Validation Data Gallery
Filter:
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | THP-1 cells, HepG2 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:500-1:1000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Published Applications
| WB | See 3 publications below |
Product Information
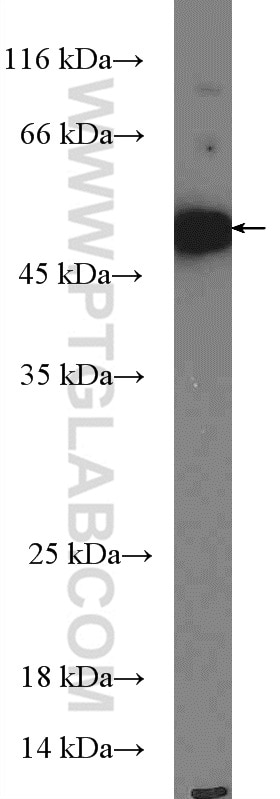
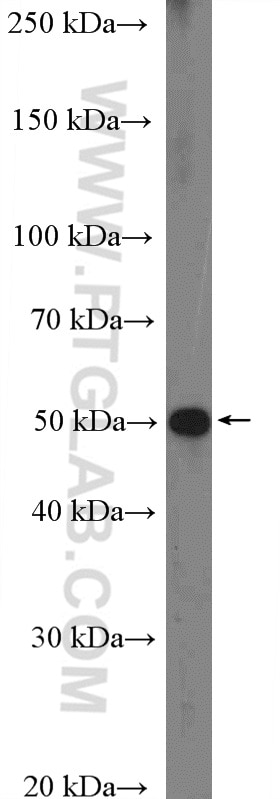
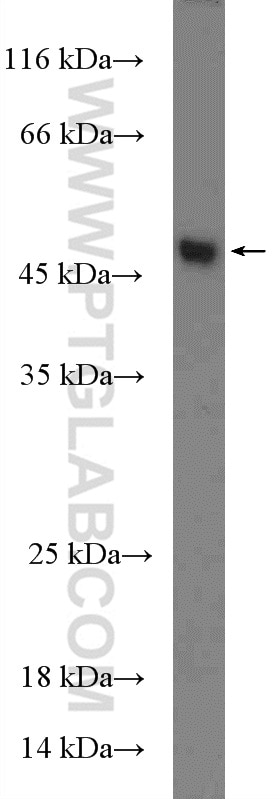
27065-1-AP targets TANK in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with human, mouse samples.
| Tested Reactivity | human, mouse |
| Cited Reactivity | human, rat |
| Host / Isotype | Rabbit / IgG |
| Class | Polyclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | TANK fusion protein Ag25740 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | TRAF family member-associated NFKB activator |
| Calculated molecular weight | 14 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 48 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | BC003388 |
| Gene Symbol | TANK |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 10010 |
| RRID | AB_2880738 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Antigen affinity purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q92844 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol{{ptg:BufferTemp}}7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for TANK antibody 27065-1-AP | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |
Publications
| Species | Application | Title |
|---|---|---|
Cancer Res FIP200 suppresses immune checkpoint therapy responses in breast cancers by limiting AZI2/TBK1/IRF signaling independent of its canonical autophagy function. | ||
Int Immunopharmacol The effect of Astragaloside IV on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats: Involvement of inflammation. | ||
J Mol Cell Biol TRIM14 promotes endothelial activation via activating NF-κB signaling pathway. |