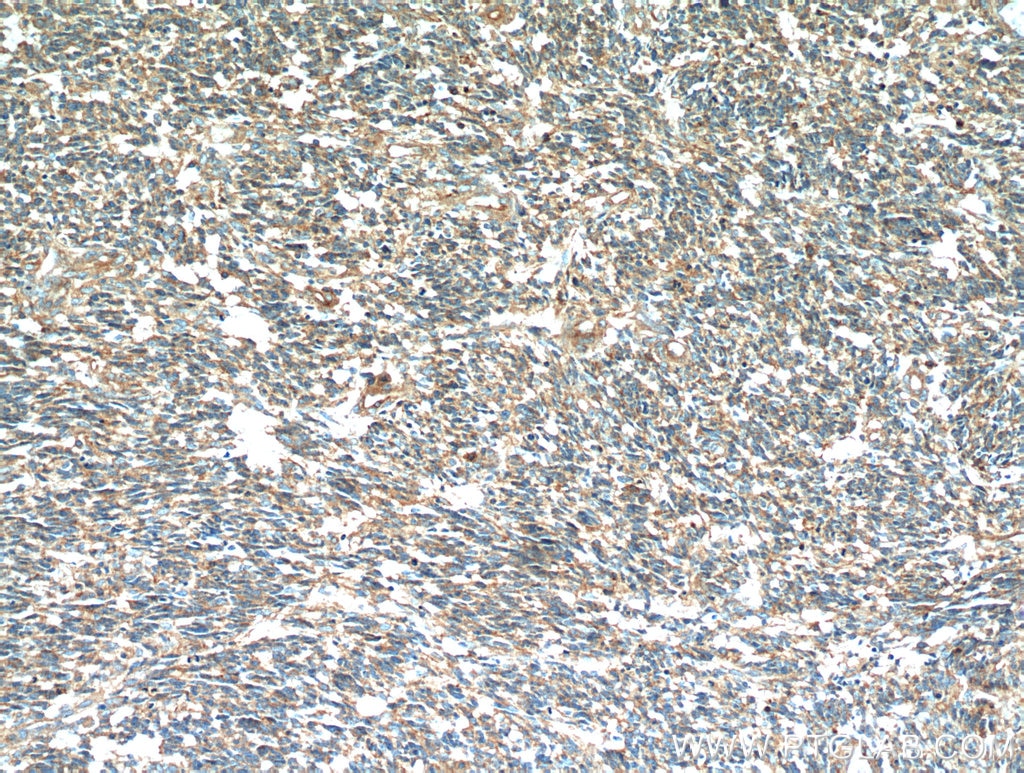
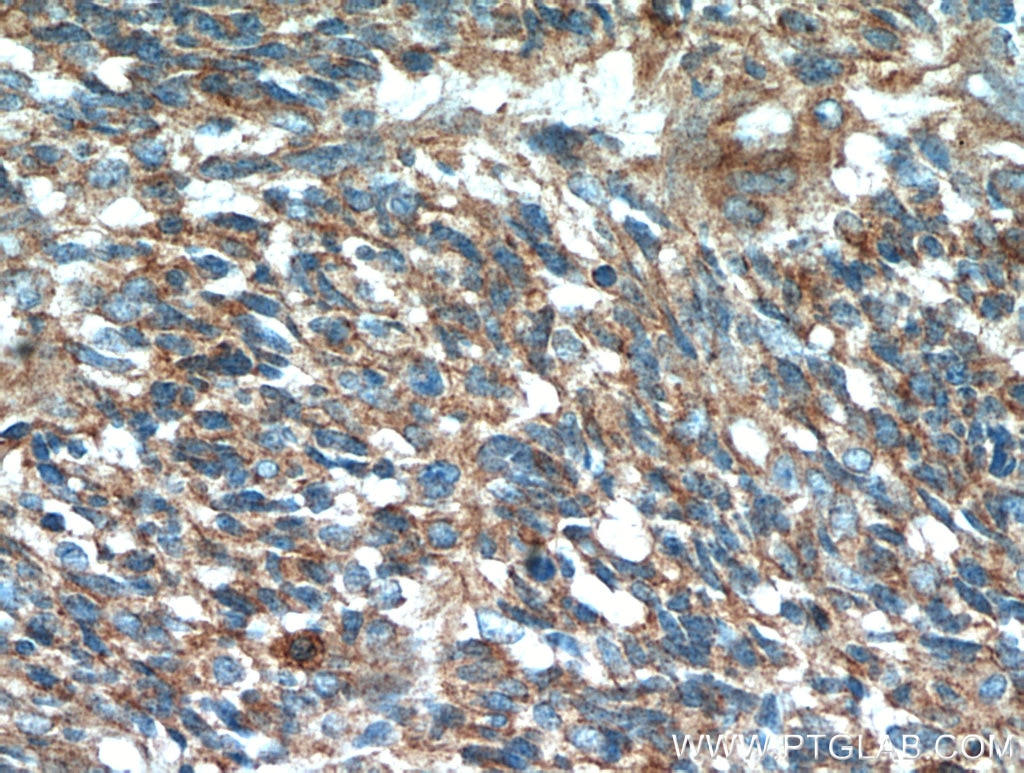
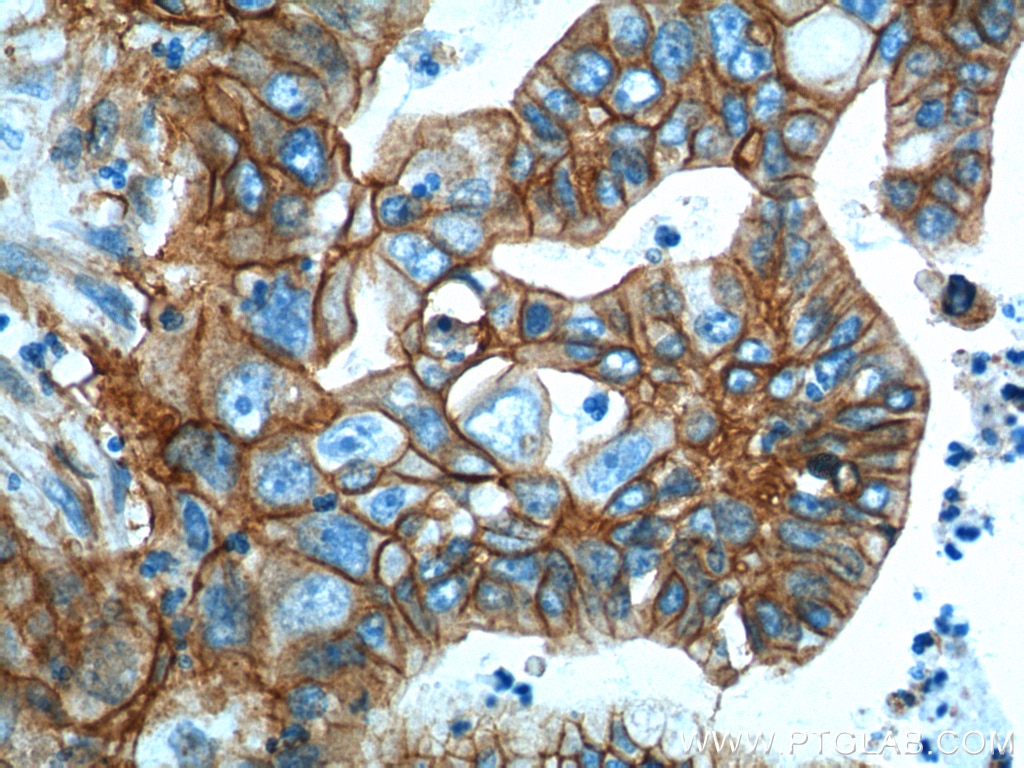
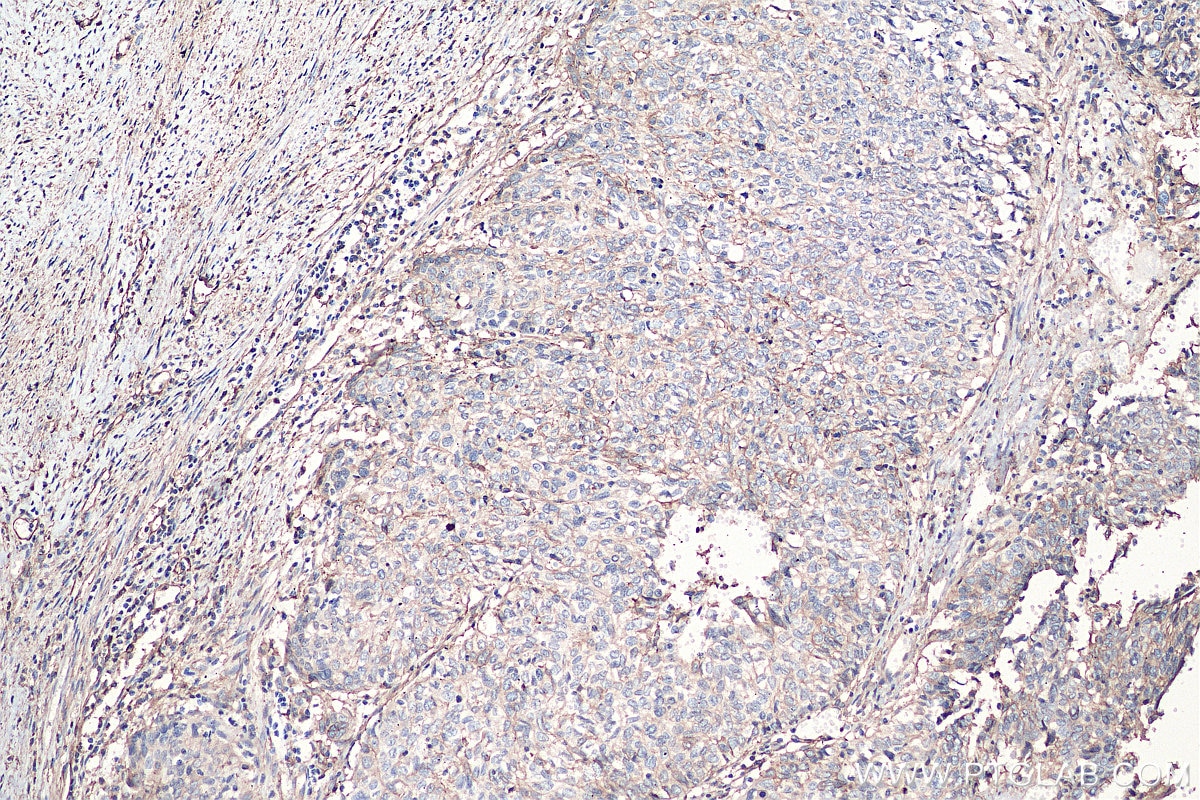
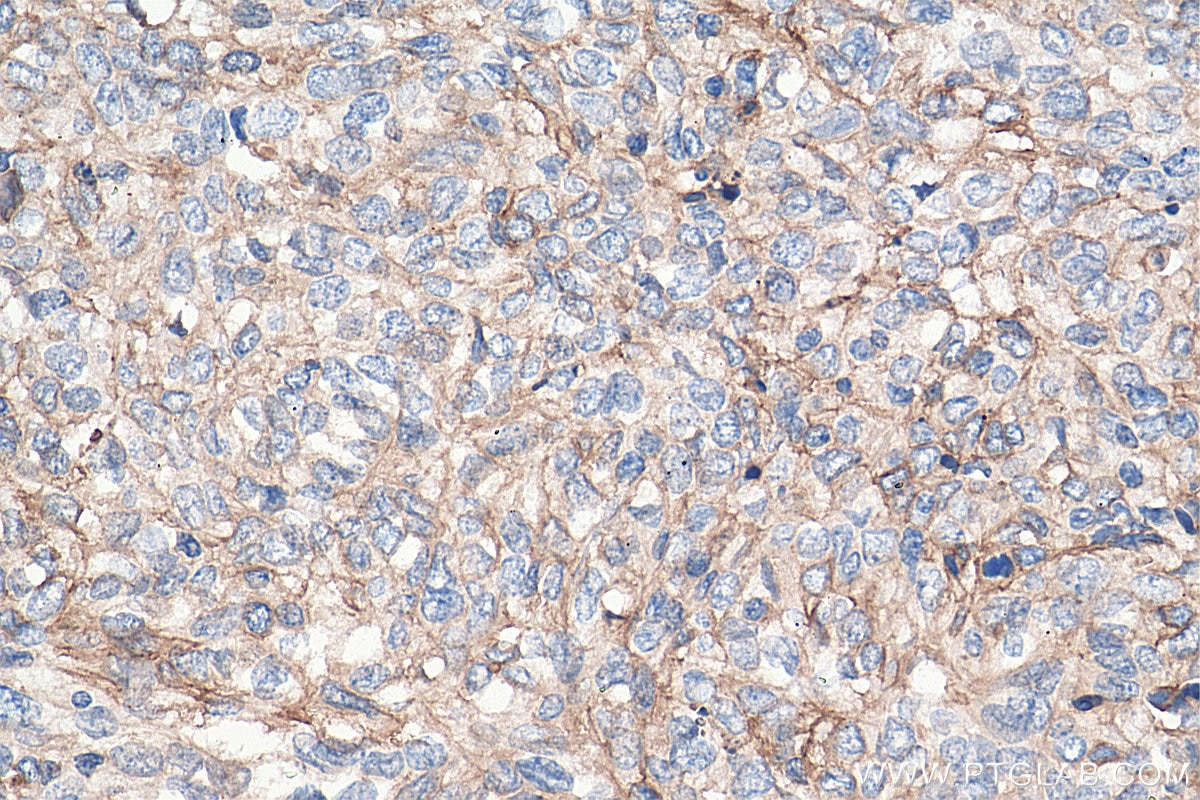
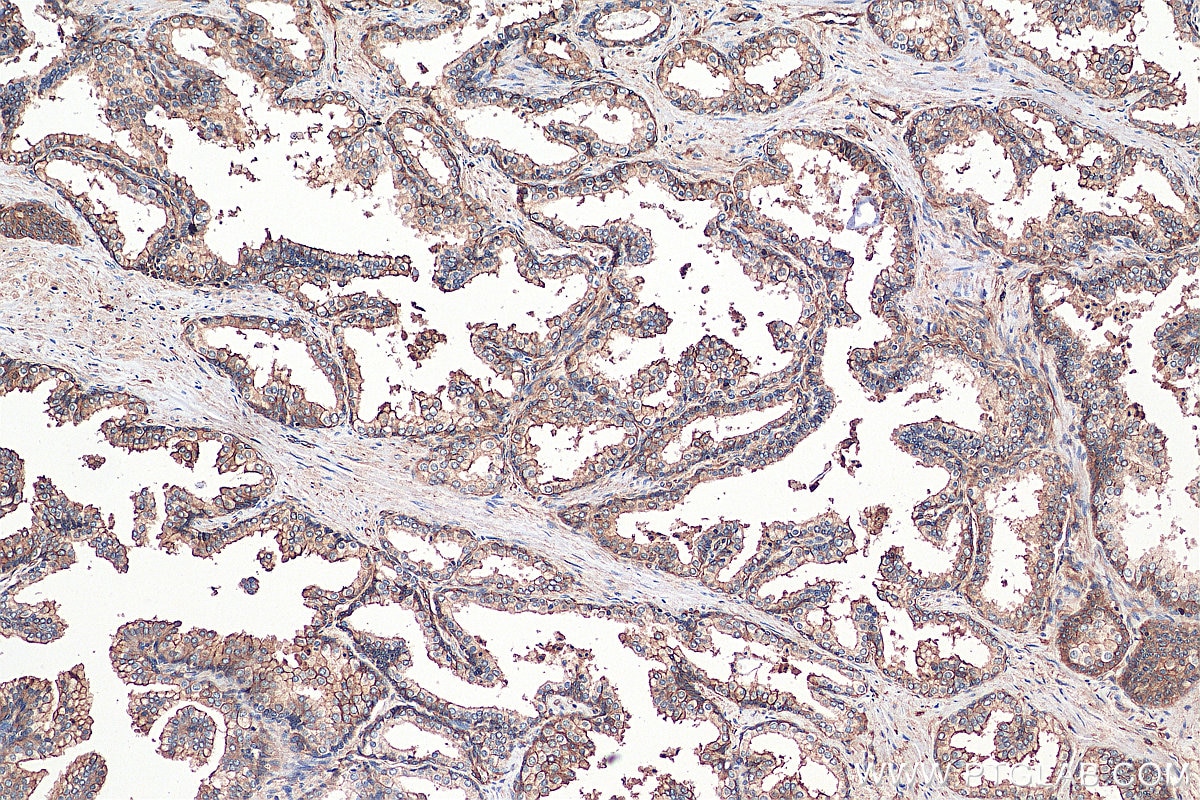
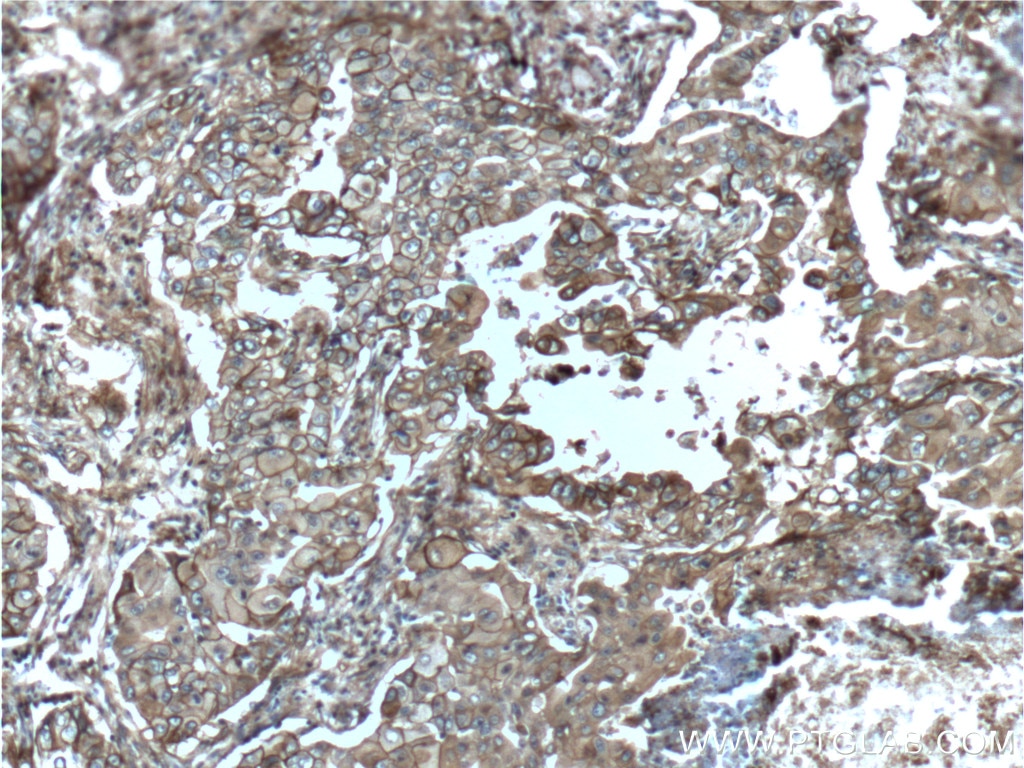
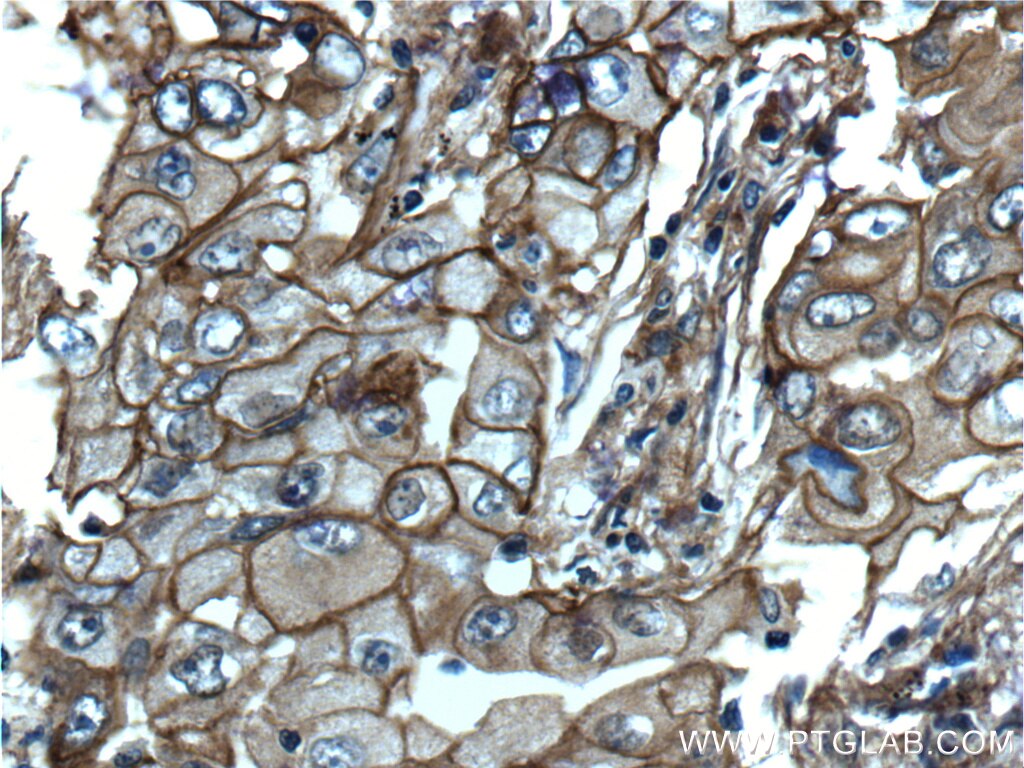
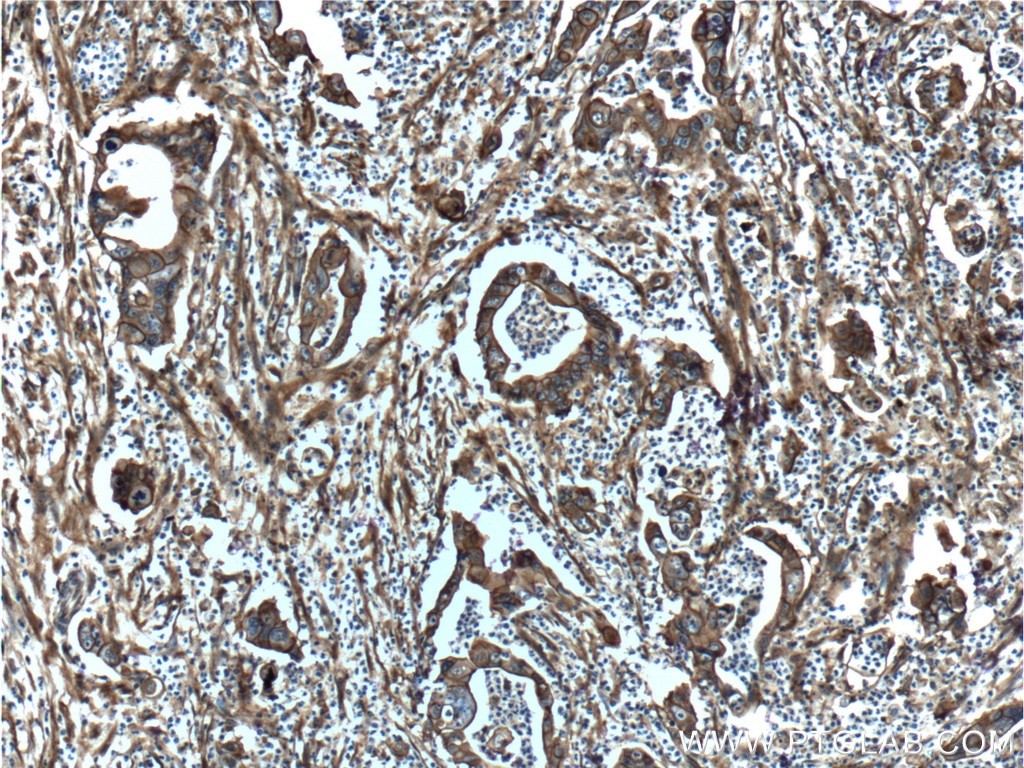
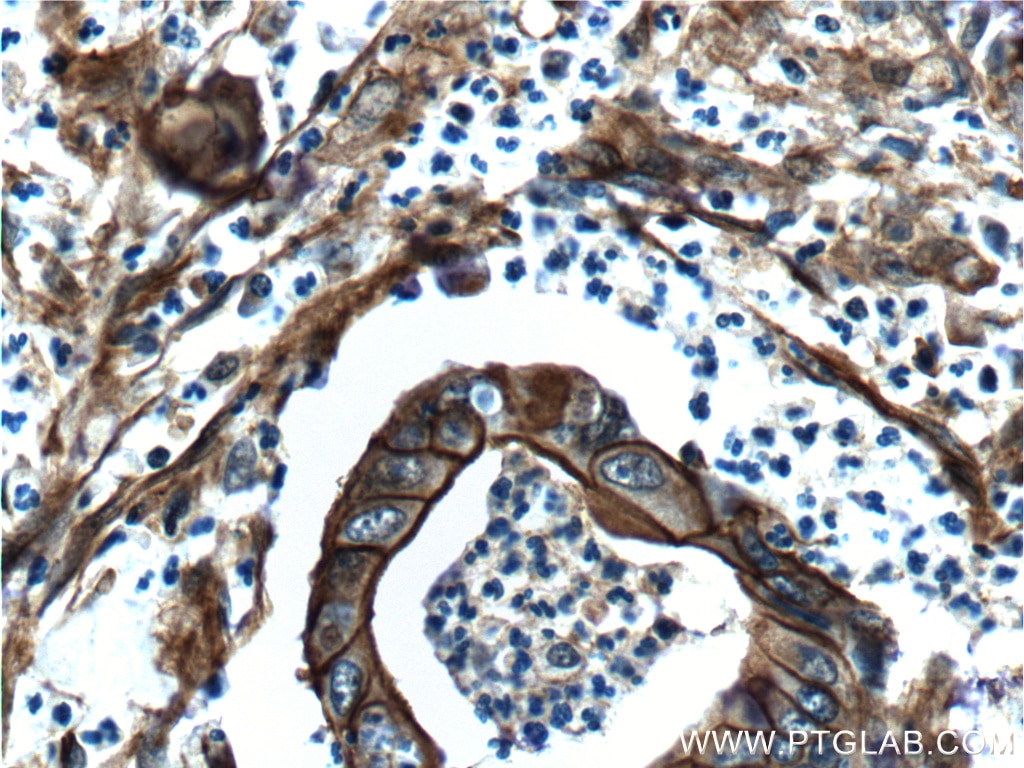
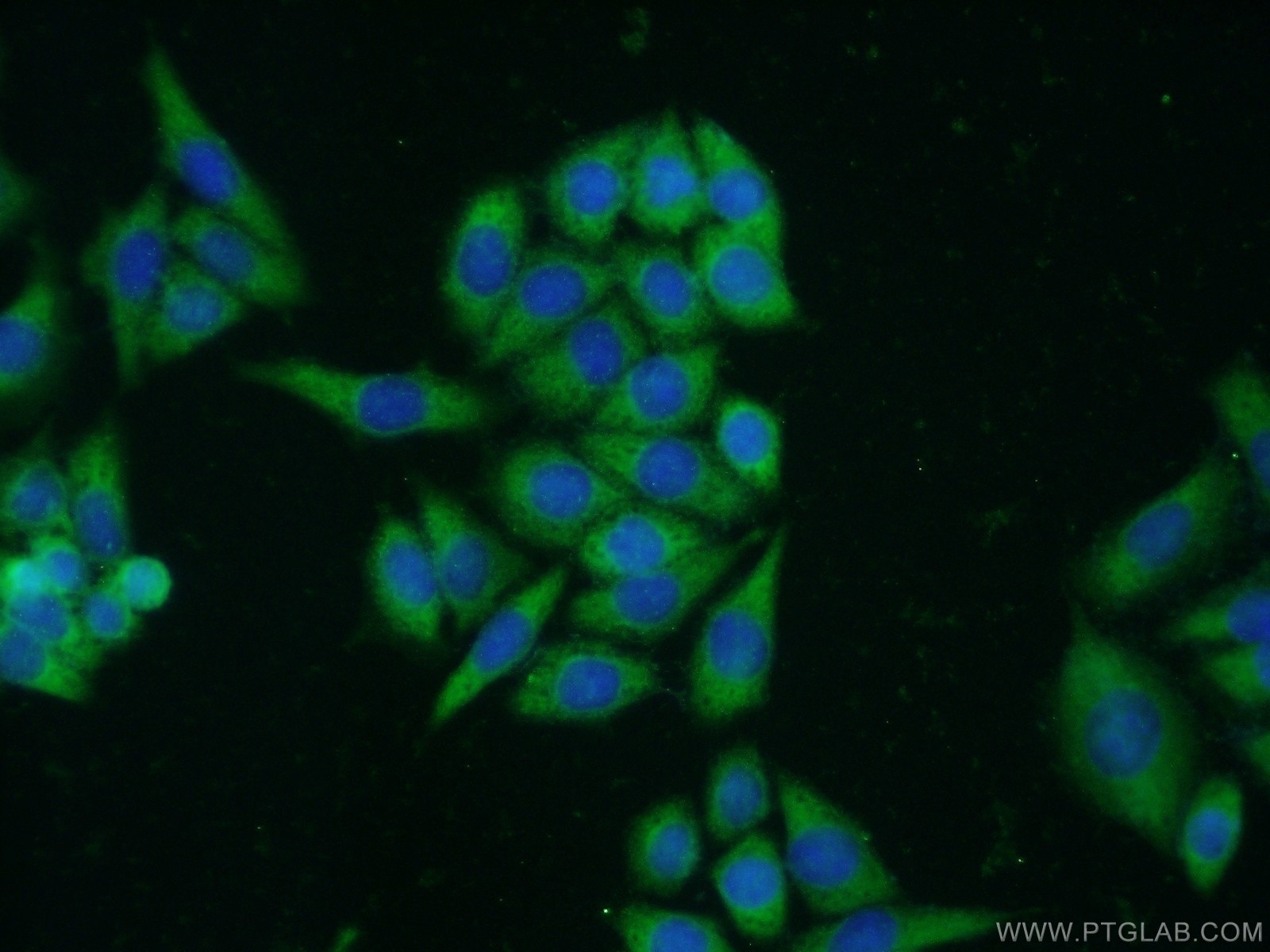
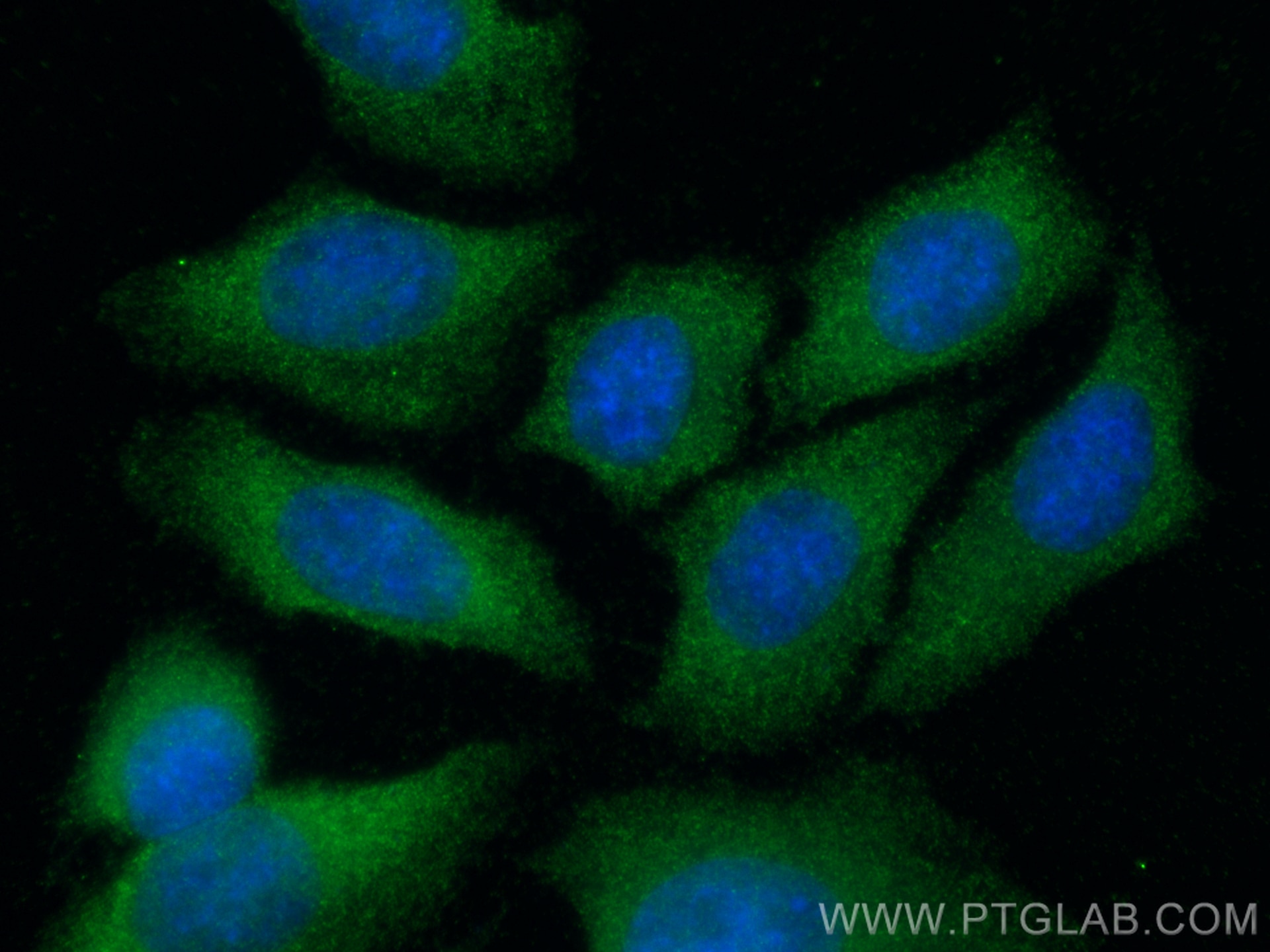
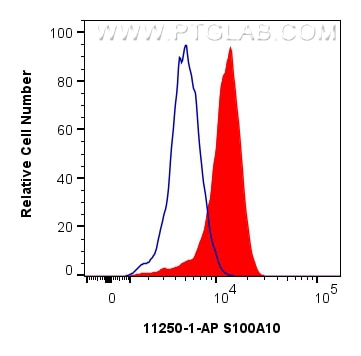
