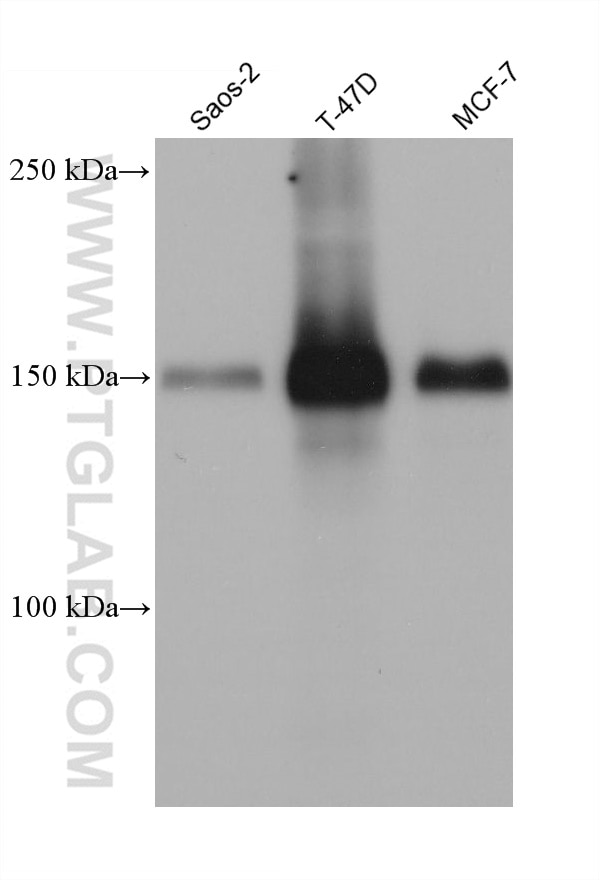
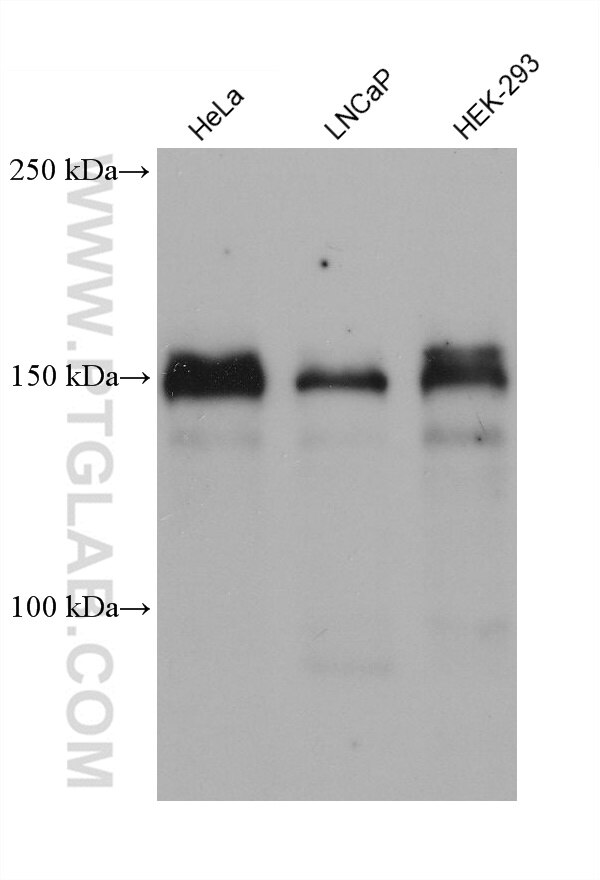
Validation Data Gallery
Tested Applications
| Positive WB detected in | Saos-2 cells, HeLa cells, T-47D cells, MCF-7cells, LNCaP cells, HEK-293 cells |
Recommended dilution
| Application | Dilution |
|---|---|
| Western Blot (WB) | WB : 1:2000-1:10000 |
| It is recommended that this reagent should be titrated in each testing system to obtain optimal results. | |
| Sample-dependent, Check data in validation data gallery. | |
Product Information
68562-1-Ig targets TRPS1 in WB, ELISA applications and shows reactivity with Human samples.
| Tested Reactivity | Human |
| Host / Isotype | Mouse / IgG1 |
| Class | Monoclonal |
| Type | Antibody |
| Immunogen | TRPS1 fusion protein Ag30199 相同性解析による交差性が予測される生物種 |
| Full Name | trichorhinophalangeal syndrome I |
| Calculated molecular weight | 142 kDa |
| Observed molecular weight | 150 kDa |
| GenBank accession number | NM_014112 |
| Gene Symbol | TRPS1 |
| Gene ID (NCBI) | 7227 |
| RRID | AB_3085264 |
| Conjugate | Unconjugated |
| Form | Liquid |
| Purification Method | Protein G purification |
| UNIPROT ID | Q9UHF7 |
| Storage Buffer | PBS with 0.02% sodium azide and 50% glycerol , pH 7.3 |
| Storage Conditions | Store at -20°C. Stable for one year after shipment. Aliquoting is unnecessary for -20oC storage. |
Background Information
TRPS1 is a zinc finger transcriptional repressor involved in the regulation of chondrocyte and perichondrium development, containing a GATA-type zinc finger through which it binds to DNA. with nine zinc-finger domains and two C-terminal Ikaros-like zinc fingers. Its reperssible function was dependent on the integrity of the Trps1 GATA-type zinc-finger domain and also required the C-terminal 119 amino acids of the protein, which harbor the two Ikaros-like zinc-finger domains
Protocols
| Product Specific Protocols | |
|---|---|
| WB protocol for TRPS1 antibody 68562-1-Ig | Download protocol |
| Standard Protocols | |
|---|---|
| Click here to view our Standard Protocols |