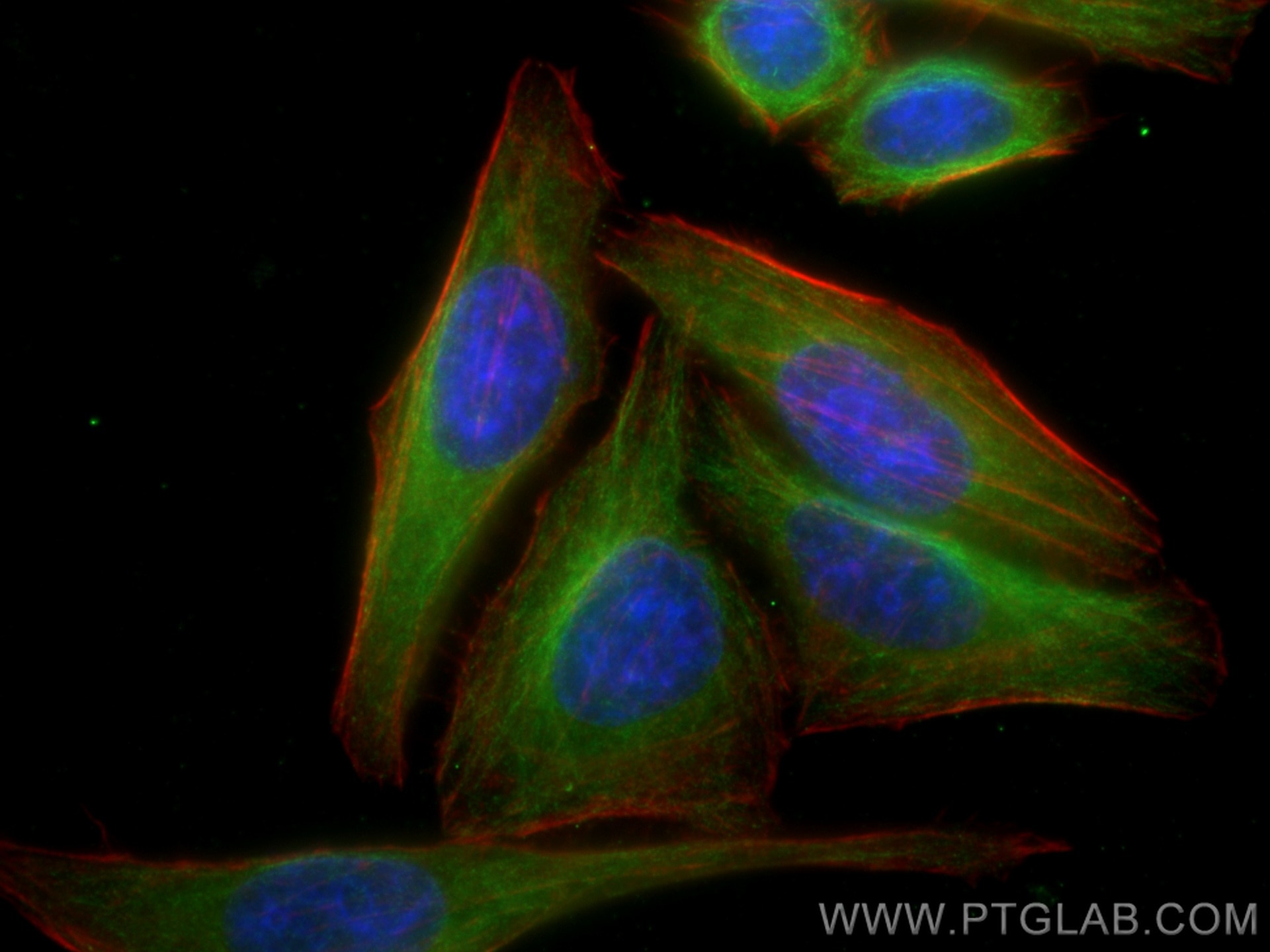
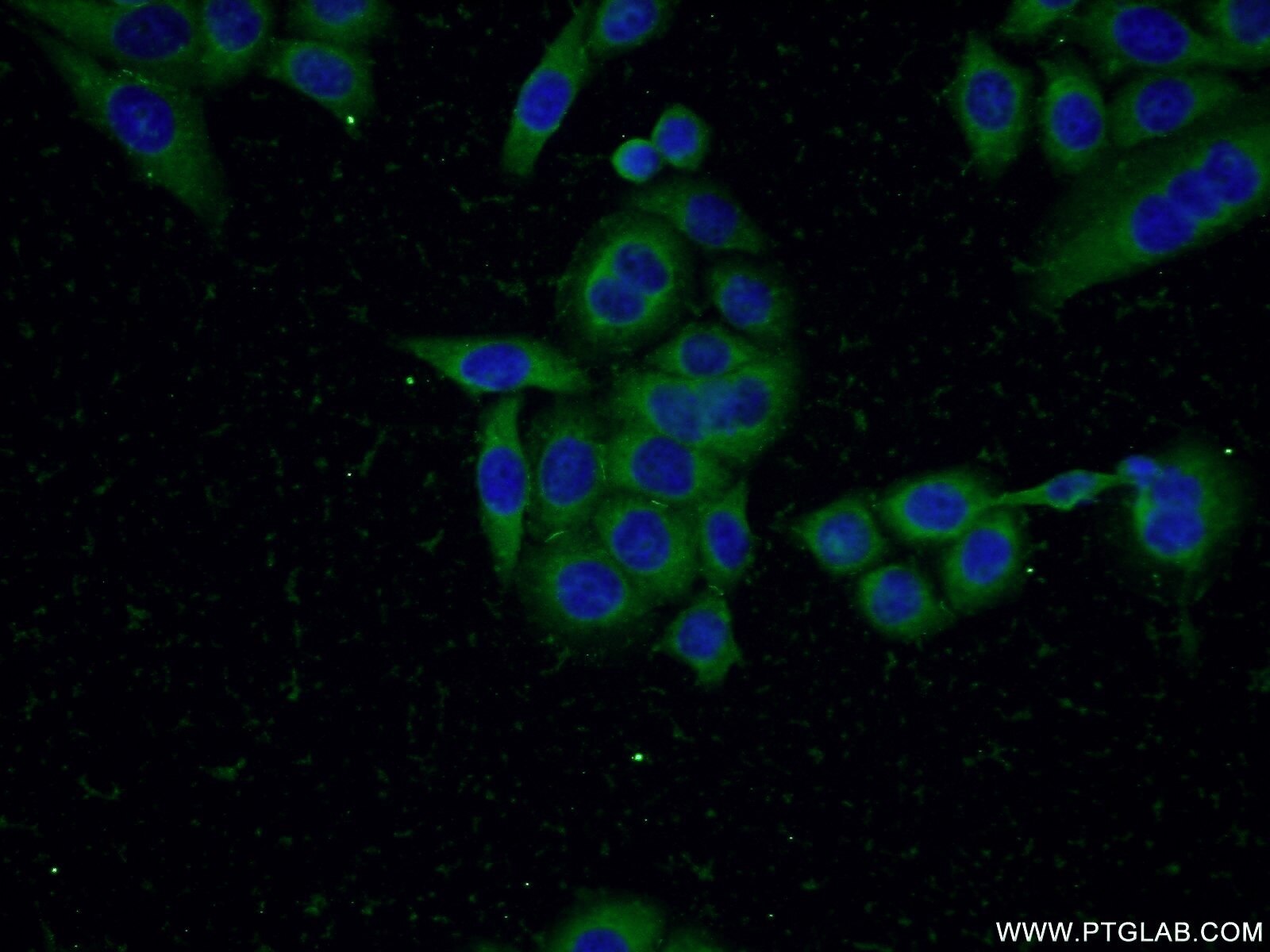
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
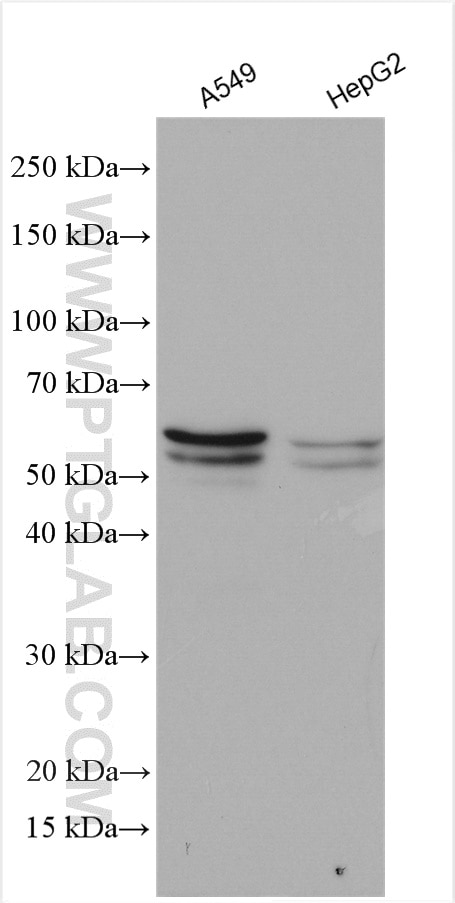
| Positive WB detected in | A549 cells, HepG2 cells |
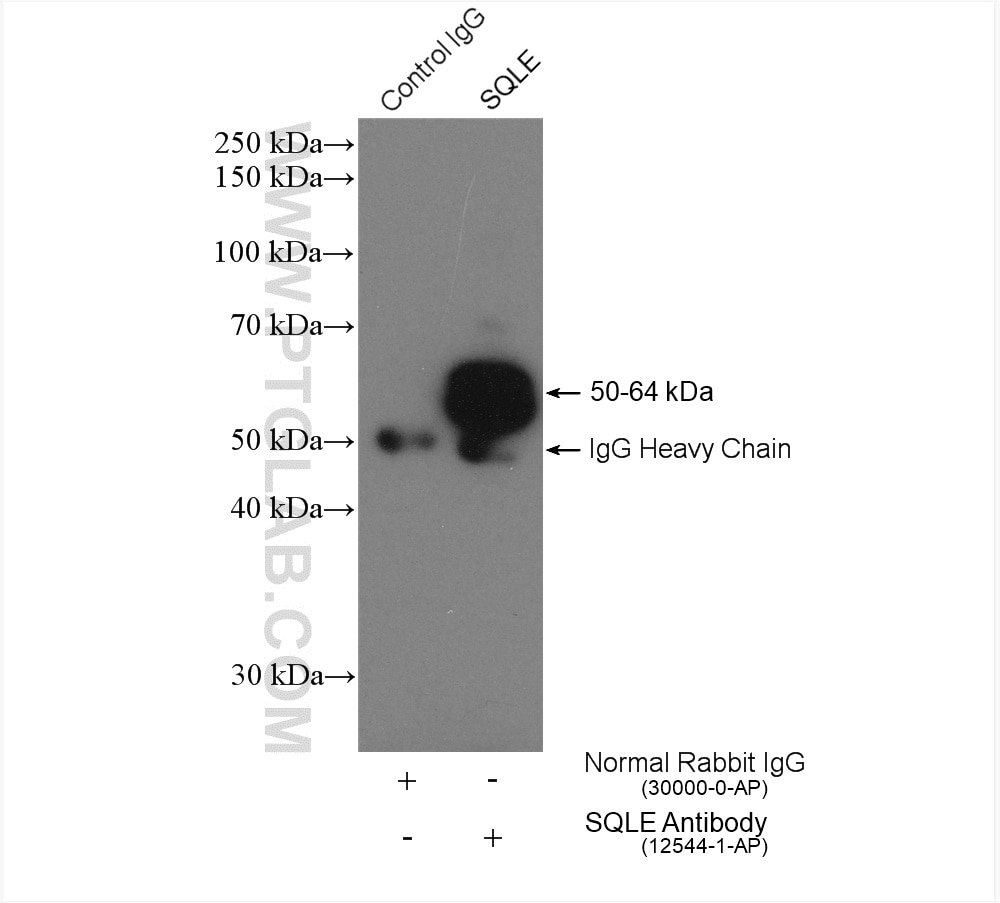
| Positive IP detected in | HepG2 cells |
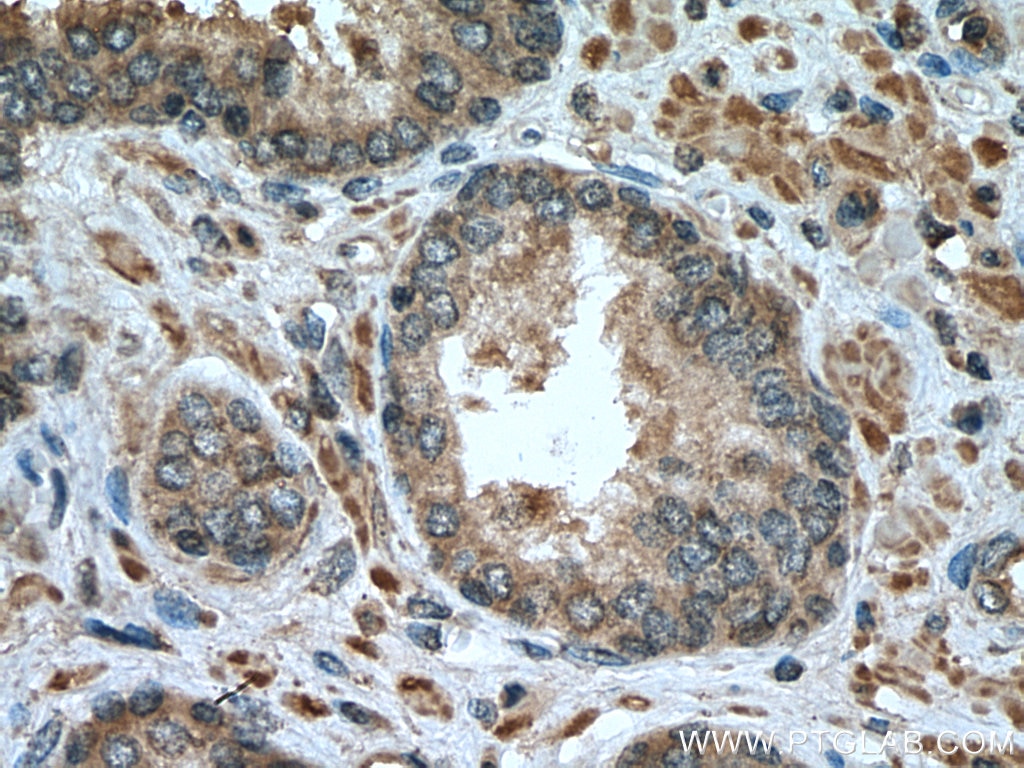
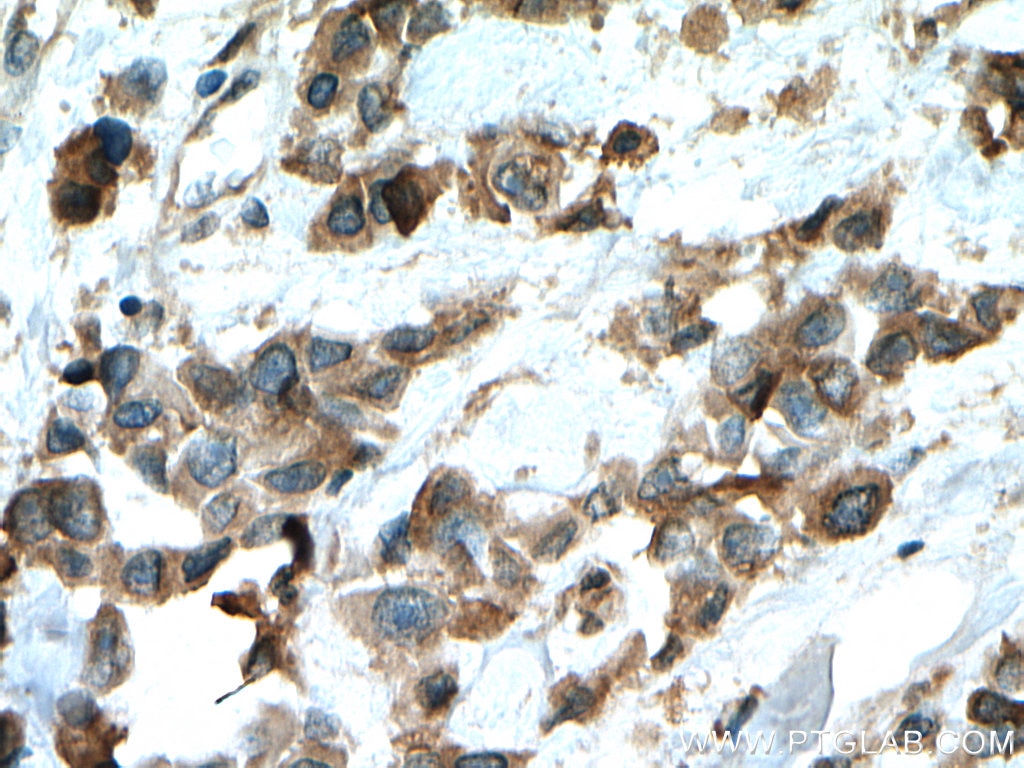
| Positive IHC detected in | human prostate cancer tissue, human breast cancer tissue Note: suggested antigen retrieval with TE buffer pH 9.0; (*) Alternatively, antigen retrieval may be performed with citrate buffer pH 6.0 |
| Positive IF/ICC detected in | HepG2 cells, PC-3 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:2000 |
| Immunoprecipitation (IP) | IP : 0.5-4.0 ug for 1.0-3.0 mg of total protein lysate |