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
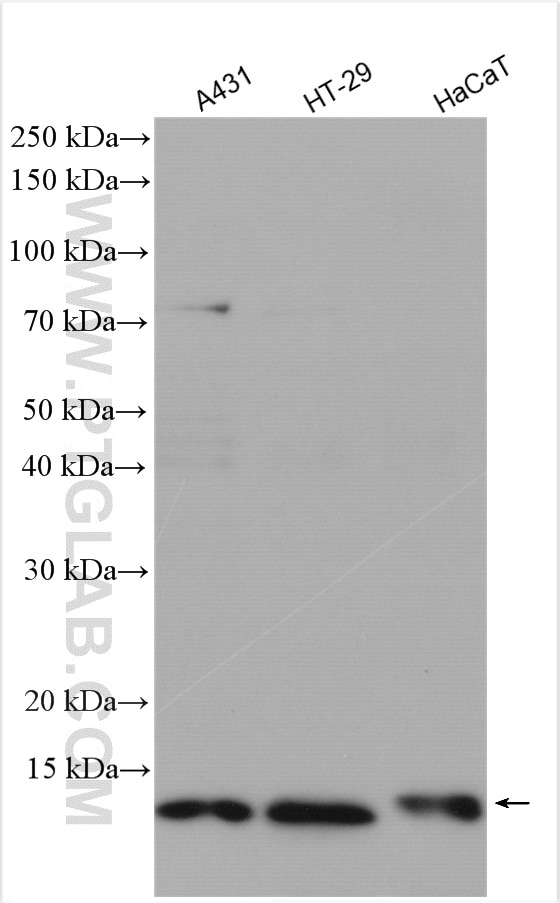
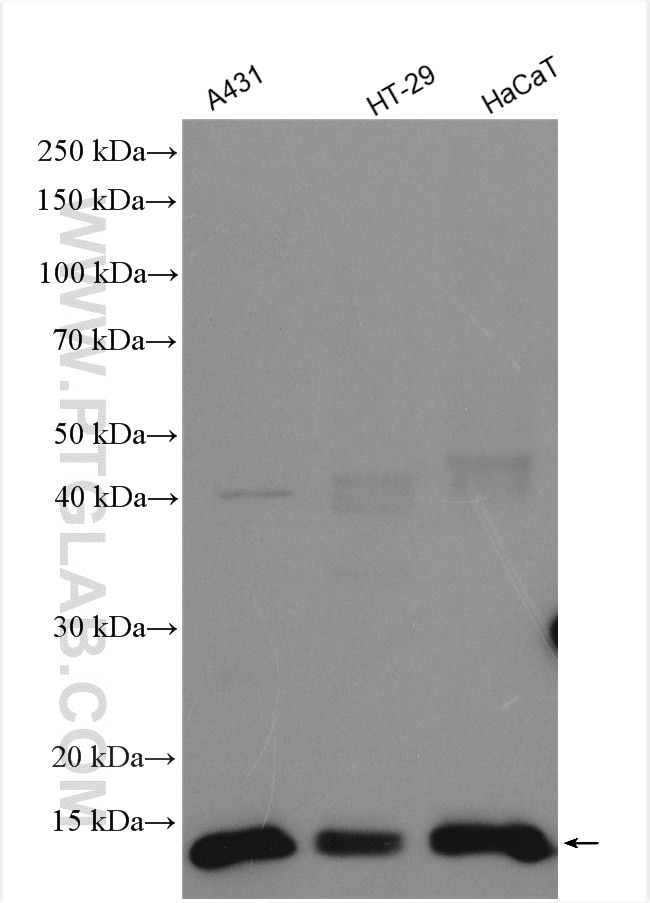
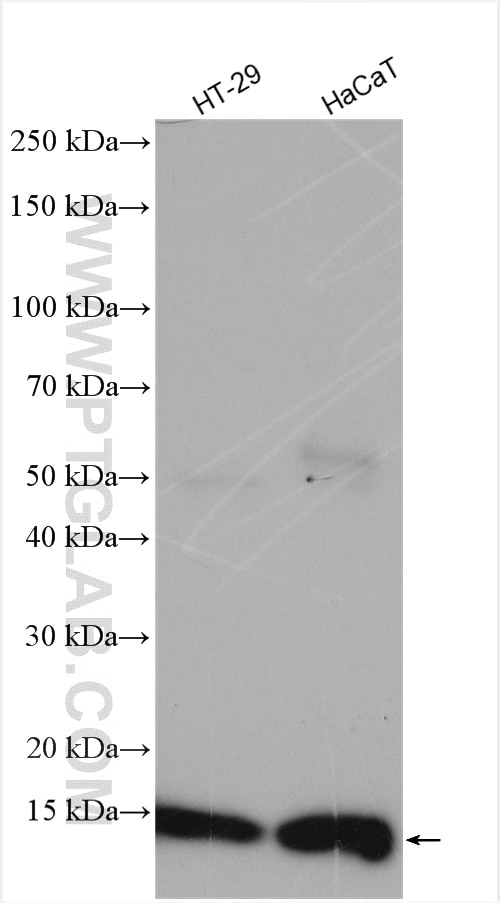
| Positive WB detected in | A431 cells, HeLa cells, HT-29 cells, human lung tissue, HaCaT cells |
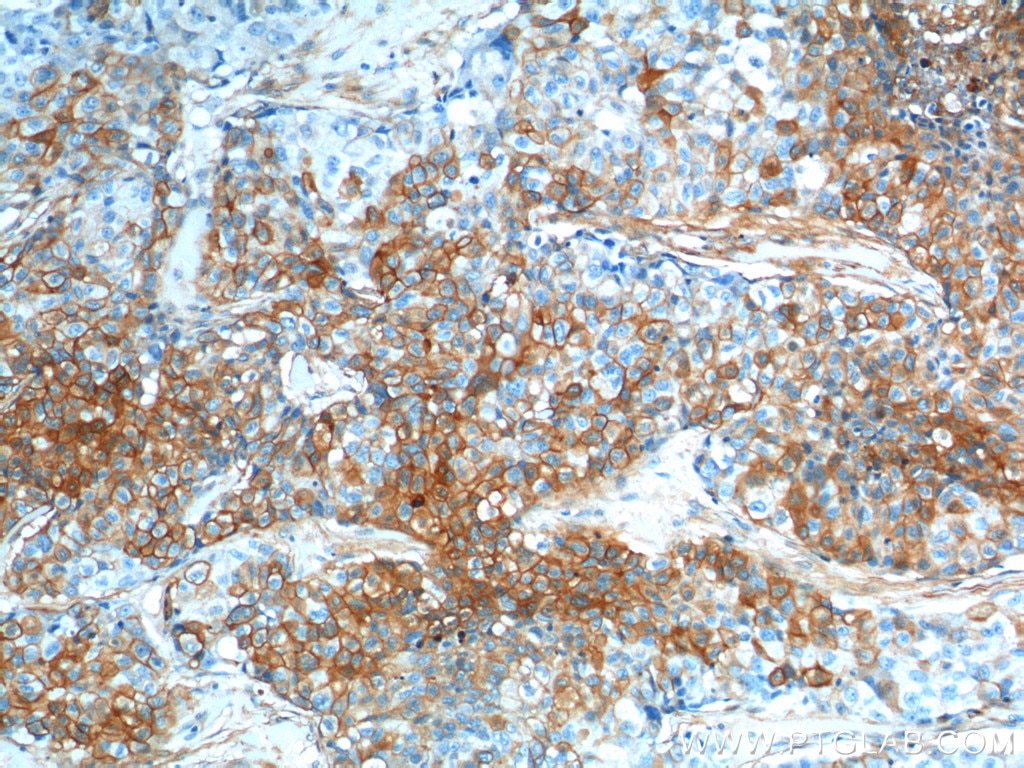
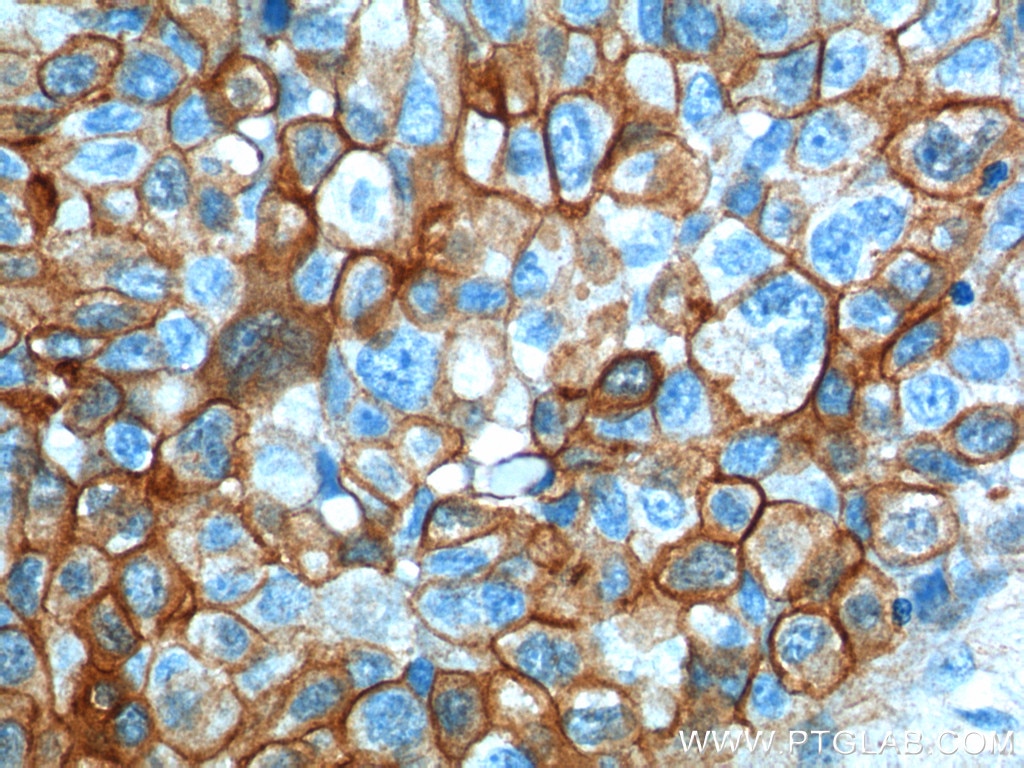
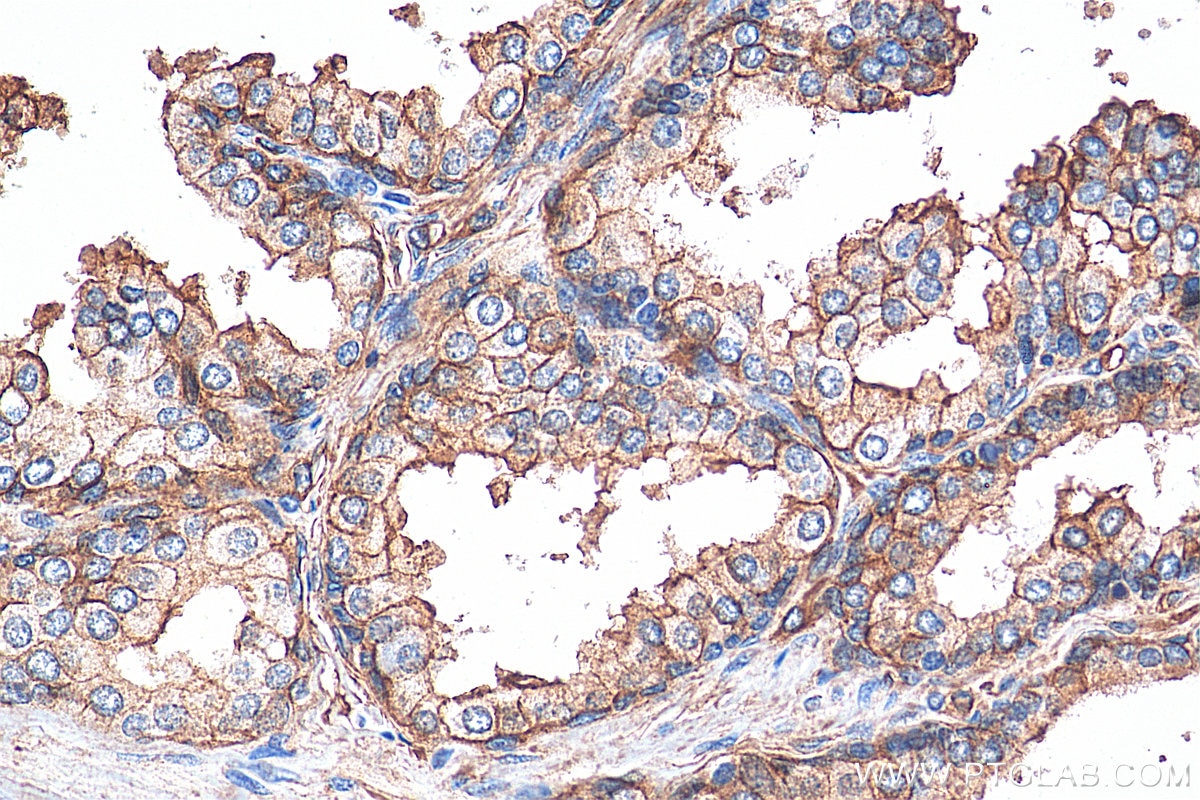
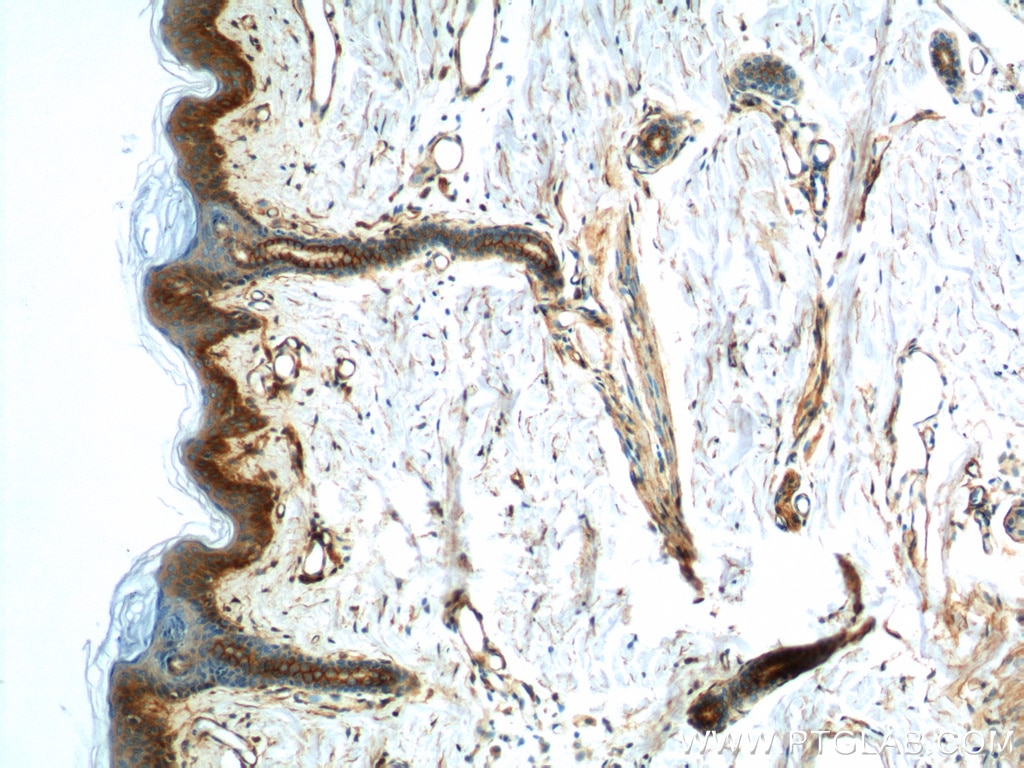
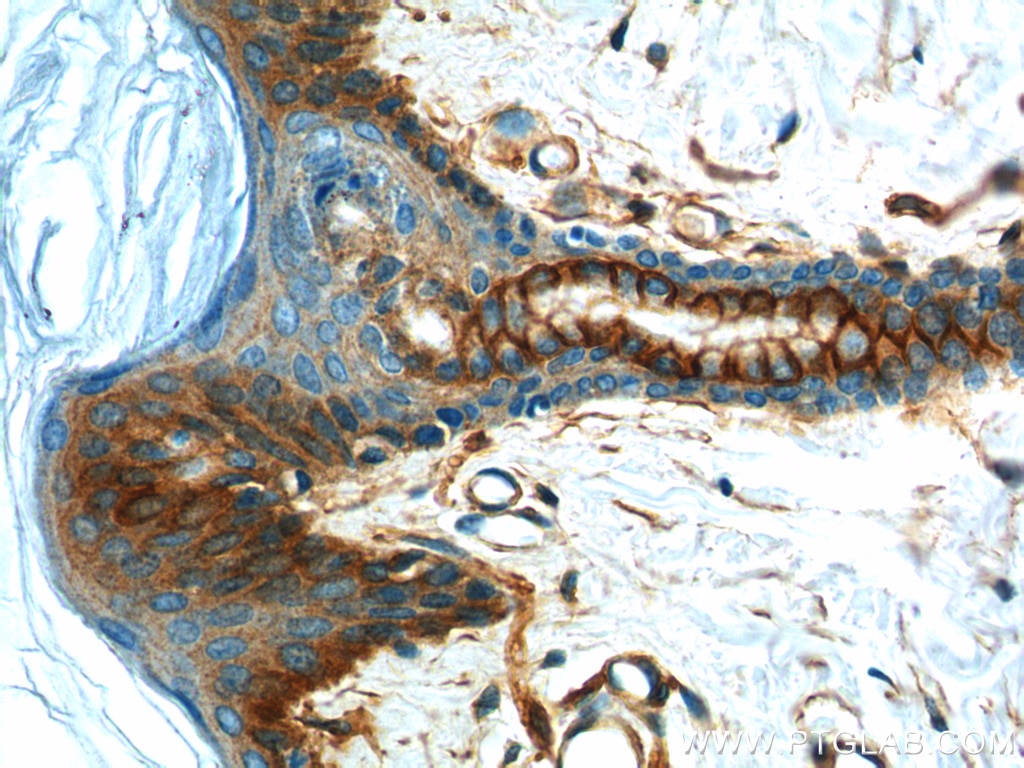
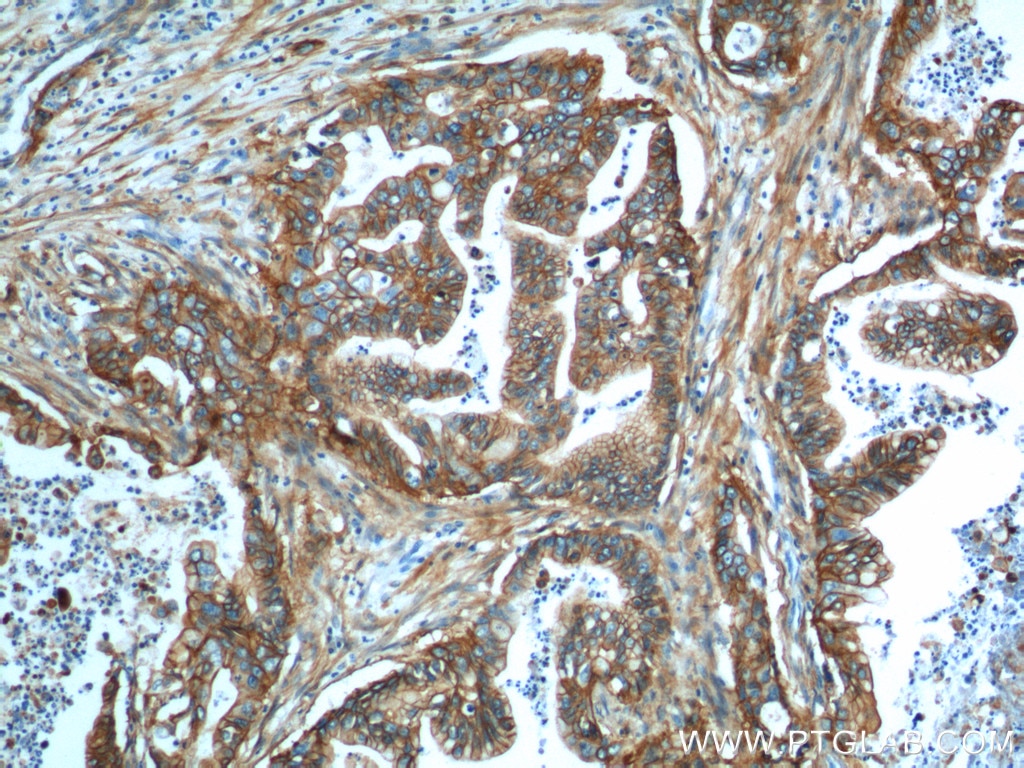