| Immunohistochemistry (IHC) | IHC : 1:50-1:500 |
| Immunofluorescence (IF)/ICC | IF/ICC : 1:200-1:800 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| KD/KO | See 16 publications below |
| WB | See 82 publications below |
| IHC | See 17 publications below |
| IF | See 4 publications below |
| ChIP | See 1 publications below |
Product Information
12544-1-AP targets SQLE in WB, IHC, IF/ICC, IP, ChIP, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse, rat samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse, rat |
| Cited Reactivity | human, mouse, rat, hamster |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | SQLE fusion protein Ag3266 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | squalene epoxidase |
| Calculated molecular weight | 574 aa, 64 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 50-64 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC017033 |
| Gene Symbol | SQLE |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 6713 |
| RRID | AB_2195888 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q14534 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
SQLE, also named as ERG1, SE and SM, belongs to the squalene monooxygenase family. It catalyzes the first oxygenation step in cholesterol synthesis, acting on squalene before cyclization into the basic steroid structure. SQLE may serve as a flux-controlling enzyme beyond 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase (HMGR, considered as rate limiting). It is also posttranslationally regulated by cholesterol-dependent proteasomal degradation. SQLE is subject to feedback regulation via cholesterol-induced degradation, which depends on its lipid-sensing N terminal regulatory domain. Truncation of SQLE occurs during its endoplasmic reticulum-associated degradation and requires the proteasome, which partially degrades the SQLE N-terminus and eliminates cholesterol-sensing elements within this region. The MW of SQLE is about 50-64 kDa. (PMID:21356516, PMID: 28972164)
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for SQLE antibody 12544-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IHC protocol for SQLE antibody 12544-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IF protocol for SQLE antibody 12544-1-AP | Download protocol |
| IP protocol for SQLE antibody 12544-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cell Metab Elevation of JAML Promotes Diabetic Kidney Disease by Modulating Podocyte Lipid Metabolism. | ||
Cell Metab Cholesterol-dependent degradation of squalene monooxygenase, a control point in cholesterol synthesis beyond HMG-CoA reductase. | ||
PLoS Biol Reduction of the cholesterol sensor SCAP in the brains of mice causes impaired synaptic transmission and altered cognitive function. | ||
Nat Commun MiR-205-driven downregulation of cholesterol biosynthesis through SQLE-inhibition identifies therapeutic vulnerability in aggressive prostate cancer. | ||
Redox Biol Lipophagy-mediated cholesterol synthesis inhibition is required for the survival of hepatocellular carcinoma under glutamine deprivation |