| Positive IHC detected in | human lung cancer tissue, human cervical cancer tissue, human gliomas tissue, human normal colon, human pancreas cancer tissue, human prostate hyperplasia tissue, human skin tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells, HeLa cells |
| Positive FC (Intra) detected in | HeLa cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:100-1:1000 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| Flow Cytometry (FC) (INTRA) | FC (INTRA) : 0.25 ug per 10^6 cells in a 100 µl suspension |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 6 publications below |
| WB | See 35 publications below |
| IHC | See 7 publications below |
| IF | See 28 publications below |
| IP | See 3 publications below |
| ELISA | See 1 publications below |
| FC | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
11250-1-AP targets S100A10 in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, FC (Intra), IP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | S100A10 fusion protein Ag1779 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | S100 calcium binding protein A10 |
| Calculated molecular weight | 11 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 11 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC015973 |
| Gene Symbol | S100A10 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6281 |
| RRID | AB_2269906 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | P60903 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
S100A10, also known as p11, is a member of the S100 family of small, EF hand containing dimeric proteins. S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and/or nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation. S100A10 is present on the surface of endothelial and other cells in a heterotetrameric complex with another Ca(2+)-binding protein, annexin II. S100A10 may function in exocytosis and endocytosis.
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for S100A10 antibody 11250-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for S100A10 antibody 11250-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for S100A10 antibody 11250-1-AP | Download protocol |
| FC protocol for S100A10 antibody 11250-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Mol Immunol Essential roles of S100A10 in Toll-like receptor signaling and immunity to infection. | ||
Acta Pharmacol Sin VEGFD/VEGFR3 signaling contributes to the dysfunction of the astrocyte IL-3/microglia IL-3Rα cross-talk and drives neuroinflammation in mouse ischemic stroke | ||
JCI Insight Fabry disease Schwann cells release p11 to induce sensory neuron hyperactivity | ||
Phytomedicine Withaferin A protects against epilepsy by promoting LCN2-mediated astrocyte polarization to stopping neuronal ferroptosis | ||
Diabetes Deficiency of Mitochondrial Glycerol 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase Exacerbates Podocyte Injury and the Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease.
| ||
J Nanobiotechnology Extracellular vesicles derived from CD73 modified human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate inflammation after spinal cord injury |